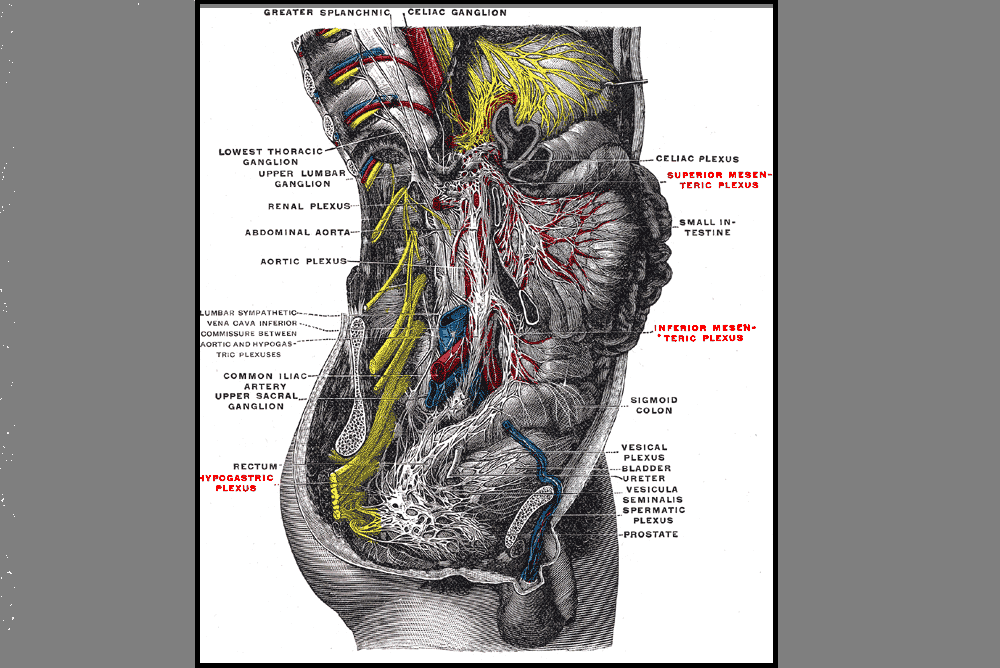
Perimenopausal pelvic health issues are, for many of us, some of the most common issues that we see in the women that we work with. Urinary incontinence is one of the most important issues for peri- and postmenopausal women. In Melville’s study1 of U.S. women, half of the participants between the ages of 50 and 90 experienced urine leakage every month. Zhu’s 2008 study2 looked at the risk factors for SUI - Multiple vaginal deliveries, Age/postmenopausal status, Chronic pelvic pain, Obesity, lack of exercise, constipation, and hypertension. But what is not often (enough) looked at in the research, is the link between urinary dysfunction and sexual dysfunction – usually because questions aren’t asked or assumptions are made. In Mestre et al’s 2015 paper3, they write ‘…Integrating sexual health in clinical practice is important. In women with pelvic floor disorders, the evaluation of the anatomical defects, lower urinary tract function and the anorectal function often receives more attention than sexual function.’
 But are they linked?
But are they linked?
In Moller’s exploration of this topic, they report that lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) have a profound impact on women’s physical, social, and sexual wellbeing. Unsurprisingly (to pelvic rehab specialists at least!), they found that the LUTS are likely to affect sexual activity. Conversely, sexual activity may affect the occurrence of LUTS. The aims of the Moller study were to elucidate to which extent LUTS affect sexual function and to which extent sexual function affect LUTS in an unselected population of middle-aged women in 1 year. A questionnaire was sent to 4,000 unselected women aged 40–60 years. Compared to women having sexual relationship, a statistically significant 3 to 6 fold higher prevalence of LUTS was observed in women with no sexual relationship. In women who ceased sexual relationship an increase in the de novo occurrence of most LUTS was observed. In women who resumed sexual relationship a decrease in LUTS was observed. In women whose sexual activity was unchanged no change in the occurrence of LUTS. So they rightfully concluded ‘…sexual inactivity may lead to LUTS and vice versa.’
In my Menopause course, we will explore the range of perimenopausal pelvic health issues that many women face and their inter-related nature – not just with each other but also how orthopaedic, endocrine and gastro-intestinal health issues influence pelvic health and wellness. Interested in learning more? Come and join the conversation in California in February 2018!
1. Melville JL, et al. Urinary incontinence in US women: a population-based study. Arch Intern Med 2005;165(5):537-42 - See more at: http://www.nursingcenter.com/lnc/JournalArticle?Article_ID=698029#sthash.cm8A90tS.dpuf
2. Zhu L1, Lang J, Wang H, Han S, Huang J. Menopause. 2008 May-Jun;15(3):566-9. The prevalence of and potential risk factors for female urinary incontinence in Beijing, China
3. Mestre M, Lleberia J, Pubill J, Espuña-Pons M Actas Urol Esp. 2015 Apr;39(3):175-82. Epub 2014 Aug 28. Questionnaires in the assessment of sexual function in women with urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse.