Specific Myofascial Release as a Treatment for Clitoral Phimosis
Myofascial release (MFR) can be one of your greatest treatment tools as a pelvic rehabilitation practitioner. Just in case you don’t think about fascia often here are a couple helpful things to remember. Fascia is the irregular connective tissue that covers the entire body, and it is the largest sensory system in the body, making it highly innervated. The mobilizing effect of MFR techniques occurs by stimulating various mechanoreceptors within the fascia (not by the actual force applied). MFR techniques can help to reduce tissue tension, relax hypertonic muscles, decrease pain, reduce localized edema, and improve circulation just to name a few physiological effects.
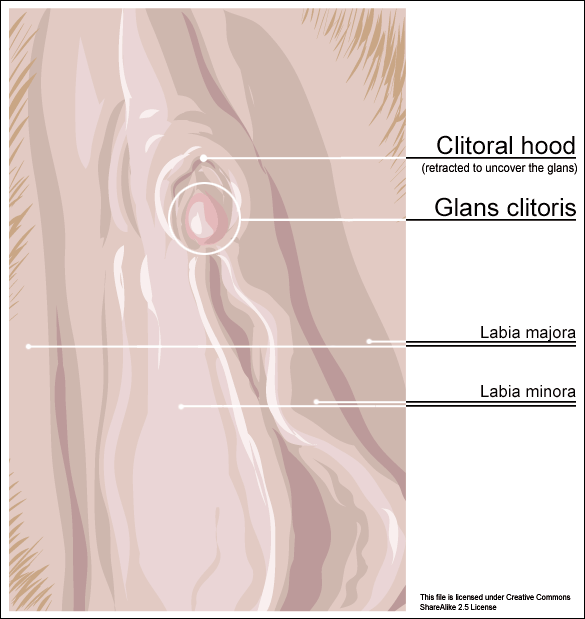 An interesting case report published in 2015 by the Journal of Women’s Health Physical Therapy1 offers a wonderful example of how a physical therapist used specific MFR techniques for a patient with clitoral phimosis and dyspareunia. The specific MFR techniques used helped to provide relief and restore mobility to the pelvic tissues for this patient.
An interesting case report published in 2015 by the Journal of Women’s Health Physical Therapy1 offers a wonderful example of how a physical therapist used specific MFR techniques for a patient with clitoral phimosis and dyspareunia. The specific MFR techniques used helped to provide relief and restore mobility to the pelvic tissues for this patient.
Clitoral phimosis is adherence between the clitoral prepuce (also known as the clitoral hood) and the glans. This condition can be the result of blunt trauma, chronic infection, inflammatory dermatoses, and poor hygiene. In this case report, the 41-year-old female patient had sustained a blunt trauma injury to the vulva (when her toddler son charged, contacting his head forcibly into her pubic region). She presented to physical therapy with complaints of dyspareunia, low back pain, a bruised sensation of her pubic region, vulvar pain provoked by sexual arousal, decreased clitoral sensitivity, and anorgasmia. The physical therapist completed an orthopedic assessment for the lower quarter (including spine and extremities), as well as a thorough pelvic floor muscle assessment.
Treatment for this patient addressed not only the pelvic complaints, but the lower quarter complaints as well. A detailed treatment summary for each visit is outlined in the case report. The clitoral MFR and stretching was performed by applying a small amount of topical lubricant to the clitoral prepuce. Then, a gloved finger or a cotton swab was used to stabilize the clitoris, a prolonged MFR or sustained stretch was applied in the direction away from the fixated clitoris by the therapist’s other finger. The therapist applied this technique along the entire length of the prepuce. The other physical therapy interventions this patient was treated with were stretching, joint mobilization, muscle energy techniques, transvaginal pelvic floor muscle massage, clitoral prepuce MFR techniques, biofeedback, Integrative Manual Therapy (IMT) techniques, nerve mobilization, and therapeutic and motor control exercises. Additionally, between the physical therapy evaluation and the second visit the patient did use topical Clobetasol 0.05% cream (commonly prescribed for vulvar dermatitis issues such as Lichen Sclerosis) for 30 days with no change to her clitoral phimosis.
After 11 sessions, the patient had resolution of dyspareunia, vulvar pain, pubic pain, and reduced low back pain. Also, the patient had 100% restored mobility of the clitoral prepuce, as well as normalized clitoral sensitivity and clitoral orgasm. The patient felt these improvements were still present at her 6-month follow-up interview over the phone. Current medical management for clitoral phimosis is surgical release or topical/injectable corticosteroids. Having a conservative treatment option, such as MFR, for this condition can be helpful for patients. As with most evolving treatment techniques, more research and studies are appropriate.
Not one health care professional had ever assessed the fascial mobility of the clitoris until this physical therapist did. This case report is an example of how MFR techniques can be effective treatment tools for your patients with pelvic disorders and a good reminder to check the fascial mobility of the pelvic tissues.
Morrison, P., Spadt, S. K., & Goldstein, A. (2015). The Use of Specific Myofascial Release Techniques by a Physical Therapist to Treat Clitoral Phimosis and Dyspareunia. Journal of Women’s Health Physical Therapy, 39(1), 17-28.
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://hermanwallace.com./