Authors: Tamara Rial, PhD, CSPS, Kathleen Doyle-Elmer, PT, DPT and Rebecca Keller, PT, MSPT, PRPC
Tamara Rial, PhD, CSPS, co-founder and developer of Low Pressure Fitness will be presenting the first edition of Low Pressure Fitness and Abdominal Massage for Pelvic Floor Care Level 2 and 3 in Princeton, New Jersey in September, 2019. Rebecca Keller and Kathleen Doyle-Elmer are certified Low-Pressure Fitness specialists with training in rehabilitative ultrasound imaging. In this article, the authors discuss and explore the use of transabdominal ultrasound during Low Pressure Fitness on the abdominal and pelvic floor structures.
Real-time ultrasound imaging is a reliable and valid method to evaluate muscle structure, activity and mobility. Over the past few years, there has been increasing interest in the use of transabdominal ultrasound in the field of rehabilitation. The additional value of ultrasound imaging is that it allows for real-time analysis and visual feedback during the performance of pelvic floor and abdominal exercises (Hides et al., 1998). In the field of pelvic health, this is of notable importance when assessing proper movement of the deep abdominal and pelvic muscles during voluntary muscle actions. Transabdominal ultrasound has been found to be a safe, noninvasive, and accurate method to assess and observe muscular and fascial activity (Khorasani et al., 2012). When therapists learn how to properly use and apply ultrasound imaging, this technique can be a comprehensive tool for the clinician and a comfortable procedure for the patient. Moreover, it may be the method of choice for some patients who don’t want to have an internal pelvic examination (Van Delft, Thakar & Sultan, 2015). In this regard, a cross-sectional study found a moderate-to-strong correlation between ultrasound measurements and both digital examination and perineometry for the assessment of pelvic floor muscle actions (Volløyhaug et al., 2016).
Recently, Low Pressure Fitness has gained popularity as a pelvic floor training program aimed at reducing pressure on the pelvic structures while engaging the stabilizing muscles through postural and breathing exercises. In order to evaluate proper execution of Low-Pressure Fitness exercises as well as abdomino-pelvic muscle function during this type of training, real-time transabdominal ultrasound can be a clinically relevant tool.
Sagittal and Transverse Pelvic Floor/Urinary Bladder Assessment
The amount of movement of the bladder base on transabdominal ultrasound is considered an indicator of pelvic floor muscle mobility during pelvic floor muscle exercises (Khorasani et al., 2012). When properly executed, the Low-Pressure Fitness technique will allow the bladder to lift and the pelvic floor muscles to contract. These observed actions can be cued and progressed due to the real-time imaging biofeedback of the ultrasound. Because of the postural activation and diaphragm lift occurring during Low Pressure Fitness, the bladder fascial support system is tensioned resulting in a desirable bladder lift.
For example, we used a Pathway® Musculoskeletal Rehabilitative Ultrasound Imaging unit with a curvilinear transducer and Prometheus Pathway® rehabilitative ultrasound software utilizing the pre-set parameters (Abdominal Wall 7.5MHz and Bladder 5.0MHz) during a Low-Pressure Fitness basic supine posture. A standardized bladder filling protocol was used before imaging to ensure sufficient bladder filling to allow clear imaging of the base of the bladder and pelvic floor muscles.
For the transverse view, radiologic standards were used, and the ultrasound transducer was placed in the transverse plane suprapubically and angled in a caudal/ posterior direction to obtain a clear image of the inferior-posterior aspect of the bladder. The participant was asked to perform the Low-Pressure Fitness Demeter exercise in the supine position with a neutral pelvis and knees flexed (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Demeter exercise with postural technique and with postural and abdominal vacuum technique combined.
The following video illustrates the pelvic floor/urinary bladder during: a) resting position; b) active pelvic floor contraction; c) Low Pressure Fitness Demeter exercise and; d) Low Pressure Fitness Demeter exercise combined with a voluntary pelvic floor muscle contraction. It is noticeable a greater bladder lift and pelvic floor activation with the postural and breathing cueing added to an active pelvic floor contraction than with the pelvic floor contraction alone.
Video of the behavior of the pelvic floor muscles in a sagital and transversal view during the supine position of Low Pressure Fitness and with the combination of an active pelvic floor muscle contraction.
