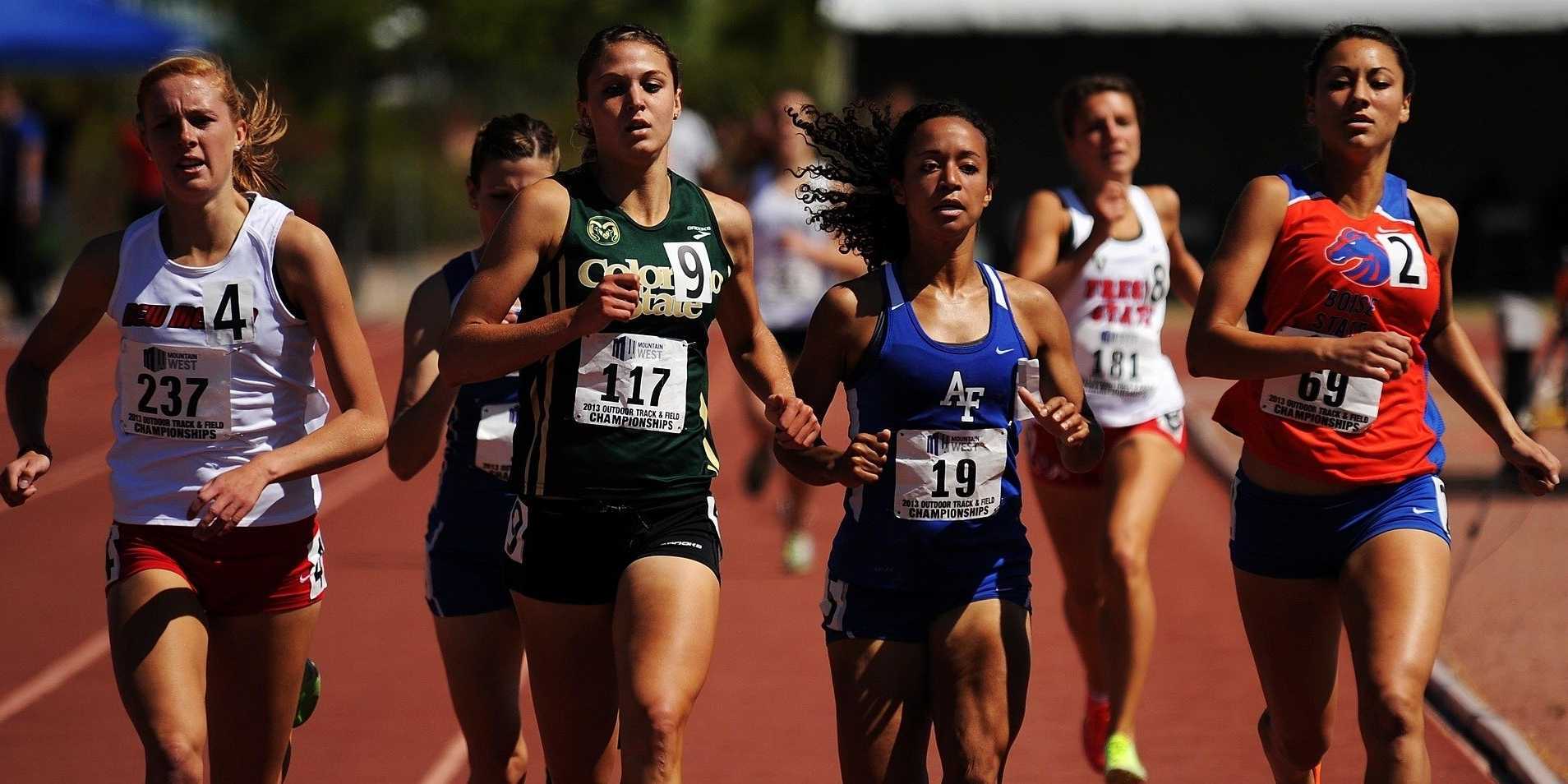
Since the passing of Title IX in 1972, which protects people from sex discrimination in education or activity programs receiving federal funding, the number of females participating in sports has greatly increased. The National Federation of State High School Associations states that in 2011 nearly 3.2 million girls are participating in high school sports.
Unfortunately, a consequence of this increased participation in sports is a higher prevalence in urinary incontinence (UI) and stress urinary incontinence (SUI) in female athletes. Borin et al looked at the ability of nulliparous female athletes to generate intracavity perineal pressure in comparison to nonathletic women. The study demonstrated that higher mean pressures were generated by nonathletic women in comparison to the athletic women group and that lower perineal pressures in the athletic women were also related to number of games per year and time spent on sport specific workouts and strength training workouts.
UI and SUI are underreported in the general population and also in the athletic population. As health care professionals it is important to screen for UI and SUI in our clients. Physical therapy interventions using pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation have shown to decrease the severity of UI and SUI (Rivalta et al, Hulme). Rivalta used internal methods to improve the function of the pelvic floor muscle. Hulme’s success was achieved through activation of the pelvic floor muscles’ extrinsic synergists.
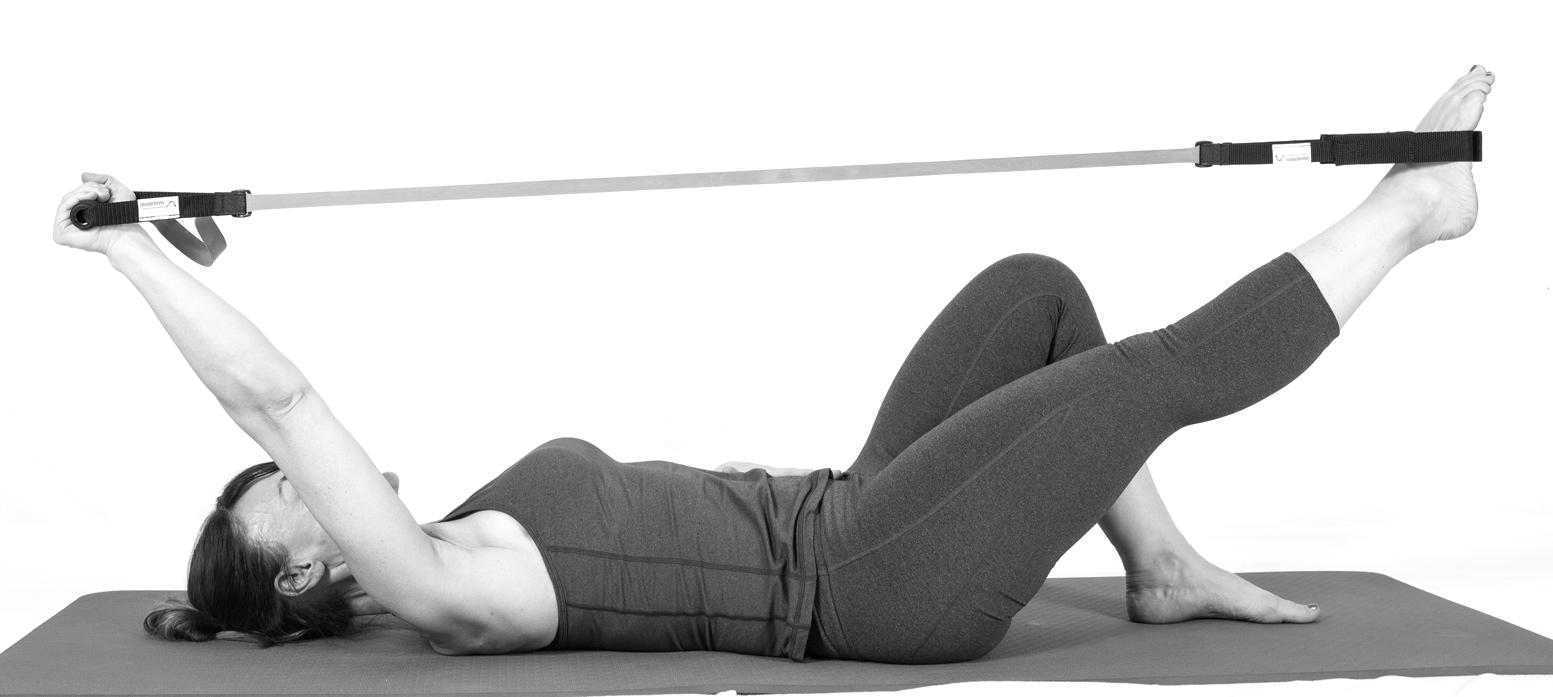
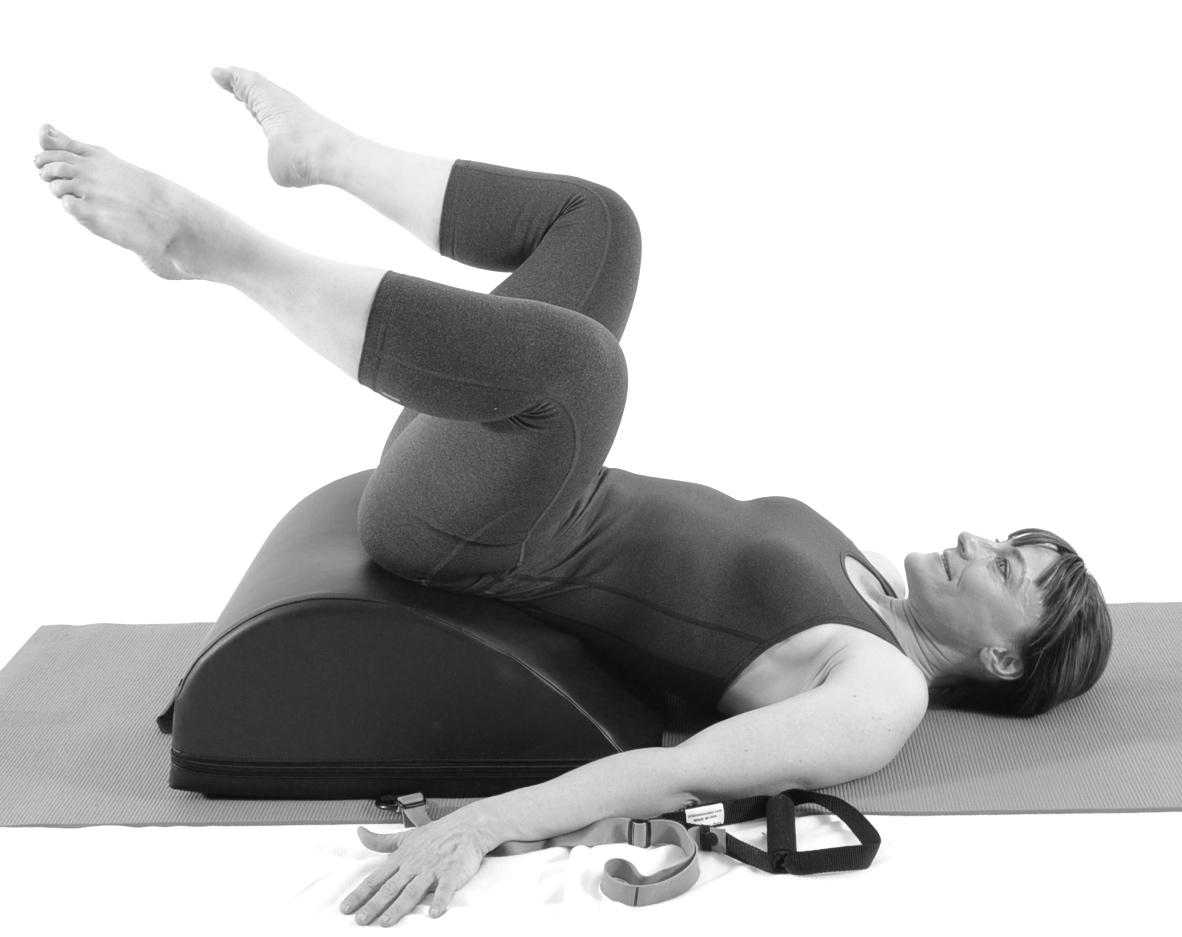
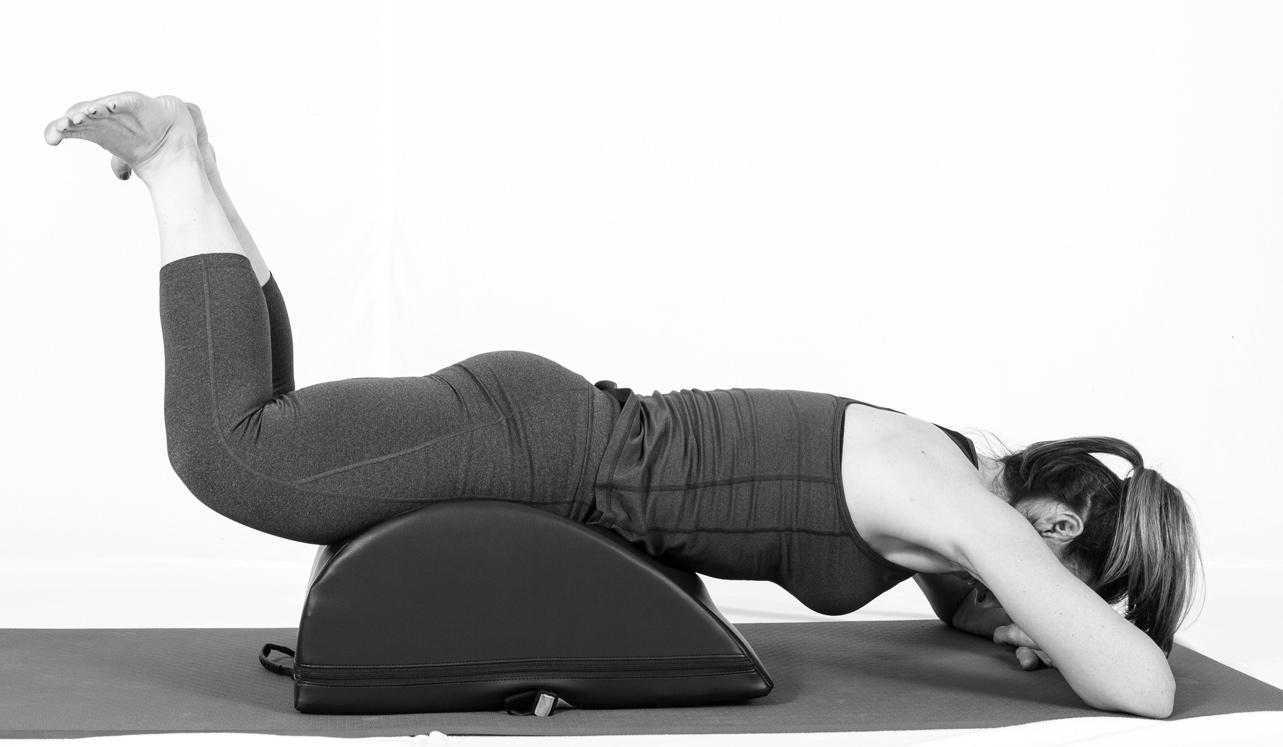
Pilates is often used in physical therapy as a therapeutic tool to improve lumbar stability with studies showing increases in abdominal strength (Sekendiz), trunk extensor endurance (Sekendiz) and to improve posture (Kloubec). Pilates is often also used in pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation and can easily be modified for low level clients. For example the use of resistance can assist supporting the weight of the leg. Practical proof, while lying supine in neutral lumbar spine position, stretch an arm and a leg away from center, notice