Faculty member Christine Stewart, PT, CMPT began her career specializing in orthopedics and manual therapy and became interested in women’s health after the birth of her second child. Christine joined Olathe Health in 2010 to further focus on women’s health and obtain her CMPT from the North American Institute of Manual Therapy. She also went through Diane Lee's integrated systems model in 2018. Her course, Menopause Transitions and Pelvic Rehab is designed for the clinician that wants to understand the multitude of changes that are experienced in the menopause transition and how they affect the aging process.
What was your motivation for creating this course?
As I was entering my mid-40s, I started to experience some physiological symptoms that were a bit unnerving. My sleep was inconsistent. My menstrual cycle which used to be every 35 days now was every 21 – and it changed. It lasted longer and was much heavier than before. I also started to experience heart palpitations. I sought out care from my primary care doctor, who ran labs and referred me to a cardiologist. I was placed on a halter monitor and underwent a cardiac ultrasound. The tests all came back..... normal. But I didn’t feel normal. What was happening with my body and why didn’t any of the health professionals that I consulted seem to have any answers? That was where my journey began. I started reading and researching. What I soon learned was that these symptoms, while bothersome and a little unnerving, were common. They often begin as the ovary is changing in its ability to produce hormones. I learned there are ways to manage symptoms through lifestyle choices and treatments that can help in a stage of life that can last for over 20 years. I then started to listen, really listen, to what my patients were telling me about their bodies. I had answers for them about what they were experiencing and could offer some solutions and referrals to the appropriate healthcare providers. While they were all very grateful, I kept hearing the same frustrations. Why don’t more healthcare providers know about perimenopause and menopause? Why am I being told that I must live with my symptoms? Why aren’t more providers well-versed in treatment options? That was my “aha” moment. If more healthcare providers knew about these changes and the symptoms that manifest as a result, hundreds if not thousands of patients could get the care that they need. I wrote Menopausal Transitions and Pelvic Rehab in an effort to bridge the gap in knowledge that currently exists for many of the health care providers treating this patient population. It is a culmination of hours of research into hormones, physiology, health impacts, and treatment options during this time.
Who do you think should take this class?
I truly believe all providers can benefit from taking this course! Nearly 50% of the population can spend most of their lifespan in perimenopause and menopause. Gaining a thorough understanding of this phase of life allows providers to educate and lead their patients down a path of more successful aging. They need this information and are eager to learn! In addition, the knowledge gained about lifestyle modifications can be extrapolated to all patients treated daily, not just those in the menopausal transition.
What is your go-to resource for questions about menopause?
One of the most exciting things to see is how the paradigm regarding menopause is changing. There are books, Instagram influencers, Facebook groups, and featured stories appearing in mainstream media. The dialogue surrounding menopause seems to be shifting in a positive way which is great! However, misinformation and false narratives are still being propagated. My resource for the most accurate information is the North American Menopause Society. It is a great site for finding efficacy with treatment options and for debunking much of the fear and myths about menopause.
What has been some of your favorite feedback from participants?
I love to hear about how participants have gained an understanding of their own symptoms and what is happening in their bodies. Getting feedback that they have learned treatment strategies in this course that they will implement in their own lives as well as in the lives of their patients is so exciting. Knowing that clinicians are educating their patients and co-workers on this transition is so meaningful. It thrills me to know the message is going forward!
Menopause Transitions and Pelvic Rehab

Price: $475.00 Experience Level: Beginner Contact Hours: 16.75 hours
Course Dates: August 27-28 and November 11-12
Description: This two-day course is designed for the clinician that wants to understand the multitude of changes that are experienced in the menopause transition and how they affect the aging process. According to the North American Menopausal Society, by the year 2025, 1.5 billion people will be in menopause worldwide. Despite the large population in this transition, health care providers are often unsure of how to treat patients experiencing menopause (Kling 2019).
As clinicians, this is an excellent opportunity to understand the physiological consequences to the body as hormones decline, in order to assist our patients in lifestyle habits for successful aging. Topics will include cardiovascular changes, metabolic syndrome, bone loss and sarcopenia, neurological changes (headache, brain fog, sleeplessness), Alzheimer’s risk, and urogenital changes. Symptoms and treatment options will also be discussed, including hormone replacement, non-hormonal options, dietary choices and exercise considerations. Upon completion of this course, participants will have a basic understanding of the hormonal changes during menopause, the impact on various health systems and interventions that can assist with improving this transition.
Kate Bailey, PT, DPT, MS owns a private practice in Seattle that focuses on pelvic health for all genders and ages and works under a trauma-informed model where patient self-advocacy and embodiment are a priority. In addition to being a physical therapist, I’ve been teaching Pilates for nearly 20 years and yoga for over 10. Kate’s course, Restorative Yoga for Physical Therapists, combines live discussions and labs with pre-recorded lectures and practices that will be the basis for experiencing and integrating restorative yoga into physical therapy practice. Kate brings over 15 years of teaching movement experience to her physical therapy practice with specialties in Pilates and yoga with a focus on alignment and embodiment.
Stress is a primary topic of conversation in all domains of our lives. Are we getting the right nutrition and exercises? Are we “balancing” our lives well? How are we attempting to stave off burnout whether we are a clinician or a patient? The stress of having medical needs, particularly when they are complex can be overwhelming: multiple appointments to juggle with education from a wide variety of medical perspectives (hopefully aligning relatively well), and then just trying to keep up with normal adulting responsibilities. If you are a clinician the idea of burnout and being drained emotionally is likely a familiar one.
When thinking about stress and overwhelm, there are a plethora of physiological consequences ranging from small, workable symptoms to severe mental and physical outcomes. In this blog we’ll look at cognition from two studies: one that looked at those experiencing breast cancer related cognitive impairment and a second looking at third year medical student wellbeing.
Cognition can be separated into two domains: Fluid intelligence and crystallized intelligence.
Fluid intelligence is the ability to process new information and solve novel problems in real time. Think about having to come up with questions for your doctor when managing medications, or simply learning what that medication does and what possible side effects to watch out for. Fluid intelligence is the domain in which we learn new precautions after a surgical procedure or learn about what to do if in a pain flare. Fluid intelligence includes learning, problem solving and comprehension.
Crystallized intelligence is the ability to use knowledge that was previously acquired through education and experience. This is how we use past experience to inform decision making. How we start at entry level education and then build on that with continuing education. Its how people who have dealt with chronic illness or pain can approach new medical issues in perhaps a more adaptable manner.
In a study by Deng et al. fluid and crystallized intelligence changes were studied using two different kinds of yoga as the catalyst. Restorative yoga compared to Vinyasa yoga, said another way, a restful practice versus a vigorous practice. The restorative group had no improvements in crystallized cognition. But they did have statistically significant improvements in fluid cognitions with effect sizes growing from participants being in the 42nd percentile to the 55th percentile among the general population after 24 weeks of practice. The change in ability to learn, comprehend and problem solve whilst working through cancer related cognitive impairment is incredibly important. The vinyasa group had no statistically significant changes in fluid cognition, but did have improvements in crystallized cognition. Thus depending on which cognitive domain is troubling the patient more, you can offer a bit of support in that decision making process.
While much of the continuing education offered to clinicians is in regards to how to become more skillful for your patients, we also need support for clinicians to ensure their own wellbeing. This can come in the form of boundaries, support groups, mental health counseling, etc. It can also come in the form of establishing a simple weekly practice of restorative yoga. In a study by Adesanya et al, 3rd year medical students were offered a 45 minute restorative class once a week for 6 weeks. This is the time in a medical student’s life where a primary focus on didactics transitions into clinical care. With this practice, once a week, medical students reported improved wellbeing marked by increased relaxation and reduced stress related to decision making. It was also noted that the efficiency of the practice was more feasible for the clinical life of having to decide how to spend one’s time outside of work. While restorative yoga is not a substitute for aerobic, strength and mobility training, it is imperative to see the cognitive benefits of this practice and how that might improve our decision making in the domains of our selfceare (nutrition, exercise, sleep), as well as our mental and relational health (friendships, partnerships, colleagues).
Resources:
- Deng, G., Bao, T., Ryan, E. L., Benusis, L., Hogan, P., Li, Q. S., Dries, A., Konner, J., Ahles, T. A., & Mao, J. J. (2022). Effects of Vigorous Versus Restorative Yoga Practice on Objective Cognition Functions in Sedentary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Integrative Cancer Therapies, 21, 153473542210892. https://doi.org/10.1177/15347354221089221
- Adesanya, O., Thompson, C., Meller, J., Naqvi, M., & TetyanaL Vasylyeva. (2023). Restorative yoga therapy for third-year medical students in pediatrics rotation: Working to improve medical student well-being. 12(1), 76–76. https://doi.org/10.4103/jehp.jehp_1027_22
Restorative Yoga for Physical Therapists

