According to the Parkinson’s Foundation, orthostatic hypotension (OH) affects 15 to 50% of people with Parkinson disease (PWP). The medical definition of orthostatic hypotension is a drop in systolic blood pressure of greater than 20 mmHg or a drop in diastolic blood pressure of greater than 10 mmHg within 3 minutes of standing. Additionally, consideration is taken to the heart rate increase upon standing and if less than 10-15 beats per minute, it may be indicative of OH.
One of the many lifestyle modifications given is to increase fluid intake. Increasing fluids for blood pressure management to reduce dizziness, syncope, and fall risk from OH can be very challenging for this population. Many PWP present with significant self-imposed fluid restrictions as they try to manage common issues with bladder urgency frequency. Getting ½ their body weight in ounces or the traditional recommendation of 8 glasses a day may feel overwhelming. A common recommendation from their neurologist or other health care providers is to have 16 ounces of fluid right away in the morning. Research has shown this to help individuals with autonomic nervous system/baroreflex dysfunction to have rapid symptomatic improvement eliciting a water-induced pressure response and raising their blood pressure. In PWP with autonomic dysfunction, the baroreceptors, which constrict to increase heart rate and blood pressure upon standing, are sluggish to respond similar to the slowness of movement observed in a PWP. Individualized and creative daytime urge control techniques, bladder retraining, timed voiding, measured bladder diary assessment, constipation management strategies, and neuromodulation strategies are crucial to maintaining quality of life in coordination with fall safety related to OH.
For those with OH who also struggle with nocturia, the shifting of fluids to earlier in the day may require closer monitoring of blood pressure to ensure our advice is safe. The Wisconsin Parkinson Association’s director of medical advising and education, Dacy Reimer, APNP, describes the recommended blood pressure tracking methods for reporting back to neurology. With the use of an electronic blood pressure cuff, blood pressure, pulse, and symptoms can be recorded after sitting for 5 minutes and a second blood pressure after standing for 3 minutes. This can be regularly tracked once in the morning and once at night. If we are giving advice for fluid management changes to modify bladder behavior, we may want our patients to monitor this at additional times throughout the day. Many of my patients who report nocturia at their evaluation, have already tried the common recommendation of stopping fluids 2-3 hours before bed without a change in their symptoms. A more aggressive fluid shifting plan, where the person will still be asked to get their recommended fluids each day, but achieve that goal much earlier, with a more dramatic tapering at the end of the day has clinically shown benefit. Trying to fill the bladder more during the day to allow for sensory training/larger fill volumes as well as to flip the circadian rhythm for urine production is the goal. Monitoring blood pressure as an additional component of the bladder diary, while your patient makes suggested changes, can ensure their safety.
If additional nuances to the pelvic health complexities involved in Parkinson disease interest you, come delve into it with me even further in my course - Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation scheduled for April 25-26 2025.
Resources:
- Ramsay, S., & Zagorodnyuk, V. (2023). Role of circadian rhythms and melatonin in bladder function in heath and diseases. Autonomic neuroscience, 246, 103083.
- Shannon, J. R., Diedrich, A., Biaggioni, I., Tank, J., Robertson, R. M., Robertson, D., & Jordan, J. (2002). Water drinking as a treatment for orthostatic syndromes. The American journal of medicine, 112(5), 355-360.
AUTHOR BIO:
Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC
 Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC (she/her) graduated with her master’s degree in Occupational Therapy from Concordia University Wisconsin in 2002 and works for Aurora Health Care at Aurora Sinai Medical Center in downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Erica specializes in female, male, and pediatric evaluation and treatment of the pelvic floor and related bladder, bowel, and sexual health issues. She is board-certified in Biofeedback for Pelvic Muscle Dysfunction (BCB-PMD) and is a Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner (PRPC) through Herman and Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute.
Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC (she/her) graduated with her master’s degree in Occupational Therapy from Concordia University Wisconsin in 2002 and works for Aurora Health Care at Aurora Sinai Medical Center in downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Erica specializes in female, male, and pediatric evaluation and treatment of the pelvic floor and related bladder, bowel, and sexual health issues. She is board-certified in Biofeedback for Pelvic Muscle Dysfunction (BCB-PMD) and is a Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner (PRPC) through Herman and Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute.
