Using sEMG biofeedback to get real-time results
Tiffany Lee, MA, OTR, BCB-PMD and Jane Kaufman, PT, BCB-PMD are internationally board-certified clinicians in the treatment of pelvic floor muscle dysfunction through the Biofeedback Certification International Alliance. Combined, they have over fifty years of treatment experience using sEMG biofeedback. Their new course, “Biofeedback for Pelvic Floor Muscle Dysfunction”, will provide the nuts and bolts of this powerful tool so that clinicians can return to the clinic after this course with another component to their toolbox of treatment strategies.
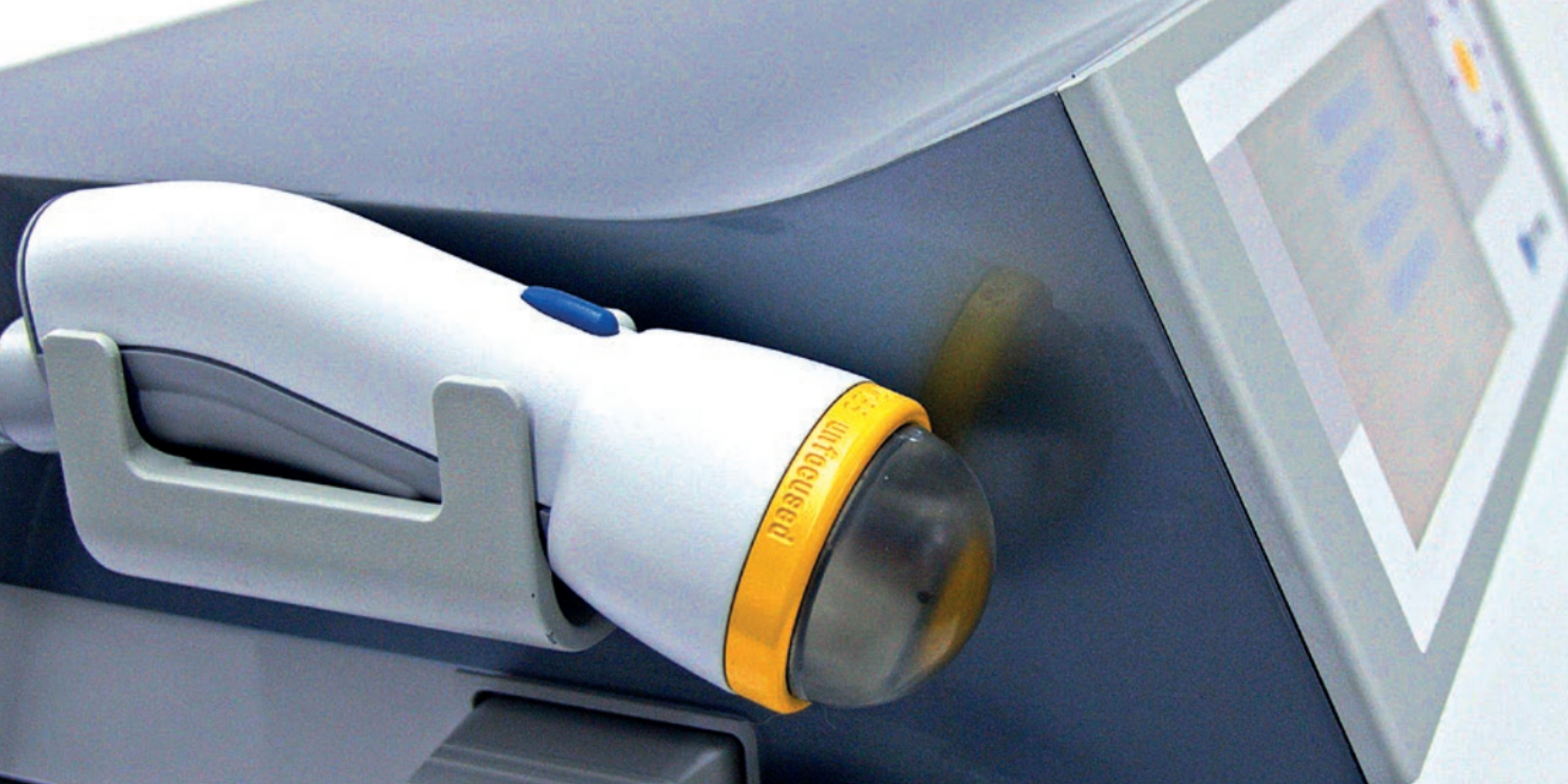
As a clinician treating patients with pelvic floor muscle dysfunction, have you gone away from a treatment session and asked yourself ‘what else can I do for this patient?’. Have you considered adding surface EMG, often referred to as biofeedback, to your treatment plan, but aren’t sure how to go about it correctly or effectively? Perhaps you think you can’t use the sensor because the patient has pain. Maybe you think biofeedback only helps with up-training or strengthening.
So exactly what is biofeedback? Why should I consider this modality? Biofeedback provides a non-invasive opportunity for patients to see muscle function visualized on a computer screen in a way that allows for immediate feedback, simple representation of muscle function, and allows the patient and the clinician the opportunity to alter the physiological process of the muscle through basic learning strategies and skilled cues. Many patients gain knowledge and awareness of the pelvic floor muscle through tactile feedback, but the visual representation is what helps patients really hone in on body awareness and connect all the dots. Here are a few comments that our patients have made; “I can now pay attention to my muscle while at work thanks to the visual of my muscle when sitting and standing”; “I needed to see my muscle to fully understand how to release the tension in it “; “I totally get what I need to do now that I have a clear picture of what you want”; “Seeing is believing”.
Everyone experiences constipation, sometime! Maybe it was on vacation and you felt bloated and miserable; or when you were busy at work and had to rush to complete a task. In any event, you felt ‘awful’. Maybe you couldn’t zip your favorite jeans due to abdominal bloating, maybe you experienced lower abdominal discomfort or experienced a painful ‘movement’ once you went. There are many people who experience these symptoms and more on a daily basis. When someone finally gets the courage to see a specialist about this problem, they might be diagnosed with ‘pelvic floor dyssynergia’ or ‘muscle incoordination’.
Pelvic muscle dyssysnergia (incoordination) refers to the action that occurs in the pelvic floor musculature at the time of defecation. It can become a withholding pattern and in the case of vacation or a change in your work schedule, it can simply be tensing the muscle to avoid the bowel movement (due to inconvenience) rather than heeding the ‘call’. Over time, if this behavior is repeated, it becomes muscle memory; instead of relaxing the pelvic muscle to defecate, the patient tenses the muscle; thus the term dyssynergia or incoordination. The function of the pelvic floor for bowel function is to provide closure of the anal canal to maintain continence. The muscle should signal the rectum and the colon when to defecate and should provide opening of the anal canal by total relaxation to allow for complete and effortless elimination. A dyssynergic pattern shuts the opening of the canal by tensing the muscle to prevent elimination. Thus an incoordination.
The research by Heymen, Scarlett, Ringman, Drossman et al entitled “Randomized, Controlled Trial Shows Biofeedback to Be Superior to Alternative Treatments for Patients with Pelvic Floor Dyssynergia-Type Constipation” supports the value of biofeedback in the treatment of this withholding pattern associated with stool elimination. This study supports the benefit of biofeedback treatments using internal sensors to provide the feedback displayed on a computer screen for visualization. This study goes on to say, “We also have shown that the machines are necessary—instrumented biofeedback is an essential element of successful training; however, there is a shortage of practitioners who are trained to provide this form of biofeedback, and there are few clinics where biofeedback instruments are available and where this form of biofeedback can be obtained”.