Lateral Abdominal Wall Assessment
The lateral abdominal muscle ultrasound assessment allows us to observe the structural changes produced in the transversal section of the abdominal muscles in the midpoint between the anterior iliac crest and the costal angle. At low levels of contraction, the extent of transverse abdominis thickening measured using ultrasound is reported to be a valid method of assessment compared with either fine wire electromyographic measures of transverse activity (McMeeken et al., 2004). It is well established in the scientific literature that the lateral abdominal muscles provide stability to the trunk in different functional activities. Therefore, the assessment of the size, thickness and sliding of the abdominal wall is important for patients who present with lumbo-pelvic and/or pelvic floor dysfunctions. In this regard, patients with low back pain show different abdominal wall muscle activation patterns (i.e. less slide of the abdominal fascia and muscle thickness) than those without low back pain (Gildea et al., 2014; Unsgaard-Tondel et al., 2012).
Figure 2 shows the three muscle layers of the lateral wall in the resting position. The superficial layer corresponds to the external oblique, the middle layer to the internal oblique and the deep layer to the transverse abdominal muscle.
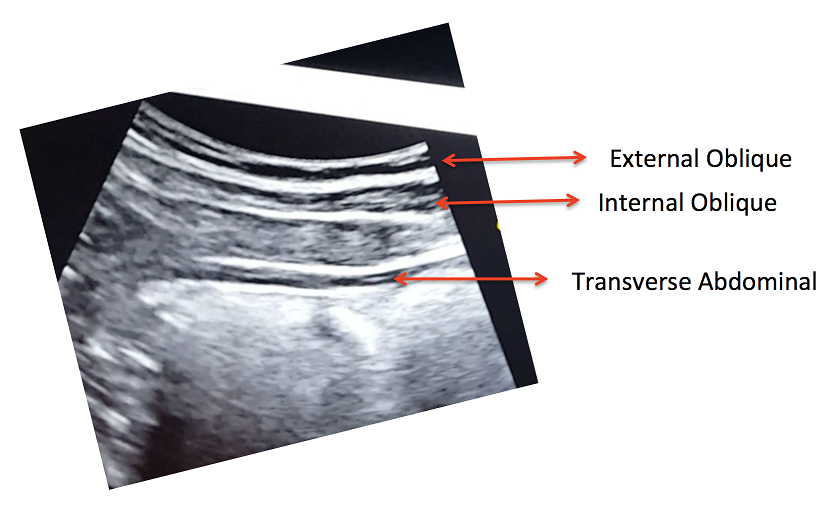
Figure 2. View of the right lateral abdominal wall at rest.
A key breathing component of the Low-Pressure Fitness program is the abdominal vacuum which manipulates intra-abdominal, intra-thoracic and intra-pelvic pressures during the breath-holding phase. Another key aspect of Low-Pressure Fitness is the shoulder girdle activation, spine elongation and ankle-dorsiflexion (Rial & Pinsach, 2017). Of note, previous studies have demonstrated greater transverse abdominis activation when performing ankle dorsi-flexion (Chon et al., 2010). We used transabdominal ultrasound to assess the lateral abdominal wall response during ankle dorsiflexion, shoulder girdle activation and the abdominal vacuum during Low Pressure Fitness.
In the following video, a voluntary (active) abdominal contraction is performed in order to distinguish this action from the involuntary abdominal contractions during Low Pressure Fitness. Afterwards, the postural technique of ankle dorsiflexion and shoulder girdle activation are performed in the Demeter exercise with arms in middle position (Figure 1). Lastly, an abdominal vacuum maneuver is added to the postural technique. If the exercises are properly executed, the progressive sliding and thickness of the abdominal muscles throughout exercise sequence should be observable (Figure 3).