Price: $275.00 Experience Level: Beginner Contact Hours: 10.75 hours
Course Dates: August 12, 2023
Description: This course is an online course that combines live Zoom discussions and labs, pre-recorded lectures, and pre-recorded practices that will be the basis for experiencing and integrating restorative yoga into physical therapy practice.
It is well known that stress is an important contributor to overall quality of life, chronic pain, and disease risk. Our society’s focus on high productivity and achievement often creates chronic fatigue and reduced ability to regulate our nervous systems. Sleep may be the only time a person actually rests during the day. For those who have survived trauma, even sleep is not restful. And so we stay in a state of stress that is difficult to manage.
Restorative yoga is an accessible practice that can teach patients (and practitioners) how to rest systematically, for short periods of time, on a regular basis to encourage the parasympathetic nervous system to balance with the sympathetic nervous system for improved neuroregulation. We will also talk about the difference between meditation and restorative yoga, and how they can support each other in order to support the ability to drop into relaxation.
Designed for the virtual classroom, the lectures are pre-recorded for viewing at convenience. A set of restorative postures, each taking 20-30 minutes are offered prior to the live meetings so that participants can experience what a patient might experience when restorative yoga is a component of their home program. We will then discuss participant experiences, questions and strategize how to reduce barriers to relaxation so that patients can integrate this practice into their lifestyle. There will also be live labs for breathing techniques and specific meditations that may be helpful to patients working with an unregulated nervous system.

Ziya “Z” Altug, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, is instructing his course, Integrative and Lifestyle Medicine Toolbox, scheduled for July 29. This remote course covers a toolbox approach for creating clinically relevant pain, anxiety, depression, and stress management strategies using lifestyle medicine, integrative medicine, expressive and art-based therapies, and nature-based therapies.
Ziya is a Board-Certified Orthopedic Clinical Specialist and a Doctor of Physical Therapy with 32 years of experience treating musculoskeletal conditions. He utilizes lifestyle and integrative medicine strategies in his clinical practice. Ziya is the author of Integrative Healing: Developing Wellness in the Mind and Body (Cedar Fort, Inc, 2018). He has been a longstanding member of the American Physical Therapy Association for the past 29 years and a member of the American College of Lifestyle Medicine since 2017. He is finishing the book Lifestyle Medicine Toolbox (Jessica Kingsley Publishers, London) for publication in early 2024.
Ziya's book Lifestyle Medicine Toolbox is available for pre-order on Amazon!
According to the ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription (American College of Sports Medicine 2022) book from the American College of Sports Medicine, “exercise programs that incorporate individual tailoring, supervision, stretching, and strengthening, coupled with client preference and practitioner expertise, are associated with the best outcomes.”
The American College of Lifestyle Medicine defines lifestyle medicine as (American College of Lifestyle Medicine 2023), “Lifestyle medicine is the use of evidence-based lifestyle therapeutic approaches including:
-
- a whole food, plant-based eating pattern
- regular physical activity
- restorative sleep
- stress management
- avoidance of risky substances
- positive social connection
Lifestyle medicine may play a role in managing chronic low back pain (Altug, 2021). For example, a retrospective longitudinal study by Roberts and colleagues (2022) found that “people who adopt optimal lifestyle behaviors and positive emotional factors are more likely to be resilient and maintain high levels of function despite suffering from low back pain.” Furthermore, a study by Williams and colleagues (2019) in the European Journal of Pain found that a healthy lifestyle intervention consisting of weight loss, physical activity, and diet may be cost-effective compared to usual care for managing chronic low back pain. Moreover, a cohort study by Bohman and colleagues (2014) found that healthy lifestyle behaviors appear to decrease the risk of back pain among women.
Case Study Patient Description:
The patient is a 50-year-old female referred to physical therapy by her family physician:
-
- Primary Complaints: Gradual onset of back pain 2-8/10
- Secondary Complaints: Shortness of breath with stairclimbing at home and fatigue with walking greater than 20 minutes
- Past Medical History: Osteopenia, prediabetes, overweight
- Pain History: Progressive back pain for the past 6 months with no known cause
- Pain Aggravating Factors: Sitting greater than 30 minutes, walking greater than 15 minutes, bending to clean and refill the cat food dish
- Pain Easing Factors: Resting in a reclining chair, self-massage to the back
- Medications: Ibuprofen, as needed
- Prior Therapy: None
- Work History: Accountant for a large company. Performs mainly seated computer-related tasks. The patient has a one-hour commute to work in each direction.
- Social History: She lives in a two-level home with her husband and two children. She volunteers at a community center on Saturdays.
- Exercise History: No formal program
- Lifestyle History: No smoking or alcohol use. The patient has difficulty sleeping greater than 5 hours secondary to work-related stress and long commute.
Interventions:
After a comprehensive assessment, a physical therapist treated the patient in the clinic and provided her with the following home program guidelines:
-
- Exercise Program: Since the patient has a long commute, she did not have time to exercise after work. The patient was encouraged to initiate a short-bout outdoor walking program at work. She performed 10 minutes of walking in the morning upon arrival at work, 10 minutes of walking during lunch, and 10 minutes of walking as she returned to her car at the end of her workday. The therapist also instructed the patient in simple core stabilization exercises she could perform at her office.
- Office Program: The patient was advised to stand and perform several stretches for one minute every 30 to 45 minutes. The patient also spoke to her supervisor and switched to remote work from her home twice weekly.
- Sleep Hygiene Program: The patient was issued sleep hygiene guidelines to help improve sleep. She was instructed in a mindfulness meditation routine to be performed before bedtime.
- Stress Management: Since the patient was saving four hours of commute time per week due to two days of remote work, she applied this time to work in her garden during the week and on the weekend. She found gardening and being in nature helped reduce her stress and improve her sleep.
In addition to the formal home program, the physical therapist encouraged the patient to consider creating a small home gym and take a cooking class at a local community college on the weekend to further establish sustainable, healthful habits.
Conclusion:
After three months of following her home program instructions, the patient’s back pain decreased to 0-2/10 with activities of daily living, her body weight was reduced by 10 pounds, and she no longer had shortness of breath with stairclimbing and fatigue with walking. This case shows that simple and cost-effective clinical recommendations using the lifestyle medicine approach may effectively help treat back pain.
References:
- Altug Z. Lifestyle medicine for chronic lower back pain: an evidence-based approach. Am J Lifestyle Med. 2021;15(4):425-433.
- American College of Lifestyle Medicine. Available at: https://lifestylemedicine.org. Accessed May 2023.
- American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM’s Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription, 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Wolters Kluwer; 2022.
- Bohman T, Alfredsson L, Jensen I, Hallqvist J, Vingård E, Skillgate E. Does a healthy lifestyle behaviour influence the prognosis of low back pain among men and women in a general population? A population-based cohort study. BMJ Open. 2014;4(12):e005713.
- Roberts KE, Beckenkamp PR, Ferreira ML, et al. Positive lifestyle behaviours and emotional health factors are associated with low back pain resilience. Eur Spine J. 2022;31(12):3616-3626.
- Williams A, van Dongen JM, Kamper SJ, et al. Economic evaluation of a healthy lifestyle intervention for chronic low back pain: A randomized controlled trial. Eur J Pain. 2019;23(3):621-634.
Further Readings:
- Arippa F, Nguyen A, Pau M, Harris-Adamson C. Postural strategies among office workers during a prolonged sitting bout. Appl Ergon. 2022;102:103723.
- Jakicic JM, Kraus WE, Powell KE, et al. Association between bout duration of physical activity and health: a systematic review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51(6):1213-1219.
- Madjd A, Taylor MA, Delavari A, Malekzadeh R, Macdonald IA, Farshchi HR. Effect of a long bout versus short bouts of walking on weight loss during a weight-loss diet: a randomized trial. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2019;27(4):551-558.
- Menardo E, Di Marco D, Ramos S, et al. Nature and mindfulness to cope with work-related stress: a narrative review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(10):5948.
- Rusch HL, Rosario M, Levison LM, et al. The effect of mindfulness meditation on sleep quality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019;1445(1):5-16.
Integrative and Lifestyle Medicine Toolbox

Price: $125.00 Experience Level: Beginner Contact Hours: 4.5 hours
Course Dates: July 29, 2023
Description: Brief lectures will focus on the research and resources and labs will cover a toolbox approach for creating clinically relevant pain, anxiety, depression, and stress management strategies using lifestyle medicine, integrative medicine, expressive and art-based therapies, and the impact of nature on health. Participants will be able to practice Tai Chi/Qigong, expressive and art-based therapies including Music, Dance, and Drama Therapy, nature and aromatic therapies, self-hypnosis, and self-massage.
This course was written and developed by Ziya “Z” Altug, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, a board-certified doctor of physical therapy with 32 years of experience in treating musculoskeletal conditions. Ziya utilizes lifestyle and integrative medicine strategies in his clinical practice. He is the author of the book Lifestyle Medicine Toolbox from Jessica Kingsley Publishers (London: United Kingdom, 2024). Ziya Altug is a member of the American Physical Therapy Association and the American College of Lifestyle Medicine. He has taken workshops in yoga, Pilates, tai chi, qigong, meditation, Feldenkrais Method, and the Alexander Technique.

Tara Sullivan, PT, DPT, PRPC, WCS, IF has specialized exclusively in pelvic floor dysfunction treating bowel, bladder, sexual dysfunctions, and pelvic pain since 2012. Alyson N. Lowrey, PT, DPT, OCS became involved with pelvic rehabilitation through working in a clinic with Tara and is a board-certified orthopedic specialist and primarily works with the ortho patient population. Tara brought along the pelvic floor population to the clinic where she and Alyson joined forces. Alyson, with her ortho perspective, is better able to recognize that in some of her orthopedic patients, a lot of their pain was coming from the pelvic floor. The pelvic pain patient population crosses over from physical therapy to the orthopedic and occupational therapy worlds. By treating their patients wholistically Tara and Alyson have been able to make a huge difference to both of their practices.
How do you explain pain to a patient?
This is the question that Tara Sullivan, PT, DPT, PRPC, WCS, IF, and Alyson N Lowrey, PT, DPT, OCS address in their new course Pain Science for the Chronic Pelvic Pain Population. By focusing specifically on the topic of pain science in their new course, Tara and Alyson delve into the true physiology of pain including the topics of central and peripheral sensitization. Pelvic specialists that can benefit from this course are those whose patients have chronic pelvic pain including endometriosis, interstitial cystitis, irritable bowel syndrome, vaginismus, vestibulodynia, primary dysmenorrhea, and prostatitis. The biggest thing is to learn how to recognize if there is a sensitization component to your patient’s pain.
Pain is in the Brain
Acute pain can indicate specific injury to the body. Chronic pain is very different. With Chronic Pelvic Pain (CPP) the initial injury has healed, but the pain continues because of changes in the nervous system, muscles, and tissues. Recognizing that the nervous system influences pain perception, especially in the chronic pelvic pain population, is the first step in treating these patients, but is it enough? The chronic pain population is often dismissed or misled that they have something drastically wrong with them, or worse, nothing wrong with them at all. Alyson and Tara share that “this population often has the most functional deficits and the worst clinical outcomes. We want to change that.”
The medical definition of pain is an unpleasant feeling that is conveyed to the brain by sensory neurons. Pain is a universal experience that serves to alert the brain to potential damage to the body. It performs the function of triggering avoidance to preserve itself from harm. Oddly, the strength and unpleasantness of pain are not directly related to the nature or extent of the damage.
When the pain signal remains active in the nervous system for longer than six months and persists after the triggering event has healed, then it is cataloged as chronic pain. There is another layer when experiencing chronic pain known as central sensitization. This is an increased responsiveness of the nervous system that results in hypersensitivity and an increased pain response outside the area of injury. Pain itself can produce systematic and chemical brain changes resulting in more pain from fewer stimuli.
Pain Science for the Chronic Pelvic Pain Population offers tools to recognize when sensitization may be playing a role and provides the framework needed to apply pain science to the chronic pelvic pain population. In this course, you will gain an understanding and expand your knowledge on how pain science specifically presents in patients suffering from endometriosis, interstitial cystitis, primary dysmenorrhea, pelvic floor muscle overactivity, vulvodynia/vestibulodynia, vaginismus, and prostatitis.
Case studies and specific intervention techniques, including how to explain pain to a patient, are discussed so participants leave with the confidence to address the missing link in treating your patient’s chronic pelvic pain. We will also discuss how common rehab interventions such as manual therapy, dry needling, biofeedback, graded exposure, and therapeutic exercise assist in downregulating the nervous system.
Alyson shares that being able to recognize chronic pain in the patient is huge, that this is “not your regular patient who has a peripheral injury and we just need to rehab them through that process. It’s a whole different ballgame when we’ve got our nervous system in a hypersensitive state.” She continues, “a huge part of the treatment is educating your patient about pain and trying to decrease the fear around movement…and how we use our words to decrease fear is huge.” This course also discusses how to desensitize the nervous system through dry needling, diaphragmatic breathing, sleep hygiene, and bowel and bladder retraining.
Pain Science for the Chronic Pelvic Pain Population

Price: $400.00 Experience Level: Beginner Contact Hours: 12 hours
This remote course is designed for the pelvic rehab specialist who wants to expand their knowledge, experience, and treatment in understanding and applying pain science to the chronic pelvic pain population including endometriosis, interstitial cystitis, irritable bowel syndrome, vaginismus, vestibulodynia, primary dysmenorrhea, and prostatitis. This course provides a thorough introduction to pain science concepts including classifications of pain mechanisms, peripheral pain generators, peripheral sensitization, and central sensitization in listed chronic pelvic pain conditions; as well as treatment strategies including therapeutic pain neuroscience education, therapeutic alliance, and the current rehab interventions' influence on central sensitization. This evidence-based course will provide the rehab professional with the understanding and tools needed to identify and treat patients with chronic pelvic pain from a pain science perspective.
Lecture topics include the history of pain, pain physiology, central and peripheral sensitization, sensitization in chronic pelvic pain conditions, therapeutic alliance, pain science and trauma-informed care, therapeutic pain neuroscience education, the influence of rehab interventions on the CNS, and specific case examples for sensitization in CPP.
Course Dates: July 22-23

In this brief blog, I hope to explore several lifestyle medicine strategies (sleep hygiene, stress management, social connectedness) and how they may be included in therapeutic interventions to improve clinical outcomes. Frates and colleagues define lifestyle medicine as "The use of evidence-based lifestyle therapeutic approaches, such as a predominately whole-food and plant-based diet, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, stress management, avoidance of risky substance use, and other non-drug modalities to treat, oftentimes reverse, and prevent the lifestyle-related, chronic disease that's all too prevalent."1 Figure 1, adapted from the American College of Lifestyle Medicine, outlines the six pillars of lifestyle medicine.
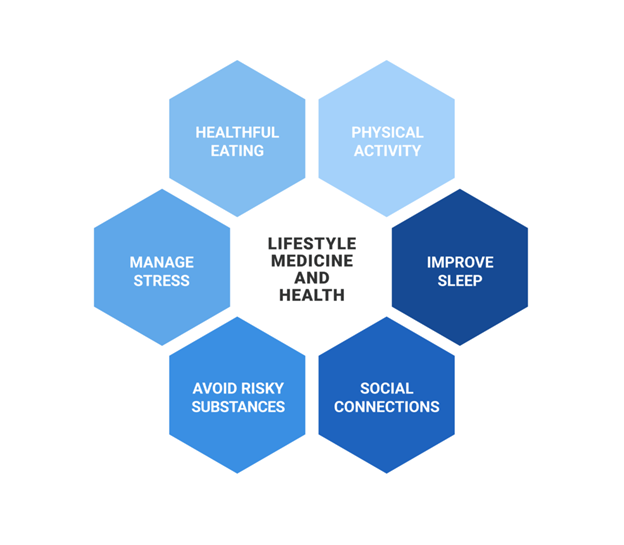
Figure 1. Components of lifestyle medicine
Sleep Hygiene in Patient Education
The following are some simple patient education strategies that may help patients improve sleep:2-5
- Establish a regular bedtime and waking hours (avoid or minimize "social jet lag" that may be due to work, school, or your personal schedule).
- Create a comfortable room that is cool, dark, and quiet.
- Sleep in a comfortable bed and make sure it's not too old.
- Use a supportive and comfortable pillow and ensure it's not too old.
- Eliminate nighttime caffeine and limit daytime caffeine.
- Do not wear tight or restrictive clothing during sleep
- Avoid alcohol within 3 hours of bedtime.
- Do not smoke or use nicotine.
- Eliminate/limit after-dinner and late-night snacking.
- Limit or avoid computer use and smartphone use near bedtime.
- Avoid intense exercise near bedtime. However, do exercise and be physically active during the day.
- Maintain a healthy body mass index (BMI).
- Avoid watching intense television shows before bedtime.
- Turn off the radio and television before going to sleep.
- Avoid bright light near bedtime, but do increase daytime exposure to sunlight.
- Consider reducing your fluid intake near bedtime to avoid (or minimize) getting up to go to the bathroom, but maintain adequate hydration during the day.
- Minimize sugar and salt intake near bedtime as it may cause increased trips to the bathroom.
- Learn strategies to reduce daily stress so it does not result in poor quality and quantity of sleep.
- Minimize a tense or stressful lifestyle since this may carry over into sleep.
- Embrace mindfulness before bedtime
- Consider meditating close to bedtime or using a body scan or progressive muscle relaxation technique.
- Consider tai chi, qigong, or yoga later in the day.
- Establish a bedtime ritual such as:
- One hour before going to sleep, shut down all phone and computer devices. Then you can either read a book or watch a funny television show (drama may be too stimulating).
- Five minutes before you go to sleep, brush your teeth and floss, wash your hands and face with lavender soap, and shut off all the lights before slipping into your cozy bed with gratitude and pleasant thoughts.
Stress Management Patient Education
The following are some simple patient education strategies that may help patients manage stress:6
- Try yoga, tai chi, qigong
- Use aromatherapy (such as lavender)
- Engage in outdoor physical activities such as walking, hiking, and biking
- Engage in outdoor activities such as gardening
- Participate in hobbies such as reading, pottery, painting, and playing music
- Play with pets
- Get a massage
- Get involved in social activities such as volunteering, coaching, and community dancing
- Listen to music
- Smile and laugh more by watching comedy movies or television shows
Social Connectedness Patient Education
The following are some simple patient education strategies that may help patients improve socialization and social connectedness to form nurturing and constructive relationships:7-13
- Attend local sporting events, music performances, or art and museum exhibits.
- Connect with family and friends locally or on Zoom.
- Connect with your physician, therapist, wellness, or fitness professional via telehealth-delivered services.
- Create or join a community garden club.
- Create or join a lunchtime walking, yoga, or tai chi club.
- Engage in conventional group exercises such as softball, volleyball, basketball, pickleball, paddle tennis, or tennis.
- Engage in mind-body exercises such as yoga, tai chi, or Pilates.
- Engage in work-related community activities and fitness programs.
- Engage in small conversations with cashiers and employees at various stores you visit.
- Engage with members at your community place of worship.
- Enroll in art-based community activities, such as art, dance, drama, music, poetry, pottery, or expressive writing classes.
- Enroll at a local or community college to take cooking, history, or astronomy classes.
- Get a library card and participate in book club events.
- Get involved in nature-based activities, such as bird watching, botanical garden and park visits, farmer's market shopping, forest bathing or hiking, gardening, or walks at a lake, river, or beach.
- Join a group, such as a local bicycling club, chess, or table tennis club, or participate in your favorite hobby.
- Join a gym or fitness center.
- Join self-help groups.
- Join social media platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, or TikTok.
- Play with your pets.
- Volunteer at a community center, hospital, school, or library.
- Volunteer to coach sports or mentor students.
- Walk with a mall club or create one in your neighborhood
If you are interested in learning more about these topics and others, please see my course Integrative and Lifestyle Medicine Toolbox for Rehab and Pain Management with Herman & Wallace.
Resources for Clinicians:
Learn how to include integrative and lifestyle medicine into your clinical practice with these resources:
- Academy of Integrative Health & Medicine
- American College of Lifestyle Medicine
- American College of Preventive Medicine
- Institute of Lifestyle Medicine
- National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health
Instructor Bio:
 Ziya "Z" Altug, PT, DPT, MS, OCS is a board-certified doctor of physical therapy with 32 years of clinical experience treating musculoskeletal injuries. Z currently provides outpatient physical therapy in the home setting in Los Angeles, California, and serves as a continuing education instructor.
Ziya "Z" Altug, PT, DPT, MS, OCS is a board-certified doctor of physical therapy with 32 years of clinical experience treating musculoskeletal injuries. Z currently provides outpatient physical therapy in the home setting in Los Angeles, California, and serves as a continuing education instructor.
Z received his Bachelor of Science in Physical Therapy at the University of Pittsburgh in 1989, Master of Science in Sport and Exercise Studies in 1985 and Bachelor of Science in Physical Education in 1983 from West Virginia University, and a Doctor of Physical Therapy from the College of St. Scholastica in 2015. Z is a long-standing member of the American Physical Therapy Association and a member of the American College of Lifestyle Medicine. He has attended workshops in yoga, tai chi, qigong, Pilates, Feldenkrais Method, and the Alexander Technique.
Z is the author of the books Integrative Healing: Developing Wellness in the Mind and Body (2018), The Anti-Aging Fitness Prescription (2006), and Manual of Clinical Exercise Testing, Prescription, and Rehabilitation (1993). In 2020, he published the chapter Exercise, Dance, Tai Chi, Pilates, and Alexander Technique in The Handbook of Wellness Medicine. In 2021, he published the article Lifestyle Medicine for Chronic Lower Back Pain: An Evidence-Based Approach in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.
References:
- Frates, B., Bonnet, J.P., Joseph, R., & Peterson, J.A. (2019). Lifestyle Medicine Handbook: An Introduction to the Power of Healthy Habits. Monterey, CA: Healthy Learning.
- Altug Z. Integrative Healing: Developing Wellness in the Mind and Body. Springville, UT: Cedar Fort, Inc.; 2018.
- Kryger MH, Roth T, Goldstein CA. Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine (2 Volume set), 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021
- Matsuo T, Miyata Y, Sakai H. Effect of salt intake reduction on nocturia in patients with excessive salt intake. Neurourol Urodyn. 2019;38(3):927-933.
- Vitale KC, Owens R, Hopkins SR, Malhotra A. Sleep hygiene for optimizing recovery in athletes: review and recommendations. Int J Sports Med. 2019;40(8):535-543.
- American College of Lifestyle Medicine. Handout: Lifestyle stress reduction. American College of Lifestyle Medicine; 2019.
- Leavell MA, Leiferman JA, Gascon M, Braddick F, Gonzalez JC, Litt JS. Nature-based social prescribing in urban settings to improve social connectedness and mental well-being: a review. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2019;6(4):297-308.
- National Institutes of Health. Social Wellness Toolkit. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health. Accessed on June 2022.
- Roland M, Everington S, Marshall M. Social prescribing - transforming the relationship between physicians and their patients. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(2):97-99.
- Choi NG, Pepin R, Marti CN, Stevens CJ, Bruce ML. Improving social connectedness for homebound older adults: randomized controlled trial of tele-delivered behavioral activation versus tele-delivered friendly visits. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2020;28(7):698-708.
- Davidson KW, Krist AH, Tseng CW, et al. Incorporation of social risk in US Preventive Services Task Force recommendations and identification of key challenges for primary care. JAMA. 2021;326(14):1410-1415.
- Eder M, Henninger M, Durbin S, et al. Screening and interventions for social risk factors: technical brief to support the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2021;326(14):1416-1428.
- Steinman L, Parrish A, Mayotte C, et al. Increasing social connectedness for underserved older adults living with depression: a pre-post evaluation of PEARLS. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2021;29(8):828-842.
Integrative and Lifestyle Medicine Toolbox for Rehab and Pain Management

Course Dates:
January 21, 2023
Price: $125
Experience Level: Beginner
Contact Hours: 4.5
Description: This course was written and developed by Ziya “Z” Altug, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, a board-certified doctor of physical therapy with 32 years of experience in treating musculoskeletal conditions, Brief lectures on the research and resources and labs will cover a toolbox approach for creating clinically relevant pain, anxiety, depression, and stress management strategies using lifestyle medicine, integrative medicine, expressive and art-based therapies, and the impact of nature on health. Participants will be able to practice Tai Chi/Qigong, expressive and art-based therapies including Music, Dance, and Drama Therapy, nature and aromatic therapies, self-hypnosis, and self-massage.

Kristina Koch, PT, DPT, is a board-certified clinical specialist in women’s health physical therapy and a certified lymphedema therapist. Kristina has been treating pelvic health conditions in individuals of all ages and genders since 2001 and works in private practice in Colorado Springs, CO. She has served as a guest lecturer for the pelvic health curriculum at Regis University in Denver and for the 3rd year medical students at the University of Colorado, Colorado Springs campus. She is the creator of Pharmacologic Considerations for the Pelvic Health Provider.
Although it is not within the scope of practice for rehab therapists to manage medications, it’s important that we review patient medications during the initial evaluation and on an ongoing basis. Therapists have a duty to assess medications impact on treatment and patient outcomes and to ensure patient safety. The population is aging and many patients over the age of 65 are on more than 5 medications, increasing the risk of medication side effects, adverse drug reactions, and drug interactions.
Primary care providers spend approximately 14-17 minutes with a patient during a visit, and the patient gets about 5 minutes to discuss their concerns, leaving little time for medication reconciliation or discussion regarding medication side effects (Tai-Seale, McGuire & Zhang, 2007). As therapists, we tend to see our patients for longer periods of time and more frequently, giving the patient more of an opportunity to discuss their signs and symptoms. Additionally, patients referred for pelvic health issues are often seeing multiple specialty providers (Ob/Gyn, urology, urogynecology, pain management, etc.) for their care, and each one is typically prescribing medications, potentially leading to polypharmacy. Understanding a medication’s actions, its impact on therapy, the side effects, and potential adverse drug reactions, can help guide treatment and improve patient outcomes.
A recent patient example is a post-menopausal cisgender female, referred by her primary care physician, for urinary urgency and nocturia. Her past medical history was significant for breast cancer. Her medications included an aromatase inhibitor, antihistamine due to seasonal allergies, and Vitamin C. After reviewing her medications and history, I recommended a non-hormonal vaginal lubricant and within 2 weeks her symptoms were 80% improved. Understanding the side effects of her medications allowed me to educate the patient about the effects of her medication and how to manage her symptoms.
More and more patients are attending therapy through direct access. As the first point of contact for patients, it's imperative that rehab professionals have a foundational knowledge of the medications often prescribed to treat pelvic floor conditions, GI, GU, and reproductive health issues. The ability to have educated conversations with our patients and other healthcare providers involved in their care can greatly improve the quality of care and outcomes, and maintain patient safety. The ability to discuss medications, vitamins, and supplements or complementary alternatives, that can minimize side effects, have fewer impacts on quality of life, and enhance function is an integral part of comprehensive patient care.
Join Kristina on Saturday, January 7, 2023, for Pharmacologic Considerations for the Pelvic Health Provider. This one-day, remote course will discuss the importance of understanding pharmacology and medication review, the current research regarding the pharmacologic treatment of numerous pelvic and reproductive health conditions and their side effects, drug interactions, and non-pharmacologic alternatives that are available for pelvic and reproductive health. Registration information and additional details are available at www.hermanwallace.com. #hermanwallacepelvicrehab, @hermanwallacepelvicrehab
References:
Ciccone, C. D. (2007). Pharmacology in Rehabilitation. (4th ed.). F.A. Davis Company.
Tai-Seale, M., McGuire, T.G., & Zhang, W. (2007). Time allocation in primary care office visits. Health Services Research. 42(5), 1871-1894. Doi: 10.1111/j.175-6773.2006.00689.x
Janes, M., & Kornetti, D. (2017). Medications: defining the role and responsibility of physical therapy practice. https://www.fsbpt.org/Portals/0/documents/free-resources/WinterForum2017Medications.pdf?ver=pf8bn4ZwoorAAg1PECZLfw%3D%3D
Pharmacologic Considerations for the Pelvic Health Provider

Course Dates:
January 7, 2023
Price: $200
Experience Level: Beginner
Contact Hours: 7.5
Description: This seven-and-a-half hour, one-day remote learning course will discuss medications used for the treatment of pelvic floor and genitourinary conditions as well as common side effects of medications routinely used for pelvic floor dysfunction. This course will be taught by Kristina Koch, PT, DPT via Zoom. Medications for constipation and GI dysfunction, as well as pelvic pain conditions such as Vulvodynia, Chronic Prostatitis, and Endometriosis, will be covered. The course will also cover medications and side effects in Gender-Affirming Care for patients who are transitioning.

Sandra Gallagher has served on varied committees and boards at the state and national level, most recently as the chair of the CAPP-OBC committee for the Academy of Pelvic Health of the APTA. She has presented on the role of PT in gender-affirming vaginoplasty at UCSF Transgender Health Summit, APTA Combined Sections Meeting, and at the 2018 international meeting of the World Professional Association for Transgender Health (WPATH). Join Transgender Patients: Pelvic Health and Orthopedic Considerations with instructors Sandra Gallagher, PT, DPT, WCS & Caitlin Smigelski, PT, DPT on April 29th.
In working with surgeons that perform and patients undergoing gender-affirming genital surgery I’ve had the chance to recognize that some of our most basic skills of assessing tissue and tissue healing play a huge role and optimizing healing. I personally have loved taking another look at some of the wound healing principles that I used early in my career in the 90s, to assist in developing timelines for post-surgical recoveries of gender surgeries.
In addition to the basic science of tissue healing, we’ve integrated current and novel neuroscience to develop Graded Motor Imagery guidelines to improve the sensory outcomes of vaginoplasty and phalloplasty surgeries. Graded Motor Imagery (GMI) is a treatment approach commonly associated with treating pain. It is generated from understanding the underlying neuroplasticity of complex pain conditions such as phantom limb pain. (1) Graded Motor Imagery in rehabilitation means that the focus is placed on synaptic exercise and health. The use of neuroplasticity to change sensory experiences occurs in other parts of rehab and goes under different names. Sensory integration, cortical integration, or mapping, are some other terms used. In addition to being used for reducing pain in complex regional pain syndrome, the techniques are used for reducing limb neglect in stroke rehab, and restoring limb function in complex hand surgeries (2,3,4,5). In pelvic rehab, we are using these concepts with urinary urgency suppression and in cis females with vaginal pain. There are handfuls of article exploring the presence and phenomena of phantom penis in trans men (6,7,8)
Using GMI for Phalloplasty
When using GMI for phalloplasty, the primary goal is to improve erogenous sensation in the penis. This is done with three main techniques: visualization of static and dynamic functions of the penis, tactile stimulation starting with a simple touch and progressing toward sensory stimulation, and sexual/erogenous stimulation (9). As people move through the process they use stimulation of the buried erectile tissue and other erogenous parts of their body while touching the penis. This can be a partnered or independent activity. This can be adapted regardless of the number of stages involved in the surgery.
Using GMI for Vaginoplasty
With vaginoplasty, the attaining pain-free and erogenous sensation typically progresses more directly than in phalloplasty, as there are fewer complications with vascular and nerve recovery. The clitoris and its neurovascular bundle are intact and continue to be perineal tissue. We use traditional pelvic rehab interventions of clinical EMG, and a robust home program of dilation, exercise, TENS, and self-care including patient-directed manual interventions. The addition of GMI guidelines for vaginoplasty more commonly is directed toward reducing vulvovaginal pain. Whereas the phalloplasty sensory protocol is initiated early in the surgical process, the vaginoplasty guidelines are more commonly applied when post-surgical pain limits someone's function. The GMI process here uses visualization and activities of seeing vulvas in one's surrounding environment, such as flowers, folded fabrics, and Georgia O'Keefe artworks. This is intended to be a neutral practice. Similar to the desensitization process in limb rehab, using various textures and depth of touch, combined with watching the light touch can help with pain reduction. As pain abates using stimulation of other erogenous tissue while touching the vulva or dilating can be added.
For providing optimal care, knowledge of the intricacies of gender transition is essential. Join me in Transgender Patients: Pelvic Health and ORTHO Considerations on April 29th to learn more regarding gender-affirming genital surgeries, discussion of other gender-affirming surgeries, and medical interventions that people transitioning might choose. We provide that overview in this course. Topics covered include:
- Societal influence on gender transition including interactions with healthcare providers
- Recognizing the difference between sex, sexuality, and gender
- Understanding the complexities of the legal system for the person transitioning genders
- Tips and tools for a trauma-informed intake and examination
- Health effects of hormones for gender transition as related to differential diagnosis in rehabilitation
- Supporting healing after gender-affirming surgery
- Operative procedures for face and chest
- Operative procedures for masculinizing and feminizing genital surgery
- Preoperative evaluation, treatment, and education issues
- Post-operative evaluation, treatment, education and follow-up for genital surgeries
- Outcome measures with rehab focus for people undergoing gender-affirming surgeries
- Fertility and pregnancy in gender-diverse people
References:
- Moseley GL. Graded motor imagery for pathologic pain: a randomized controlled trial. Neurology. 2006 Dec 26;67(12):2129-34. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000249112.56935.32. Epub 2006 Nov 2. PMID: 17082465.
- Smart KM, Wand BM, O'Connell NE. Physiotherapy for pain and disability in adults with complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) types I and II. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Feb 24;2(2): CD010853. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010853. Pub2. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 17;5:CD010853. PMID: 26905470; PMCID: PMC8646955.
- Leifert-Fiebach G, Welfringer A, Babinsky R, Brandt T. Motor imagery training in patients with chronic neglect: a pilot study. NeuroRehabilitation. 2013;32(1):43-58. doi: 10.3233/NRE-130822. PMID: 23422458.
- Simon JJ, Welfringer A, Leifert-Fiebach G, Brandt T. Motor imagery in chronic neglect: An fMRI pilot study. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2019 Feb;41(1):58-68. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2018.1500527. Epub 2018 Aug 6. PMID: 30080434.
- Kahn LC, Moore AM. Donor Activation Focused Rehabilitation Approach: Maximizing Outcomes After Nerve Transfers. Hand Clin. 2016 May;32(2):263-77. doi: 10.1016/j.hcl.2015.12.014. PMID: 27094897.
- Chris Straayer (2020) Phantom Penis: Extrapolating Neuroscience and Employing Imagination for Trans Male Sexual Embodiment, Studies in Gender and Sexuality, 21:4, 251-279, doi: 10.1080/15240657.2020.1842075.
- Ramachandran VS, McGeoch PD. Occurrence of phantom genitalia after gender reassignment surgery. Med Hypotheses. 2007;69(5):1001-3. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2007.02.024. Epub 2007 Apr 8. PMID: 17420102.
- Gherovici, Patricia. (2020). A Phantom Phallus? Studies in Gender and Sexuality. 21. 296-301, doi: 10.1080/15240657.2020.1842070.
- Peters BR, Annen AA, Berli JU, Gallagher S, Smigelski C, Kahn LH, Skelton HE. Neurosensory Re-education following Gender-affirming Phalloplasty: A Novel Treatment Protocol. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022 Oct 24;10(10):e4616. DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004616. PMID: 36299822; PMCID: PMC9592297.
Transgender Patients: Pelvic Health and ORTHO Considerations

Price: $500 .00 Experience Level: Beginner Contact Hours: 17 hours
This course is appropriate for any physical rehabilitation professional, regardless of their specialty area, who has an interest in better serving the people who are gender diverse. There is specific content aimed at teaching pelvic health therapists how to expand their skills for working with people of all gender identities. There will be particular education regarding gender-affirming genital surgeries as well as discussion of other gender-affirming surgeries and medical interventions that people transitioning might choose.
Course Dates: April 29 and August 19

Allison Ariail, PT, DPT, CLT-LAANA, BCB-PMD is one of the creators of the Herman & Wallace Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Course Series. Allison Ariail is a physical therapist who started working in oncology in 2007 when she became certified as a lymphatic therapist. She worked with breast cancer, lymphedema patients, head and neck cancer patients, and the overall oncology team to work with the whole patient to help them get better. When writing these courses, Allison was part of a knowledgeable team that included Amy Sides and Nicole Dugan among others.
June is National Cancer Survivor Month. When individuals talk about “survivorship,” they are referring to the process of navigating their life experiences and the difficulties that they have as a result of their cancer diagnosis. Survivorship begins at the time of diagnosis and includes those individuals that are undergoing treatment, those after treatment with no signs of cancer, those undergoing extended treatment to control the cancer, those undergoing extended treatment to reduce the risk of the return of cancer, and those individuals with advanced cancer. According to cancer.net, there were 18 million people in the United States living with a history of cancer.1 Considering the number of people surviving cancer, and the degree of medical treatment can vary for each of them, there will be a wide range of needs from cancer survivors. Rehabilitation professionals are in a unique position where we can help patients in many different ways to help improve their function, ability to participate in activities that they enjoy and improve their quality of life.
There are multiple studies that show how rehabilitation can help cancer survivors. The research varies in its focus; it could be examining specific side effects such as chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, looking at the effects of fatigue after treatment, or to sexual health after cancer diagnoses. In January of this year, a study came out that showed a physical rehabilitation program of moderate intensity promoted a relief of general and physical fatigue.2 This is huge for cancer patients! Fatigue is an immense problem that survivors suffer from. Another study from 2019 showed that a 12-week exercise-based training program can negate some of the deficits that occur in strength and physical function that occur from the medical treatment of cancer.3 The exercise program, which included both aerobic and resistance training, helped both middle-aged and older adults improve their physical function and strength. In 2018 Dennet et al performed a qualitative study of cancer survivors’ experiences of an exercise-based rehabilitation program. They determined that an exercise-based cancer rehabilitation program was important in facilitating a ‘return to normal’ and helped patients increase their ability to participate in physical activities.4
We as clinicians should embrace this research and work to get these patients referred to us for rehab! As we can see from the above research, this is a population that could greatly use rehabilitation, yet they may not be getting the referrals they need. In 2022, Thorsen et al surveyed almost 1000 young adult survivors. They found that a large proportion of long-term young adult cancer survivors report needing information about lifestyle and rehabilitation more than a decade after they completed their treatment.5 Let’s get these and other aged survivors in for treatment so we can help them feel better and get back to living their lives! Working with oncology patients can be very rewarding. When asked how therapy has influenced her, one patient responded “My PT has played a significant role in my recovery from surgery and the side effects of cancer treatment. She pays attention to and treats ‘the little things’ that are often forgotten about but yet have the biggest impact on my quality of life. She is there helping me long after my other doctors are done treating me.”
Herman & Wallace offers an Oncology Series that can help you gain the knowledge and skills to be able to help these patients. In Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1, we cover general oncology. In this course, we learn about cancer treatment, short-term side effects, and long-term side effects, and learn rehab techniques to help these patients. In Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2A and Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2B we go more in-depth with pelvic-related cancers. In Level 2A we cover topics related to testicular cancer, prostate cancer, penile cancer, and colorectal cancers while in Level 2B we cover topics related to gynecological cancers and bladder cancer. In both courses, you learn hands-on treatment techniques to help patients recover function, and feel better. Please join us by taking this series to be able to help these patients!
Resources:
- What is cancer survivorship? Cancer.net. 7/2021 https://www.cancer.net/survivorship/what-cancer-survivorship
- Penna GB, Otto DM, D Silva T, et al. Physical rehabilitation for the management of cancer-related fatigue during cytotoxic treatment” a systemic review with meta-analysis. Support Care Cancer 31 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-022-07549-7
- Dittus K, Toth M, Priest J, et al. Effects of an exercise-based oncology rehabilitation program and age on strength and physical function in cancer survivors. Support Care Cancer 28, 3747-3754 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-019-05163-8
- Dennett AM, Peiris CL, Taylor NF, et al. “A good stepping stone to normality’: a qualitative study of cancer survivors’ experiences of an exercise-based rehabilitation program. Support Care Cancer 27, 1729-1736. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4429-1
- Thorsen L, Bohn SK.H, Lie HC, et al. Needs for information about lifestyle and rehabilitation in long-term young adult cancer survivors. Support Care Cancer. 30, 521-533 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-021-06418-z

*Certified Lymphatic Therapists may skip Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1 and move on to the Level 2A and Level 2B courses.*
Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1
No partner needed for registration
Price: $550.00 Experience Level: Beginner Contact Hours: 17.5 hours
Description: The course will address issues that are commonly seen in a patient who has been diagnosed with cancer such as cardiotoxicity, peripheral neuropathy, and radiation fibrosis. Some holistic medicine topics, including yoga and mindfulness, will be discussed in order to fully prepare the participant to be able to competently work with cancer survivors.
The basics of the lymphatic system will be covered, as well as when to refer the patient to a lymphatic specialist for further treatment. Red flags and warning symptoms will be discussed so the participant feels comfortable with knowing when to refer the patient back to their medical provider for further assessment.
This introductory course is aimed to get the participant comfortable with working with oncology patients and as part of an interdisciplinary oncology team.
Course Dates: July 8-9 and December 2-3
Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2A
Participants MUST register with a partner, or plan to have a volunteer available to work on during course labs.
Price: $495.00 Experience Level: Intermediate Contact Hours: 17.25 hours
This course was designed to build on the information that was presented in Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1.
Description: Information will be provided focusing on male pelvic cancers, colorectal cancer, and anal cancer including risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. The participant will also understand the sequelae of the medical treatment of cancer and how this can impact a patient’s body and quality of life. Other topics will include rehabilitation and nutritional aspects focusing on these specific cancers, as well as home program options that patients can implement as an adjunct to therapy.
Course Dates: September 23-24
Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2B
Participants MUST register with a partner, or plan to have a volunteer available to work on during course labs.
Price: $600.00 Experience Level: Intermediate Contact Hours: 19.25 hours
This course was designed to build on the information that was presented in Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1.
Description: Information will be provided focusing on gynecological and bladder cancers including risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. The participant will also understand the sequelae of the medical treatment of cancer and how this can impact a patient’s body and quality of life. Other topics include rehabilitation and nutritional aspects focusing on these specific cancers, as well as home program options that patients can implement as an adjunct to therapy.
Course Dates: December 9-10
Allison Ariail, PT, DPT, CLT-LAANA, BCB-PMD is one of the creators of the Herman & Wallace Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Course Series. Allison Ariail is a physical therapist who started working in oncology in 2007 when she became certified as a lymphatic therapist. She worked with breast cancer, lymphedema patients, head and neck cancer patients, and the overall oncology team to work with the whole patient to help them get better. When writing these courses, Allison was part of a knowledgeable team that included Amy Sides and Nicole Dugan among others.
As pelvic rehab professionals, we know the importance of the microbiome of the digestive tract and how this can influence issues our bowel patients may experience. You also may know that the GI microbiome can influence immune function as well as mental health. Did you know that the urinary bladder has its own microbiome? Recent developments in next-generation sequencing and bioinformatic platforms have allowed for the detection of microbial DNA in the urinary tract.(1) This could be a game changer for those who suffer from chronic urinary tract infections. However, it could be even more important as a way to prevent bladder cancer. May is Bladder Cancer Awareness Month. In honor of this month, let’s further discuss how the urinary microbiome may influence the development of bladder cancer.
Dysbiosis of the urinary microbiome could be related to bladder cancer through chronic inflammation in the urothelial microenvironment. Chronic inflammation is a hallmark of genomic instability and the development of cancer. A study in 2021 compared the urinary microbiome of patients with muscle-invasive and non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. They found the microbial profiles differed in patients with cancer compared to healthy individuals. They also found that there were different microbial profiles from the less invasive non-muscle invasive versus the more invasive types of bladder cancer.(2)
The urinary microbiome is a growing area of research and I would expect to see more information come out on this, what influences the urinary microbiome, as well as how modulating this can prevent and fight urothelial cell carcinoma. I would anticipate more treatment options including some new immunotherapy agents to emerge that can help to fight bladder cancer.
If you do not know much about bladder cancer and would like to learn more, Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2B covers topics on bladder cancer and gynecological cancers. Join us to learn more about these diagnoses, medical treatments, and ways a pelvic rehab professional can help these patients recover.
Resources:
1. Neugent ML, Hulyalkar NV, Nguyen VH, Zimmern PE, and De Nisco NJ. Advances in understanding the human urinary microbiome and its potential role in urinary tract infection. mBio. 2020; 11(2): e00218-20.
2. Hussein AA, Elsayed AS, Durrani M, et al. Investigating the association between the urinary microbiome and bladder cancer: an exploratory study. Urol Oncol. 2021; 39(6): 370.e9-370e19.