Erica has attended extensive post-graduate rehabilitation education in the area of Parkinson disease and exercise. She is certified in LSVT (Lee Silverman) BIG and is a trained PWR! (Parkinson’s Wellness Recovery) provider, both focusing on intensive, amplitude, and neuroplasticity-based exercise programs for people with Parkinson disease. Erica is an LSVT Global faculty member. She instructs both the LSVT BIG training and certification course throughout the nation and online webinars. Erica partners with the Wisconsin Parkinson Association (WPA) as a support group, event presenter, and author in their publication, The Network. Erica has taken a special interest in the unique pelvic floor, bladder, bowel, and sexual health issues experienced by individuals diagnosed with Parkinson disease.
![]()
Central nervous system damage or disease can have a significant negative impact on pelvic organ and pelvic muscle function, adding to the functional burden that we may observe with movement, ADL, and communication/cognition deficits. The intricacies of central nervous system involvement in pelvic organ function can be traced back to our early years of development. Learning to walk and talk as a child happens before the ability to control our bladder and bowel emptying. This level of control requires a well-developed, intricately organized central and autonomic nervous system. It is understandable then, that even minor damage to our central nervous system and nerve pathways can compromise the intricacies of the complexly integrated pelvic viscera and pelvic floor dynamic.
Neurogenic bladder, bowel, and sexual dysfunction are generally defined as an impairment in these organs that results from neurologic damage or disease. The prevalence of neurogenic bladder, bowel, and sexual dysfunction is somewhat uncertain due to limited studies in the neurologic population, however, typically the reports present a wide range. Neurogenic pelvic impairments can be highly variable and dependent on several factors including, but not limited to, lesion level, traumatic etiology (i.e., head, or spinal cord injury), non-traumatic etiology (i.e., stroke, Parkinson’s, Multiple Sclerosis), and comorbidities. The complexity of the person with a central nervous system pathology, whether it be damage or disease, can challenge even the most experienced clinician, and evaluating and treating these individuals can seem like a daunting and intimidating endeavor. Additionally, therapeutic intervention studies in the neurologic population are also less abundant, and individuals with neurologic deficits are often excluded.
Understanding your patient’s neurologic diagnosis, level of injury and corresponding probable neurological system impairments can help you decide on the best assessment and intervention strategy for your patient. Let’s first consider an upper motor neuron (UMN) lesion. This type of lesion can occur in the cortex and even down through the spinal cord descending motor tracts, which are located in the columns of the spinal cord. These individuals typically experience predominant bladder storage dysfunction or detrusor overactivity, increased muscle tone/spasticity in the pelvic floor, and reflexive bowel function. In contrast, a lower motor neuron (LMN) lesion can occur anywhere along the spinal cord within the LMN cell bodies in the anterior horns, along the pathway of a peripheral motor nerve, or at the motor neuromuscular junction. These individuals typically experience bladder storage or voiding symptoms, possible elevated post-void residuals if injury affects the sacral reflex arc, pelvic floor laxity or weakness, impaired descending and rectosigmoid transit, and areflexive bowel function.
In my course Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation scheduled for November 1-2, we will review basic neuroanatomy concepts. We will take a deep dive into the autonomic nervous system's control of the bladder, bowel, and sexual health organs. This will provide a general overview for considering the level of neurologic injury and the impairments you will likely observe. Parkinson disease will be our primary focus, however, my hope is that you can also begin to generalize this knowledge to other neurologic conditions that you treat in your clinic.
Resources:
- Fowler, C. J., Panicker, J. N., & Emmanuel, A. (Eds.). (2010). Pelvic organ dysfunction in neurological disease: clinical management and rehabilitation. Cambridge University Press.
- Lamberti, G., Giraudo, D., & Musco, S. (Eds.). (2019). Suprapontine Lesions and Neurogenic Pelvic Dysfunctions: Assessment, Treatment and Rehabilitation. Springer Nature.
AUTHOR BIO:
Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC
 Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC (she/her) graduated with her master’s degree in Occupational Therapy from Concordia University Wisconsin in 2002 and works for Aurora Health Care at Aurora Sinai Medical Center in downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Erica specializes in female, male, and pediatric evaluation and treatment of the pelvic floor and related bladder, bowel, and sexual health issues. She is board-certified in Biofeedback for Pelvic Muscle Dysfunction (BCB-PMD) and is a Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner (PRPC) through Herman and Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute.
Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC (she/her) graduated with her master’s degree in Occupational Therapy from Concordia University Wisconsin in 2002 and works for Aurora Health Care at Aurora Sinai Medical Center in downtown Milwaukee, Wisconsin. Erica specializes in female, male, and pediatric evaluation and treatment of the pelvic floor and related bladder, bowel, and sexual health issues. She is board-certified in Biofeedback for Pelvic Muscle Dysfunction (BCB-PMD) and is a Certified Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner (PRPC) through Herman and Wallace Pelvic Rehabilitation Institute.
Erica has attended extensive post-graduate rehabilitation education in the area of Parkinson disease and exercise. She is certified in LSVT (Lee Silverman) BIG and is a trained PWR! (Parkinson’s Wellness Recovery) provider, both focusing on intensive, amplitude, and neuroplasticity-based exercise programs for people with Parkinson disease. Erica is an LSVT Global faculty member. She instructs both the LSVT BIG training and certification course throughout the nation and online webinars. Erica partners with the Wisconsin Parkinson Association (WPA) as a support group, event presenter, and author in their publication, The Network. Erica has taken a special interest in the unique pelvic floor, bladder, bowel, and sexual health issues experienced by individuals diagnosed with Parkinson disease.

Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC has attended extensive post-graduate rehabilitation education in the area of Parkinson disease and exercise. She is certified in LSVT (Lee Silverman Voice Treatment) BIG and is a trained PWR! (Parkinson Wellness Recovery) provider, both focusing on intensive, amplitude, and neuroplasticity-based exercise programs for people with Parkinson disease. You can learn more about this topic in Erica's remote course, Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation.
Does the person with Parkinson disease sense where to contract their pelvic floor and the level of contraction they need to overcome the strength of the urge they experience? The sensorimotor deficit that we can visually observe as degradation in movement amplitude in the limb motor system, for example shuffling steps and micrographia, is also suspect in the pelvic floor. Also, consider the lengthening of the pelvic floor that must occur for emptying the bowels. Adequate descent amplitude of the pelvic floor and proper coordination with the abdomen to do so may also not be sensed. Further, strengthening of the pelvic floor is an effective technique for improved sexual health functioning, but may also be challenged by impaired sensorimotor feedback. Treatment of this sensorimotor mismatch in the pelvic floor in a person with Parkinson disease requires specialized expertise and feedback from an OT or PT who treats pelvic floor dysfunction and understands how the neurodegeneration affects their abilities.
When most people think about people with Parkinson disease, they think about stooped posture, shuffling gait, slow and rigid movement, balance difficulties, and tremoring. Often these motor symptoms are the main target of pharmacological treatments with neurologists and many experience positive functional gains. Non-motor symptoms, however, can be more disabling than motor symptoms and have significant adverse effects on the quality of life in people with Parkinson disease.
The pharmacologic management of non-motor autonomic dysfunction, including urinary, bowel, and sexual health impairments, is often ineffective, not supported by adequate research, or causes intolerable side effects for people with Parkinson disease. In a recent article titled “Update on Treatments for Nonmotor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease – An Evidence-Based Medicine Review.” Seppi, K, et al., 2019, the authors state this about the use of a pharmacological treatment approach - “Before attempting any treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms, urinary tract infections, prostate disease in men, and pelvic floor disease in women should be ruled out.” It is rare to see a mention of the pelvic floor within the literature that addresses helping people with Parkinson disease.
Pelvic rehabilitation specialists have a unique opportunity to step in and help these individuals improve their quality of life and many neurologists are unaware of the benefits our services could provide for their patients. Please join me in an exciting dive into understanding the physiology of how Parkinson disease affects a person’s pelvic health and develop your skills to effectively assess and develop treatment plans to change the life of these individuals.
Here is a sneak peek acronym into some of the teaching strategies discussed in Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation!
- P - Pacing
- A - Amplitude training
- R - Reinforcement feedback loop
- K - Kinesthetic training
- I - Internal cue restoration training
- N - Neuroplasticity training principles
- S - Sensorimotor retraining
- O - Occupation & goal-directed task training
- N - New skill restoration

Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation
Course Date:
January 27-28, 2023
Price: $300
Experience Level: Beginner
Contact Hours: 10
Description: This course introduces basic neuroanatomy with a detailed overview of pelvic neurophysiology in preparation for an extensive in-depth look at pelvic health treatment options for Parkinson disease. Pelvic floor external and internal neuro-musculoskeletal assessment considerations will be instructed with the understanding that participants have prior experience in pelvic health coursework or pelvic health patient treatment experience.
Preparatory lectures about Parkinson disease will help develop a clear understanding of the neurophysiology of the disease to establish an equal foundation between experienced practitioners and those who have never worked with this patient demographic. Live course lectures deep-dive into characteristic pelvic health conditions that people with Parkinson's disease may face, discuss multiple assessment and treatment planning options, and will also discuss applications for TENS in the neurologic population.
Course Reviews:
- Erica was a phenomenal instructor. She is very passionate and it showed throughout the session. The information she provided was very evidence-based and filled in the gaps for many other types of patients besides patients with Parkinson's. Would highly recommend this class even for learning about treating pelvic floor patients with neurological disorders.
- Erica is a skilled, interesting instructor. Her passion for this topic came through in her teaching style. She enhanced the course with her passion and delivery.
- I learned a great deal about Parkinson's and really felt that the course was worthwhile and valuable. I am very appreciative of the fact that she created a course about this specific topic as there is a large need.
- This was an awesome class. Erica is an incredible teacher! I can't wait to use what I learned this weekend in the clinic to help my patients!
This week for the Pelvic Rehab Report, Holly Tanner sat down to interview faculty member Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC on her specialty course Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation. If you would like to learn more about working with this patient population join Erica on June 24th-25th for the next course date!
This is Holly Tanner with the Herman and Wallace Pelvic Rehab Institute and I'm here with Erica Vitek who's going to tell us about of course that she has created for Herman and Wallace. Erica, will you tell us a little bit about your background?
Yes. Absolutely. Thanks for chatting with me today about my course! So my course is Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation. I'm just so excited to be part of the team and to be sharing all this great information. How I got the idea for the course is that there was a need for more neuro-type topics related to pelvic health, and individuals were reaching out to me because my specialty is in both Parkinson disease, rehabilitation, as well as pelvic health, and I always talked about the connections and wanting to bring that information to more people. So I wanted to plate all that information together in this great course.
I got started specializing in Parkinson's back in the early 2000s. I was hired at a hospital as an occupational therapist working with people with Parkinson disease. But when I was in college my real interest was pelvic health. So I kind of got thrown into learning a whole lot about Parkinson disease at that time and I got really interested in how it all related to what I really wanted to do, which was pelvic health. I was able to connect that all, really right from the beginning of my career. Even though I started more on the physical rehabilitation side of Parkinson disease, which I continue to this day. I am able to combine those two passions of mine.
I also am an instructor with LSVT Global(1)and so we do LSVT BIG®(2) course training and certification workshops and I work with them a lot. I also have still a physical rehab background, as well as my connection to the public health background, and I bring that all together in my course Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation. We have two packed-full days of information and I think really it does translate well to the virtual environment.
What are the connections between neuro and pelvic health? Can you talk about what some of the big cornerstone pieces are that you get to dive into with your class?
The beginning of the course on the first day is going back to the basics of neuro in general. Really getting our neuro brains on and thinking about terminology, topics related to neurotransmitters and the autonomic nervous system. Individuals with Parkinson’s specifically, their motor system is affected but also their non-motor systems. This includes autonomic function, the limbic system, and all of the different motor functions that also affect the pelvic floor in addition to all of the other muscles in the body.
We have all of this interplay of things going on that affect the bladder, bowel, and sexual health systems in individuals with Parkinson's that is a little bit different than your general population. There are a multitude of bladder issues that are very specific to the PD population, for example, overactive bladder.
This is just one example of the depths we go into right in the beginning on day one where we get into the neuroanatomy and neurophysiology of why that is actually happening. This then helps us go into day two where we talk about the practicality of what you do in the clinic about the things that are happening neurologically which is causing all of these bladder, bowel, and sexual health issues.
What kind of tools do you give to people to help practitioners understand and implement a treatment program?
People with PD are on very complex medication regimens and many of them are elderly, so the medication complexity is much more challenging in this population. At the end of day one, the last lecture, we go through the pharmacology very specifically for people with Parkinson’s in order to have a base of understanding of how that is interplaying with the pelvic health conditions.
We set the baseline of getting that information from your patient off the bat, then discuss what you want to be looking for when you start off with that patient and the importance of finding out what kind of bladder and bowel medications they have taken thus far and how that can potentially interplay with their Parkinson’s. Individuals with PD can have potentially worse side effects from some of those medications that are used for bladder issues specifically. We dig into what to look for, we talk a lot about practical behavioral modifications using bladder and bowel diaries and things like that to weed out some things in addition to using our other skills as pelvic health practitioners.
How can people prepare themselves to come to Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation, are there required readings or things that would be helpful for people to catch up a little bit on the pelvic health or neuro side?
I feel like, and I hope, that I did a really good job at the basic review right at the beginning so we can talk through these topics together. I prefer to take a course and not have to spend a lot of extra time on the pre-recordings because sometimes that can be overwhelming with busy lifestyles. When I put together this course I really wanted us to focus together as a group as we start the class to dig into those basics at the beginning and not have a lot of required things to do prior.
So what I did at the beginning of the course is to make a lot of tables, a lot of charts, and a lot of drawings, that we can reference (we don’t have to memorize it) and look at as needed. We can look at a chart and a drawing right next to it in the manual. I spent a lot of time just putting it all down in words, what I’m saying, so you don’t have to take a lot of notes. I think this has really helped practitioners as we get into the course and learn about the details of Parkinson’s and pelvic health.
What is it that makes you so passionate about working with these patients and continuing to learn and share your knowledge?
It is so heartwarming and feels so good to help these individuals. The motor symptoms of PD are really the ones recognized by physicians or even outwardly noticed even by other individuals. These private conditions of pelvic health that we are helping with are things that they might not even mention to their physician. Maybe we find out when we are doing other physical rehab or when colleagues refer them to us because they know what we do, and to help them with something of this magnitude that affects their everyday life - when they have trouble just walking, or moving or transferring.
Their caregiver burden for these individuals is so high because their loved one - now turned caregiver - is helping them do everything. We can make such an impact on these individuals. I mean, we do on other people too, but when you have a progressive neurologic condition and we can make an effect on shaping techniques they can use to improve their day-to-day. It’s just so great to be able to help them.
Sometimes these patients with PD can have cognitive impairments, they can have difficulties learning, and that can be helpful for the care partner. It can be a significant reduction in their burdon. I do talk a lot in the course about cognitive impairment and I give a lot of tips about how we can train and some ideas. People with Parkinson’s muscles and minds are a little different so there are some great tips that I can provide and lots of clinical experience.
I’ve been an occupational therapist for over 20 years, so I have a ton of clinical experience with this population. It’s been the population I’ve worked with my entire career. I hope I can provide the passion that I have for working with these individuals as well as the individuals who take my class.
I’m sure you would agree that we need more folks knowledgeable about Parkinson’s and combine that with pelvic health knowledge as well.
There are over a million people in the United States alone that have Parkinson disease. It’s the second most common neuro-degenerative disorder just behind Alzheimer’s disease. So there are so many individuals dealing with this and I think we can really expand our practices. I don’t think a lot of individuals that work in pelvic health market themselves to neurologists. There is an opening there for additional referrals and more people that we can help.

References:
- SVT Global is an organization that develops innovative treatments that improve the speech and movement of people with Parkinson’s disease and other neurological conditions. They train speech, physical and occupational therapists around the world in these treatments so that they can positively impact the lives of their patients.
- LSVT BIG®: Physical Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease and Similar Conditions. LSVT BIG trains people with Parkinson disease to use their body more normally.

Erika Vitek is kicking off the new year with her remote course Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitationscheduled for January 14-15, 2022. In this course, she explains that akinesia is a term to describe the movement dysfunction observed in people with Parkinson Disease (PD). Akinesia is defined as poverty of movement, impairment or loss of the power to move, and slowness in movement initiation. This is observable in the loss of facial expression, associated nonverbal communicative movements, arm swing with gait, and overall small amplitude movements throughout all skeletal muscles in the body.
The cause of this characteristic profile of movement is due to loss of dopamine production in the brain, which causes a lack of cortical stimulation for movement(1). If the loss of dopamine production in the brain causes this poverty of movement in all skeletal muscles of the body, how does the pelvic floor function in people with PD, and what should the pelvic floor rehabilitation professional know about treating the pelvic floor in this population of patients?
Common pelvic floor dysfunctions often involve functions controlled through reflexes and voluntary actions such as bladder, bowel, and sexual functions. PD-related pelvic floor dysfunctions impact the non-motor portion of the bladder, bowel, and sexual functions. A recent study by Gupta et al. showed that “urinary dysfunction and constipation, manifestations of pelvic floor dysfunction are common sources of disability and impaired quality of life in women with PD(2).” This study concluded that pelvic floor dysfunction is underreported and undertreated in people with Parkinson's Disease.
As there is no cure for PD, the goal for all treatment strategies is to slow the disease progression and achieve neuroprotection while improving quality of life. There are five common strategies in treating this patient demographic: rehabilitation, therapy, restoration, maintenance, and surgery, as found by Frank Church. Rehabilitate follows the diagnosis and treatments and includes physical, occupational, and speech therapy. Therapy refers to the use of levodopa or other dopamine agonists to preserve dopamine. The restorative strategy includes aerobic exercise programs. Maintenance strategy uses complementary and alternative medicine to support and protect the brain microenvironment, while surgery includes deep brain stimulation(3).
Patients with PD can benefit from physical and occupational therapy as part of their rehabilitative management strategy. A trained practitioner can work with the patient to introduce neuromuscular re-education training. In this type of training, reflexive actions are optimized by promoting repetitive firing of the neurons in the circuits to allow the body to adapt to the most efficient path. Practitioners can also introduce strength training for those muscles under voluntary control to reduce muscle strain and improve contract-relax properties. Exercise-based interventions have been shown to promote improvements and allow a better quality of life in pelvic floor function of Parkinson's patients.
As part of the Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation course curriculum, Erica Vitek delves into the characteristic pelvic health dysfunctions that people with PD face. Options for assessment and treatment planning are also provided, including applications for TENS in the neurologic population. Erica shares “There is no pathological evidence that in Parkinson Disease there is any break in the continuity of the motor system. The neurologic pathways are all intact and the ability to produce muscle power is retained. However, a strong base of clinical knowledge of the disease is required to help these patients activate these intact motor pathways.”
References:
- Caligiore D, et al. Different Dopaminergic Dysfunctions Underlying Parkinsonian Akinesia and Tremor. Front. Neurosci., 29 May 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00550
- Gupta, Ankita et al. Pelvic Floor Health in Women with Parkinson’s Disease. Journal of Parkinson's Disease 1 Jan. 2021: 857 – 864. DOI: 10.3233/JPD-202491 | https://content.iospress.com/articles/journal-of-parkinsons-disease/jpd202491
- Church FC. Treatment Options for Motor and Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(4):612 | https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11040612

Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC has attended extensive post-graduate rehabilitation education in the area of Parkinson disease and exercise. She is certified in LSVT (Lee Silverman Voice Treatment) BIG and is a trained PWR! (Parkinson Wellness Recovery) provider, both focusing on intensive, amplitude, and neuroplasticity-based exercise programs for people with Parkinson disease. Erica has taken a special interest in the unique pelvic floor, bladder, bowel, and sexual health issues experienced by individuals diagnosed with Parkinson disease. You can learn more about this topic in Erica's course, Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation, scheduled for July 23-24, 2021.
Parkinson disease (PD) non-motor symptoms can be even more impactful on quality of life than the cardinal motor symptoms most are familiar with, bradykinesia, rigidity, tremor, and postural instability. The list of non-motor symptoms is extensive affecting many body systems including cognitive, sensory, and autonomic.
Constipation is one of the most common autonomic non-motor symptoms experienced by people with Parkinson disease with studies showing 20-89% prevalence (1). As the disease progresses, individuals are more likely to experience symptoms that suggest a strong relationship between neurodegeneration and bowel dysfunction, such as, decreased frequency of bowel movements, difficulty expelling stool, and diarrhea (2). Constipation has also been hypothesized to be an early indicator for the development of Parkinson disease, and there is ongoing research in this area. It has yet to be shown that constipation is specific enough to predict the development of PD.
Developing an understanding of Parkinson disease constipation and how it differs from other individuals with constipation can have a strong impact on our recommended pelvic rehabilitation plans of care. In a study published by Zhang, M. et al., 2021, they looked at the characteristics of Parkinson disease with constipation (PDC) compared to functional constipation (FC). Functional constipation is generally defined as difficult, infrequent, or incomplete defecations (3). One of the main findings in this study was a significant difference between the groups when looking at resting rectal and anal canal pressures. In the PDC group, resting rectal and anal pressures were significantly lower. These resting pressures are mainly controlled by the internal anal sphincter resting tension which is supported by the autonomic nervous system. This leads the researchers to speculate there may be autonomic nervous system neuropathy in people with PD
They then looked at simulated defecation, which also showed that the PDC group had significantly lower rectal defecation pressure and a lower anal relaxation rate. Since rectal pressures during defecation assist in effective anal relaxation, the researchers state, “a coordinated movement disorder results” and that people with PD may have “pelvic floor cooperative motion disorder” (1). Additionally, the researchers noted that abnormal abdominal pressure is another main contributing factor to the low rectal defecatory pressure in PDC. Abdominal pressure is a key factor in driving complete and efficient rectal defecation. This is also a finding in numerous other studies in the literature unique in PDC.