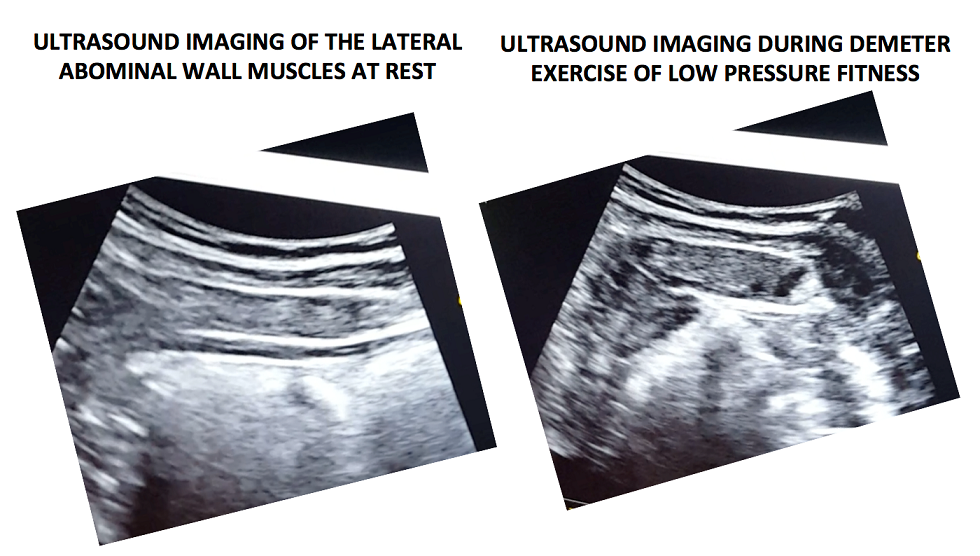
Figure 3. Ultrasound imaging at rest and during the complete LPF technique.
Video of a voluntary (active) abdominal contraction or draw-in maneuver is performed in order to distinguish this action from the involuntary abdominal contractions that occur during Low Pressure Fitness in a supine position
Muscle thickness of the transverse and internal oblique as well as a noticeable slide of the anterior abdominal fascia are observable during the Demeter exercise of Low-Pressure Fitness. This exercise pattern reflects an abdominal draw-in maneuver and a “corseting effect”. In this regard, notice the lateral pull or displacement of the edge of the anterior fascial insertion of the transverse the internal oblique muscle.
Navarro et al., (2017) used transabdominal ultrasound to assess the muscular responses of the pelvic floor and abdominal muscles in a group of women who underwent pelvic physiotherapy over two months. They found a significant increase in the transversal section of the transverse abdominis, external oblique, and internal oblique muscles when compared to resting in the supine position. Similar to the position assessed by Navarro et al. (2017), we also assessed the pelvic floor and abdominal muscle responses during a Low-Pressure Fitness supine exercise.
Transabdominal ultrasound can provide a noninvasive and informative visual biofeedback when training patients with Low Pressure Fitness. This ultrasound imaging can be a valuable tool to both the client and the clinician to objectify progress, assist with validating correct Low-Pressure Fitness form with positioning and vacuum/hypopressive maneuver as well as a motivational technique for the client. As demonstrated during our rehabilitative ultrasound imaging, observable bladder lift, pelvic floor activation and desirable lateral abdominal muscular corseting (slide and thicking) occurs during Low Pressure Fitness postural exercises and breathing. Since Low Pressure Fitness is a progressive exercise program, qualified instruction, technique driven progression and understanding pelvic floor health are needed to optimize patient outcomes.
Chon SC, Chang KY, You JS. Effect of the abdominal draw-in manoeuvre in combination with ankle dorsiflexion in strengthening the transverse abdominal muscle in healthy young adults: a preliminary, randomised, controlled study. Physiotherapy 96: 130-6, 2017.
Gildea JE, Hides JA, Hodges PW. Morphology of the abdominal muscles in ballet dancers with and without low back pain: a magnetic resonance imaging study. J Sci Med Sport. 17(5): 452-6, 2014.
Khorasani B, Arab AM, Sedighi Gilani MA, Samadi V, Assadi H. Transabdominal ultrasound measurement of pelvic floor muscle mobility in men with and without chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Urology, 80: 673-7, 2012.
McMeeken JM, Beith ID, Newham DJ, Milligan P, Critchley DJ. The relationship between EMG and change in thickness of transversus abdominis. Clin Biomech 19: 337–342, 2004.
Hides JA, Richardson CA, Jull GA. Use of real-time ultrasound imaging for feedback in rehabilitation. Man Ther. 3:125-131,1998.
Navarro B, Torres M, Arranz B, Sanchez O. Muscle response during a hypopressive exercise after pelvic floor physiotherapy: Assessment with transabdominal ultrasound. Fisioterapia 39: 187-94, 2017.
Rial T, Pinsach P. Practical Manual Low Pressure Fitness Level 1. International Hypopressive & Physical Therapy Institute, Vigo, 2017.
Unsgaard-Tøndel M, Lund Nilsen TI, Magnussen J, Vasseljen O. Is activation of transversus abdominis and obliquus internus abdominis associated with long-term changes in chronic low back pain? A prospective study with 1-year follow-up. Br J Sports Med, 46(10): 729-34, 2012.
