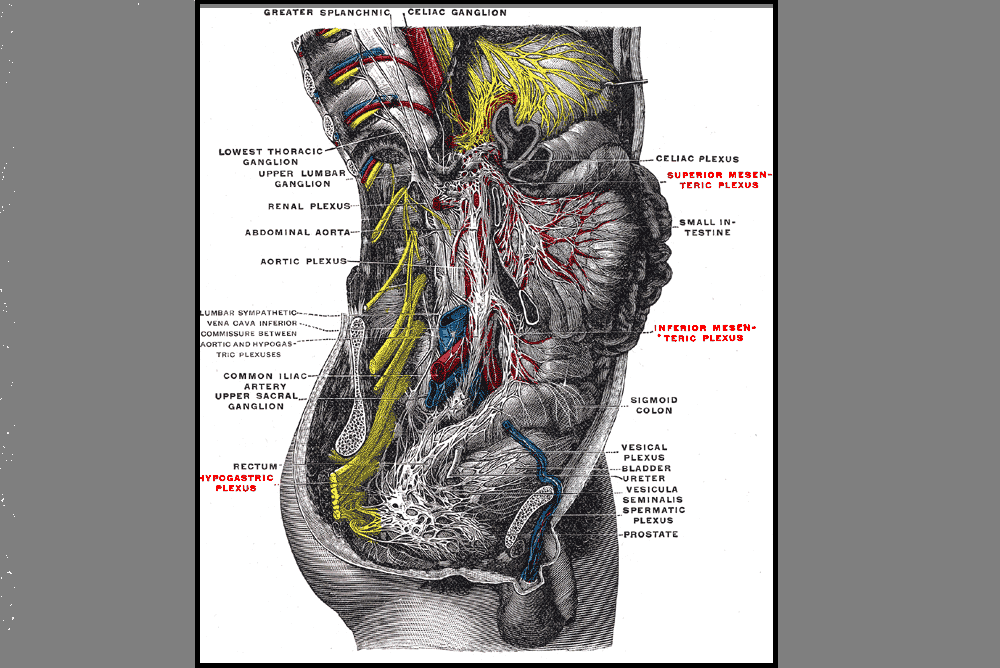
Sacroiliac Joint: Some Confusion over Fusion
Rarely does a patient with sacroiliac joint dysfunction come to see us with a goal of having surgery. Sometimes surgery winds up being the last resort for relief if our efforts and the patient’s commitment to physical therapy and prescribed exercises fail. Some of the most recent research shows positive results from minimally invasive surgery; however, the bottom line is to make sure the most educated, clinically accurate diagnosis has been made in implicating the SI joint as the source of pain.
Capobianco et al (2015) performed a prospective multi-center trial regarding SI joint fusion using a minimally invasive technique in women with post-partum pain in the pelvic girdle. Eligibility for the study required subjects to have 3 out of 5 positive SI joint stress tests and at least 50% relief with image-guided intra-articular SI joint block with a local anesthetic. Of the 172 subjects in the study, 20 of the 100 females had post-partum pelvic girdle pain, and 52 subjects were male. Significant improvements in pain, quality of life, and function were found for not only the post-partum group but all groups 12 months after surgery. Worth noting is one to three weeks after surgery, the subjects engaged in physical therapy, two times per week for six weeks.
Whang et al (2015) assessed the 6-month outcomes of SI joint fusion using triangular titanium implants versus non-surgical management in a prospective randomized controlled trial. Of the 148 subjects chosen based on similar diagnostic criteria as the study mentioned above, 102 underwent surgery, and 46 had non-surgical management. Non-surgical management involved appropriate pain medication administration, physical therapy, intra-articular SI joint steroid injections, and radiofrequency ablation of sacral nerve roots, all based on individual needs. The surgical group subjects in this study were also asked to have physical therapy two times per week for six weeks anywhere from one to three weeks post-op. The results in a six month follow up showed “clinical success” of >80% in the surgical group and <25% in the non-surgical management group.
The Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine presented an article in July 2015 by Zaidi et al with results of a systematic review of literature regarding the surgical and clinical effectiveness of SI joint fusion. The studies included open as well as minimally invasive surgery, and the causes of surgery included SI joint degeneration and arthritis, SIJ dysfunction, postpartum instability, posttraumatic, idiopathic, pathological fractures, and HLA-B27+/rheumatoid arthritis. A mean rate of satisfaction with open surgery was 54%; whereas, the mean was 84% with minimally invasive surgery. Ultimately, the authors concluded, “serious consideration of the cause of pain” is necessary before embarking on SI joint fusion as the evidence for the surgery’s efficacy is lacking.
So, who is responsible for making the definite diagnosis for SI joint dysfunction? As many patients get minimal time in doctor offices, we have a professional responsibility to competently perform a thorough evaluation for our patients. When the diagnosis is “SI joint dysfunction,” rule out the lumbar spine and hip; and, of course, when “low back pain” or “hip pain” fills the diagnosis line, rule out/in the SI joint. If you are confused about how, it is time to consider taking the Sacroiliac Joint Evaluation and Treatment course!
References:
Capobianco, R., Cher, D., & for the SIFI Study Group. (2015). Safety and effectiveness of minimally invasive sacroiliac joint fusion in women with persistent post-partum posterior pelvic girdle pain: 12-month outcomes from a prospective, multi-center trial. SpringerPlus, 4, 570. http://doi.org/10.1186/s40064-015-1359-y
Zaidi, Hasan A., Montoure, Andrew J., and Dickman, Curits A. (2015). Surgical and clinical efficacy of sacroiliac joint fusion: a systematic review of the literature. Journal of Neurosurgery: Spine. (23)1:59-66. DOI: 10.3171/2014.10.SPINE14516
Whang, P., Cher, D., Polly, D., Frank, C., Lockstadt, H., Glaser, J., … Sembrano, J. (2015). Sacroiliac Joint Fusion Using Triangular Titanium Implants vs. Non-Surgical Management: Six-Month Outcomes from a Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial. International Journal of Spine Surgery, 9, 6. http://doi.org/10.14444/2006
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://hermanwallace.com./