*Certified Lymphatic Therapists may skip Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1 and move on to the Level 2A and Level 2B courses.*
Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1 - no partner needed for registration
Price: $550.00 Experience Level: Beginner Contact Hours: 17.5 hours
Description: The course will address issues that are commonly seen in a patient who has been diagnosed with cancer such as cardiotoxicity, peripheral neuropathy, and radiation fibrosis. Some holistic medicine topics, including yoga and mindfulness, will be discussed in order to fully prepare the participant to be able to competently work with cancer survivors.
The basics of the lymphatic system will be covered, as well as when to refer the patient to a lymphatic specialist for further treatment. Red flags and warning symptoms will be discussed so the participant feels comfortable with knowing when to refer the patient back to their medical provider for further assessment.
This introductory course is aimed to get the participant comfortable with working with oncology patients and as part of an interdisciplinary oncology team.
Course Dates: July 8-9 and December 2-3
Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 2B - partner needed for registration
Price: $600.00 Experience Level: Intermediate Contact Hours: 19.25 hours
This course was designed to build on the information that was presented in Oncology of the Pelvic Floor Level 1.
Description: Information will be provided focusing on gynecological and bladder cancers including risk factors, diagnosis, and prognosis. The participant will also understand the sequelae of the medical treatment of cancer and how this can impact a patient’s body and quality of life. Other topics include rehabilitation and nutritional aspects focusing on these specific cancers, as well as home program options that patients can implement as an adjunct to therapy.
Course Dates: December 9-10

Megan Pribyl, PT, CMPT is a physical therapist at the Olathe Medical Center in Olathe, KS treating a diverse outpatient population in orthopedics including pelvic rehabilitation. Megan’s longstanding passion for both nutritional sciences and manual therapy has culminated in the creation of her remote course, Nutrition Perspectives for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist, designed to propel understanding of human physiology as it relates to pelvic conditions, pain, healing, and therapeutic response.
I have always viewed resultant health as the sum total of nutrition, exercise, lifestyle factors, environmental/toxicant & chemical exposure, genetics, and spiritual confluences. In balance, health and vitality flourish. Out of balance, health struggles manifest. If we take a look around, we bear witness to modern culture’s harmful effects upon our physiology – and specifically on our blood-brain barrier (BBB). Health struggles affecting the brain and impacted by BBB dysfunction are diverse and can include anxiety, depression, chronic pain, and neurodevelopmental disorders. Other disorders linked to a compromised BBB include Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, Parkinson’s Disease, and MS. So we ought to care a lot about our BBB – yet most of us don’t make conscious lifestyle choices based on protecting this vital gatekeeping system. Perhaps if we examine one specific angle of this issue - that diet and short-chain fatty acids influence the integrity of the blood-brain barrier – we might decide to care a lot more about protecting our brain – like we mean it.

For starters, it helps to acknowledge that our entire body IS an immune system – one that is constantly surveying potential threats to our existence. It is very well established that 70% of our immune system resides in our gut. This placement makes sense because the very act of eating exposes our inner workings to whatever “food” passes through the alimentary canal. Our digestive tract is a frontline sorting station that decides what can pass through the intestinal barrier and what cannot. Having a strong intestinal barrier is critical to maintain health as evidenced by a wealth of both animal and human studies.
Most of us also don’t constantly think about our intestinal barrier – but science contends that we should. Because what happens there impacts our entire body and all systems – including our nervous system. A recent study even describes a “Gut Spinal Cord Immune Axis” wherein the health of our spinal cord itself is dependent on immune factors regulated by the gut microbiota. (3) That’s how far your gut health influence goes.
So, let’s talk about one way our gut, a.k.a. microbiome, keeps us healthy. The microbes in our large intestine should be numerous and diverse. These microbes thrive in the presence of prebiotic fiber components (sources of prebiotic fiber are diverse, from the plant world and include things like Jerusalem artichoke, bananas, onions, berries, garlic, and other herbs and spices) which arrive in the colon because they are consumed by the host – us. When your microbes feast on the prebiotic fibers, they produce a by-product, and this byproduct is SCFA’s or short-chain fatty acids. It is well established that these SCFAs play a powerful immunomodulatory role both locally (in the intestine) and distantly (e.g. at the blood-brain barrier). This is the best way to create healthy short-chain fatty acids so they can do what they do best in our system – modulate inflammation.
But what happens if we don’t have richness (as in ample number) or diversity (as in different health-promoting species) of microbes in our large intestine? We can’t produce as many SCFAs.
What happens if we don’t consume the food (eg. prebiotic fiber) our microbes like to eat? Or if we aren’t eating foods that contain microbes (eg. cultured foods)? We can’t produce as many SCFAs.
What happens if we are deficient in healthy SCFAs? We may end up with undesirable physiological sequelae such as systemic inflammation. Which can include blood-brain barrier inflammation. (2)
Remember that we have nerves everywhere in our body – centrally and peripherally. If any of the nerves in our body (peripheral nerves), brain (CNS), or gut (ENS) are inflamed, this can be termed neuroinflammation. Neuroinflammation in the CNS leads to blood-brain barrier inflammation resulting in increased permeability – this ultimately allows substances to reach the brain that shouldn’t.
Neuroinflammation is at the root of many of the health sequelae we currently see in non-communicable conditions. (5) Maybe in your patient it manifests as chronic pain. Maybe in your friend, it’s anxiety and depression. Maybe in your aunt it’s MS, your uncle it’s Alzheimer’s. Maybe in your neighbor it’s fibromyalgia. Neuroinflammation has many faces.
When we look at factors that contribute to blood-brain barrier dysfunction, many can be traced to the cumulative effects of a standard American diet and lack of nutrient density. Further, and more ubiquitous – is our unseen exposure to toxicants such as herbicides and pesticides as well as a multitude of other potential cell health disruptors. (1, 4)
Because of the massive implications of human disease states, we need to pay attention to what the literature is telling us about the interconnected nature of health and lifestyle. We must stop polluting our human physiology and we must start feeding ourselves food that isn’t paradoxically decimating our microbiome. It’s that simple. And complicated. At the same time.

Taking a deep breath is the first step. A crucial second step is staring down the truth of our country’s health care and agricultural realities. The third is gaining perspective on what actions each of us can take today – wherever we live, whatever our socioeconomic status, and whatever our current health status. There is much work to do.
I invite you to an opportunity to learn about many actions we can take today and examine nutritional concerns in depth that have implications not only for the population you treat as a pelvic rehab therapist but for yourself, your friends, and your extended human family.
We must prioritize protective health choices. We must care for our gut, propagate healthy short-chain fatty acids, and therefore care for our blood-brain barrier. And subsequently, protect our brain - like we mean it. Because our modern culture will not do that for us. Solving our nation’s health crises will take each of us collectively to make a difference. The health status of our nation can improve – one protected brain at a time.
Join us for our next offering of Nutrition Perspectives for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist scheduled for June 10-11, 2023.
References:
- Abou Diwan M, Lahimer M, Bach V, Gosselet F, Khorsi-Cauet H, Candela P. Impact of Pesticide Residues on the Gut-Microbiota-Blood-Brain Barrier Axis: A Narrative Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 24;24(7):6147. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076147. PMID: 37047120; PMCID: PMC10094680.
- Fock E, Parnova R. Mechanisms of Blood-Brain Barrier Protection by Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Cells. 2023 Feb 18;12(4):657. doi: 10.3390/cells12040657. PMID: 36831324; PMCID: PMC9954192.
- Raue KD, David BT, Fessler RG. Spinal Cord-Gut-Immune Axis and its Implications Regarding Therapeutic Development for Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2023 Mar 10. doi: 10.1089/neu.2022.0264. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 36509451.
- Sharma T, Sirpu Natesh N, Pothuraju R, Batra SK, Rachagani S. Gut microbiota: a non-target victim of pesticide-induced toxicity. Gut Microbes. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2187578. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2187578. PMID: 36919486; PMCID: PMC10026936.
- Takata F, Nakagawa S, Matsumoto J, Dohgu S. Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction Amplifies the Development of Neuroinflammation: Understanding of Cellular Events in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells for Prevention and Treatment of BBB Dysfunction. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Sep 13;15:661838. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.661838. PMID: 34588955; PMCID: PMC8475767.
Nutrition Perspectives for the Pelvic Rehab Therapist

Price: $525.00 Experience Level: Beginner Contact Hours: 17.5 hours
Course Dates: June 10-11, September 16-17, and December 2-3
Description: Participants will be introduced to the latest research in nutrition through immersive lectures and hands-on labs. The course will cover essential digestion concepts, nourishment strategies, and the interconnected nature of physical and emotional health across the lifespan. Further, clinicians will delve into nutritional relevancies in bowel and bladder dysfunction, pelvic health, pain, and healing. Labs throughout include insightful demonstrations and breakout sessions. The course participant will acquire new, readily applicable tools for patient empowerment, engagement, and self-management utilizing presented principles.