Van Delft K, Thakar R, Sultan AH. Pelvic floor muscle contractility: digital assessment vs transperineal ultrasound. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol, 45: 217-22, 2015. Volløyhaug I, Mørkved S, Salvesen Ø, Salvesen KÅ. Assessment of pelvic floor muscle contraction with palpation, perineometry and transperineal ultrasound: a cross-sectional study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 47: 768-73, 2016.
Tamara Rial, PhD, CSPS, co-founder and developer of Low Pressure Fitness will be presenting the first edition of “Low Pressure Fitness and abdominal massage for pelvic care” in Princeton, New Jersey in July, 2018. Tamara is internationally recognized for her work with hypopressive exercise and Low Pressure Fitness. In this article she presents the novel topic of hypopressives as a complementary pelvic floor muscle training tool for incontinence after prostate cancer surgery.
Urinary Incontinence is the most common side effect men suffer after prostate cancer surgery along with erectile dysfunction. Although it is not life threatening, urinary incontinence definitely has a negative impact on the patient’s quality of life Sountoulides et al., 2013. Beyond the frustration and embarrassment associated with pelvic floor dysfunction, many patients describe it as depressing, disheartening and devastating.
The first line of conservative treatment - and most often recommended - is pelvic floor muscle training Andersen et al., 2015. Over the past few years, some researchers have also recommended alternative exercise programs with a holistic approach such as Pilates and hypopressives to improve the patient’s quality of life and urinary incontinence symptoms (Santa Mina et al., 2015). These alternative pelvic floor muscle training programs draw upon the connection between the pelvic floor, it’s synergistic muscles (abdominal, pelvic, lumbar) and their interrelated role in posture and breathing Hodges, 2007; Sapsford, 2004; Madill and McLean, 2008; Talasz et al., 2010. Among these complementary exercise programs, hypopressives have gained increasing attention for the recovery of post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence Santa Mina et al., 2015; Mallol-Badellino, et al. 2015.
What is known about hypopressives for post-prostatectomy incontinence?
Although hypopressive exercise has become popular for women, some researchers, clinicians and practitioners have begun to apply these exercises for specific male issues such as urinary incontinence following a prostatectomy. Recently, a case-study I co-authored about an adapted program of hypopressive exercise for urinary incontinence following a radical prostatectomy surgery was published in the Journal of the Spanish physiotherapy association Chulvi-Medrano & Rial, 2018. We describe the case of a 46-year-old male with severe stress urinary incontinence six months after surgery. We used a pelvic floor exercise program consisting of hypopressive exercises as described in the Low Pressure Fitness level 1 practical manual Rial & Pinsach, 2017 combined with contraction of the pelvic floor muscles. Satisfactory results were obtained after the rehabilitation protocol as evidenced by a reduction from 3 daily pads to none. Of note, clinical trails have demonstrated the benefits of initiating a rehabilitation program to strengthen the pelvic floor as soon as possible after prostatectomy. Previously, I’ve studied hypopressive exercise for female urinary incontinence Rial et al., 2015 and for the improvement of female athletes pelvic floor function Álvarez et al., 2016. However, this was the first time we’ve studied hypopressives in the context of male urinary leakage.
In the same light, other researchers have also included hypopressives in their pelvic floor training protocol for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence. For example, Serda et al (2010) and Mallol-Badellino (2015) used protocols that combined pelvic floor contractions with postural re-education and hypopressives. Both studies found improvements in the severity of involuntary leakages and improvements in the patients’ quality of life. Similar results are also described in the clinical case by Scarpelini et al. (2014) who used hypopressives and psoas stretching exercises to reduce urinary incontinence after prostatectomy.
But how do hypopressives work?
The hypothesis underlying the use of hypopressives as a complementary pelvic floor and core exercise program is that it retrains the core system with specific postural and breathing strategies while reducing pressure on the pelvic organs and structures. The most striking part of hypopressives breathing technique is the abdominal vacuum. This breathing maneuver involves a low pulmonary volume exhale-hold technique followed by a rib-cage expansion involving the activation of the inspiratory muscles. The rib-cage expansion during the breath-holding phase leads to a noticeable draw-in of the abdominal wall and simultaneously to the rise of the thoracic diaphragm. Recent observational studies have shown how the hypopressive technique was able to elevate the pelvic viscera and to activate the pelvic floor and deep core muscles in women trained with hypopressives Navarro et al., 2017. From an historical point of view, this characteristic breathing maneuver was first described and practiced as a yoga pranayama called Uddiyanha Bandha Omkar & Vishwas, 2009.

Figure 1 shows the anatomical behavior of the rib cage and the abdominal wall when performing the hypopressive breathing maneuver, which should not be confused with an abdominal hollowing, or a bracing maneuver. Anatomical observation of the thoracic and abdominal behavior during the breathing maneuver of the hypopressive exercise. Figure elaborated by the author.
In addition to breath control, the hypopressive technique involves a series of static and dynamic poses which operate on the hypothesis of training the stabilizing muscles of the spine, such as the core and pelvic muscles. In this sense, hypopressives are not exclusively a breathing technique, but rather they are an integrated whole-body technique. The practice of hypopressives involves body control, body awareness, postural correction and mindfulness throughout its different poses and postural techniques. The introduction of holistic exercise programs to train the synergist pelvic floor muscles and breathing patterns can be viewed as complementary tools for the restoration of a patient’s body awareness and functionality.
Another hypothesis of the effects of the hypopressive-breathing in the pelvic floor is the ability to move the pelvic viscera cranially as a consequence of the ribcage opening up after the breath-hold. This vacuum lifts the diaphragm and consequently creates an upward tension on the transversalis fascia, the peritoneum and other related fascial structures. In addition to the diaphragmatic suction effect, a correct alignment of the rib cage and pelvis during the exercise contributes to an improved suspension and position of the viscera in the pelvis. The mobility achieved with the breathing and its body sensations may be one of the reasons why hypopressives have also been recommended as a proprioceptive facilitator for those with low ability to “find their pelvic floor” Latorre et al., 2011.
It’s crucial to highlight that a complete surgical resection of the prostate will cause - in most of the cases - post-operative fibrosis and neurovascular damage Hoy-Land et al., 2014. Both, the neurovascular and musculoskeletal injuries are contributing factors for urinary incontinence post-prostatectomy. Subsequently, exercises focusing on increasing local vascular irrigation and re-activating the damaged musculature have been highlighted as the main goals to help patients recover continence. In this sense, breathing movements, fascia manipulation and decreased pelvic pressure can result in increased vascular supply. A previous study has shown an improvement in venous return of the femoral artery during the hypopressive-breathing maneuver Thyl et al., 2009. Collectively, all these factors may favor microcirculation in the pelvic area. Finally, the muscle activation of the pelvic floor and core muscles observed during the practice of hypopressives (Ithamar et al., 2017) and the changes of puborectalis and iliococcygeus muscles after an intensive pelvic floor muscle training (Dierick et al., 2018) are other factors that could have impact on urge incontinence, stress incontinence and overflow incontinence symptoms common after prostatectomy surgeries.
To date, the results from these investigations and clinical reports open new complementary pelvic floor training strategies for the treatment of post-prostatectomy incontinence. Hypopressives and pelvic floor muscle exercises are non-invasive, don’t require expensive material, and provide an exercise-based approach as part of a healthy lifestyle. However, qualified instruction, technique-driven progression and adherence to the intervention are critical components of any pelvic floor and hypopressive training protocol.
Álvarez M, Rial T, Chulvi-Medrano I, García-Soidán JL, Cortell JM. 2016. Can an eight-week program based on the hypopressive technique produce changes in pelvic floor function and body composition in female rugby players? Retos nuevas Tendencias en Educación Física, Deporte y Recreación, 30(2): 26-29.
Anderson CA, Omar MI, Campbell SE, Hunter KF, Cody JD, Glazener CM. 2015. Conservative management for postprostatectomy urinary incontinence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 1:CD001843.
Chulvi-Medrano I, Rial T. 2018. A case study of hypopressive exercise adapted for urinary incontinence following radical prostactetomy surgery. Fisioterapia, 40, 101-4. Doi: DOI: 10.1016/j.ft.2018.01.004
Dierick F, Galrsova E, Laura C, Buisseret F, Bouché FB, Martin L. 2018. Clinical and MRI changes of puborectalis and iliococcygeus after a short period of intensive pelvic floor muscles training with or without instrumentation. European Journal of Applied Physiology, doi:10.1007/s00421-018-3899-7
Ithamar, L., de Moura Filho, A.G., Benedetti-Rodrigues, M.A., Duque-Cortez, K.C., Machado, V.G., de Paiva-Lima, C.R.O., et al. 2017. Abdominal and pelvic floor electromyographic analysis during abdominal hypopressive gymnastics. J. Bodywork. Mov. Ther. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2017.06.011.
Latorre G, Seleme M, Resende AP, Stüpp L, Berghmans B. Hypopressive gymnastics: evidences for an alternative training for women with local proprioceptive deficit of the pelvic floor muscles. Fisioterapia Brasil 2011; 12(6): 463-6.
Hodges P. 2007. Postural and respiratory functions of the pelvic floor muscles. Neurourol Urodyn, 26(3): 362-371.
Hoyland K, Vasdev N, Abrof A, Boustead G. 2014. Post-radical prostatectomy incontinence: etiology and prevention. Rev Urol. 16(4), 181-8.
Madill, S., McLean, L. 2008. Quantification of abdominal and pelvic floor muscle synergies in response to voluntary pelvic floor muscle ontractions. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 18, 955-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jelekin.2007.05.001.
Mallol-Badellino J., et al. 2015. Resultados en la calidad de vida y la severidad de la incontinencia urinaria en varones prostatectomizados por neoplasia de próstata. Rehabilitación, 49(4); 210-215.
Navarro, B., Torres, M., Arranz, B. Sánchez, O. 2017. Muscle response during a hypopressive exercise after pelvic floor physiotherapy: Assessment with transabdominal ultrasound. Fisioterapia. 39, 187-194. doi:10.1016/j.ft.2017.04.003.
Omkar, S., Vishwas, B. 2009. Yoga techniques as a means of core stability training. J. Bodywork Mov. Thep. 13, 98-103. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2007.10.004.
Rial T, Chulvi-Medrano I, Cortell-Tormo JM, Álvarez M. 2015. Can an exercise program based on hypopressive technique improve the impact of urinary incontinence on women´s quality of life? Suelo Pélvico, 11:27-32.
Rial, T., Pinsach, P. 2017. Low Pressure Fitness practical manual level 1. International Hypopressive and Physical Therapy Institute, Vigo.
Santa Mina D, Au D, Alibhai S, Jamnicky L, Faghani N, Hilton W, Stefanky L, et al. 2015. A pilot randomized trial of conventional versus advanced pelvic floor exercises on treat urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a study protocol. BMC Urology, 15. DOI 10.1186/s12894-015-0088-4
Sapsford R. 2004. Rehabilitation of pelvic floor muscles utilizing trunk stabilization. Man Ther, 9(1): 3-12.
Serdá B, Vesa, A. del Valle, y Monreal P. 2010. La incontinencia urinaria en el cáncer de próstata: diseño de un programa de rehabilitación. Actas Urológicas Españolas, 34(6): 522-30.
Scarpelini P, Andressa Oliveira F, Gabriela Cabrinha S, Cinira H. 2014. Protocolo de ginástica hipopressiva no tratamento da incontinência urinária pós-prostatectomia: relato de caso. UNILUS Ensino e Pesquisa, 11(23): 90-95
Talasz, H., Kofler, M., Kalchschmid, E., Pretterklieber, M., Lechleitner, M. 2010. Breathing with the pelvic floor? Correlation of pelvic floor muscle function and expiratory flows in healthy young nulliparous women. Int. Urogynecol. J. 21, 475-81. doi: 10.1007/s00192-009-1060-1.
Thyl S., Aude P, Caufriez M, Balestra C. 2009. Incidence de l'aspiration diaphragmatique associée à une apnée expiratoire sur la circulation de retour veineuse fémorale: étude par échographie-doppler. Kinésithérapie scientifique, 502; 27-30.
Angie Mueller PT, DPT is the instructor of Low Pressure Fitness and Abdominal Massage for Pelvic Floor Care, a new course on the hypopressive technique and abdominal massage for pelvic health. Join Dr. Mueller on July 27-29 in Princeton, NJ to learn more!
One of the first things I do as a pelvic PT when helping a woman recover from pelvic or core dysfunction, is center her uterus. I believe the uterus is the center of a women- biomechanically, physiologically, and energetically. I have seen that when the uterus is out of position, everything else in the pelvis and core is largely impacted and functions less efficiently. This includes muscular, gastrointentinal, liver, bowel and bladder, hormonal and sexual function.
 The uterus is supported by several important ligaments, which extend from the uterus out to the pelvic bones, as well as to the organs surrounding it- bladder, bowel and intestines. So if this magnificent central organ is out of her “center”- leaning forwards or backwards, or tipped to on side or the other- this can lead to a myofascial imbalance in the pelvis and cause symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction, pain, and hormonal imbalances.
The uterus is supported by several important ligaments, which extend from the uterus out to the pelvic bones, as well as to the organs surrounding it- bladder, bowel and intestines. So if this magnificent central organ is out of her “center”- leaning forwards or backwards, or tipped to on side or the other- this can lead to a myofascial imbalance in the pelvis and cause symptoms of pelvic floor dysfunction, pain, and hormonal imbalances.
In treating thousands of women with pelvic dysfunction, I have observed that a uterus which is leaning too far forward (anteflexed) is often associated with urinary incontinence, issues with bladder urgency and frequency, and bladder prolapse (cystocele). A uterus that is tipped backwards is often associated with constipation, hemorrhoids and bowel prolapse (rectocele). A uterus that is leaning left or right is often associated with hip dysfunction, sacroiliac joint dysfunction and lumbo-pelvic alignment issues. This leads to and hip and/or knee and/or back pain due to asymmetrical pulling of the internal abdomino-pelvic fascia, especially the uterosacral and cardinal ligaments, which affects pelvic and sacral bone alignment, and then knee and ankle tracking. So centering the uterus will balance the internal pelvic and abdominal fascia, and can significantly improves cases of back pain, hip pain, knee or ankle pain.
Ensuring our organs are in their best position for receiving blood, lymph, nerve and hormonal support is critical to their health and function! If any organ in the body, especially the uterus, is not in its optimal position to receive blood, nerve, lymphatic and hormonal circulation, its function will be impacted. Therefore a mal-positioned uterus can also lead to problems with the menstrual cycle, painful periods, and fertility. When assisting any woman through a rehabilitative process, I have found it critical to appreciate how her uterine position contributes to and impacts her overall pelvic and core health- from a musculoskeletal, biomechanical and physiological perspective.
I have found that the best pelvic therapy outcomes result from use of both passive and active techniques to center the uterus. The first step is passive positioning of the uterus, which is most efficiently accomplished through abdominal massage. Abdominal self massage should be done daily. Abdominal massage will help to release any myofascial and ligamentous restrictions that are leading to a mal-positioned uterus. Abdominal massage also greatly improves blood flow and lymphatic circulation to the gut and pelvic organs leading to improved digestion and organ detoxification. Once her uterus is centered by the massage, it is important to immediately implement an active technique that will keep the uterus centered. This active uterine positioning technique must trigger the appropriate posture and breath that will keep her uterus centered with movement and throughout the activities of the day.
The second step to positioning her uterus is active activation of abdomino-pelvic musculature and key fascial chains that elevate and center the pelvic organs. This is accomplished through one of the latest core neuro-reeducation techniques- Low Pressure Fitness®. The Low Pressure Fitness methodology involves a seamless progression of postures and poses that cause a reduction in pressure in the abdomen and trigger an automatic response from the core muscles- abdominals, pelvic floor, multifidus, diaphragm. Low Pressure Fitness uses a breathing technique known as Hypopressive Breathing to reduce intra-abdominal pressure and optimize organ position. The term Hypopressive means “low pressure”. Traditional exercise, core training, sports, and most of our everyday activities are Hyperpressive – they increase the pressure in the abdomen. When the pressure in the abdomen is not appropriately managed, pressure increases, and this causes the spine to compress and the organs (especially the uterus) to move downward and away from their optimal “centered” position. But when the hypopressive breath is triggered, the pressure in the abdomen is reduced, the spine decompresses, the core musculature is gently strengthened, all of the organs lift, and the uterus is centered.
When the uterus is centered, magic happens… the fascial tension in the pelvis balances out; the resting tone of the abdominal and pelvic muscles improve and become easier to strengthen; the blood flow and lymphatic circulation in the pelvis is improved and sexual function and fertility is enhanced; hormones are better regulated and monthly cycles regulate; bowel and bladder function is optimized; the waistline reduces; pain in the back, abdomen and hips is reduced and posture improves. When all of these wonderful things occur, it is directly associated with improved energy, mood, creativity and self confidence. So remember, centering the uterus, through both active and passive techniques, is key when treating any woman. Self abdominal massage followed up by Low Pressure Fitness® are the most powerful techniques I have found to center the uterus and resolve pelvic and core dysfunction in women of all ages and lifestyles.