the difficulty to maintain neutral spine. Now hold a resistance strap, which is also attached to the foot, and notice how maintaining neutral lumbar spine is easier to maintain (pictured above).
Today we hear from Martina Hauptmann, PT, PMA-CPI, instructor of "Pilates for the Pelvic Floor: Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, Osteoporosis and Peripartum". Join Martina this September 19-20 in Chicago, IL to learn how to incorporate Pilates into your treatment plans!
Because the cost of staying in business is increasing and the insurance reimbursement rates are dropping, many physical therapy clinics are looking for cash based supplemental services (medically-orientated gym memberships, Pilates classes, yoga classes, durable exercise supplies etc). Offering Pilates as part of the physical therapy clinic’s therapeutic interventions will differentiate your clinic and may be marketed to physicians and the community to increase your clinic’s market share. Post rehabilitation, the offering of cash based Pilates wellness classes can increase the clinic’s bottom line, allowing for further rehabilitation of the client beyond the time frame allowed by insurances and improve retention of clients.
Pilates is a system and philosophy of exercises based on the work of Joseph Pilates (1883-1967) that focuses on precision and optimal alignment. This approach requires the client to focus her mind on the exercise in order to increase motor control. Women are attracted to the Pilates method because of its gentle but effective nature. Offering Pilates as part of your therapeutic offerings is a great marketing tool to physicians and to the community as well as an effective method for instructing specific muscle re-training.
Today's post is written by faculty member Martina Hauptmann, who instructs the Pilates for Pelvic Dysfunction, Osteoporosis, and Peripartum course. Come learn how to apply Pilates in your practice this September 19-20 in Chicago, IL!
Treating the incompetent pelvic floor (urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse) is a staple of therapists who have specialized in this complex area.
Ever since Dr. Arnold Kegel published his research “A Non-surgical Method of Increasing the Tone of the Sphincters and Their Supporting Structures” back in 1942 women have been strengthening their pelvic floor by conscious contraction of their perineum by either squeezing or lifting.