The results of Zhang, M. et al., 2021 reveal the need for pelvic health practitioners to help train coordinated defecation efforts in people with Parkinson disease. In my course, Parkinson disease and Pelvic Rehab, we will have an in-depth discussion about how training defecatory dynamics is different in people with PD. Muscle training principles in this population are very unique. Understanding the underlying causal factors of dysfunction will have a significant impact when helping patients with Parkinson disease manage constipation.
- Zhang, M., Yang, S., Li, X. C., Zhu, H. M., Peng, D., Li, B. Y., ... & Tian, C. (2021). Study on the characteristics of intestinal motility of constipation in patients with Parkinson's disease. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 27(11), 1055.
- Sakakibara, R. (2021). Gastrointestinal dysfunction in movement disorders. Neurological Sciences, 1-11.
- Lacy, B. E., Mearin, F., Chang, L., Chey, W. D., Lembo, A. J., Simren, M., & Spiller, R. (2016). Bowel disorders.Gastroenterology 150 (6), 1393-1407.
Parkinson disease is the second most common neurologic disorder. When most people think about people with Parkinson disease, they think about stooped posture, shuffling gait, slow and rigid movement, balance difficulties and tremoring. Often these motor symptoms are the main target of pharmacological treatments with neurologists and many experience positive functional gains. Non-motor symptoms, however, can be more disabling than the motor symptoms and have significant adverse effects on the quality of life in people with Parkinson disease.

Pelvic rehabilitation specialists have a unique opportunity to step in and help these individuals improve their quality of life and many neurologists are unaware of the benefits our services could provide for their patients.
Please join me in an exciting dive into understanding the physiology of how Parkinson disease affects a person’s pelvic health and develop your skills to effectively assess and develop treatment plans to change the life of these individuals.
Seppi, K., Ray Chaudhuri, K., Coelho, M., Fox, S. H., Katzenschlager, R., Perez Lloret, S., ... & Hametner, E. M. (2019). Update on treatments for nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson's disease—an evidence‐based medicine review. Movement Disorders, 34(2), 180-198.
Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC is the author and presenter of the new Parkinson Disease and Pelvic Rehabilitation course, and she is the co-author of the Neurologic Conditions and Pelvic Floor Rehab course. She is a certified LSVT (Lee Silverman) provider and faculty member, and is a trained PWR! (Parkinson’s Wellness Recovery) provider, both focusing on intensive, amplitude and neuroplasticity based exercise programs for people with Parkinson disease. Erica partners with the Wisconsin Parkinson Association (WPA) as a support group and event presenter as well as author in their publication, The Network. Erica has taken a special interest in the unique pelvic floor, bladder, bowel and sexual health issues experienced by individuals diagnosed with Parkinson disease.

The pharmacologic management of non-motor autonomic dysfunction, including urinary, bowel, and sexual health impairments, is often ineffective, not supported by adequate research, or causes intolerable side effects for people with Parkinson disease. In a recent article titled Update on Treatments for Nonmotor Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease – An Evidence-Based Medicine Review Seppi, K, et al., 2019, the authors state that “before attempting any [pharmacological] treatment for lower urinary tract symptoms, urinary tract infections, prostate disease in men, and pelvic floor disease in women should be ruled out.” It is rare to see a mention of pelvic floor within the literature that addresses helping people with Parkinson disease.
Pelvic rehabilitation specialists have a unique opportunity to step in and help these individuals improve their quality of life and many neurologists are unaware of the benefits our services could provide for their patients. Please join me in an exciting dive into understanding the physiology of how Parkinson disease affects a person’s pelvic health and develop your skills to effectively assess and develop treatment plans to change the life of these individuals.
Seppi, K., Ray Chaudhuri, K., Coelho, M., Fox, S. H., Katzenschlager, R., Perez Lloret, S., ... & Hametner, E. M. (2019). Update on treatments for nonmotor symptoms of Parkinson's disease—an evidence‐based medicine review. Movement Disorders, 34(2), 180-198
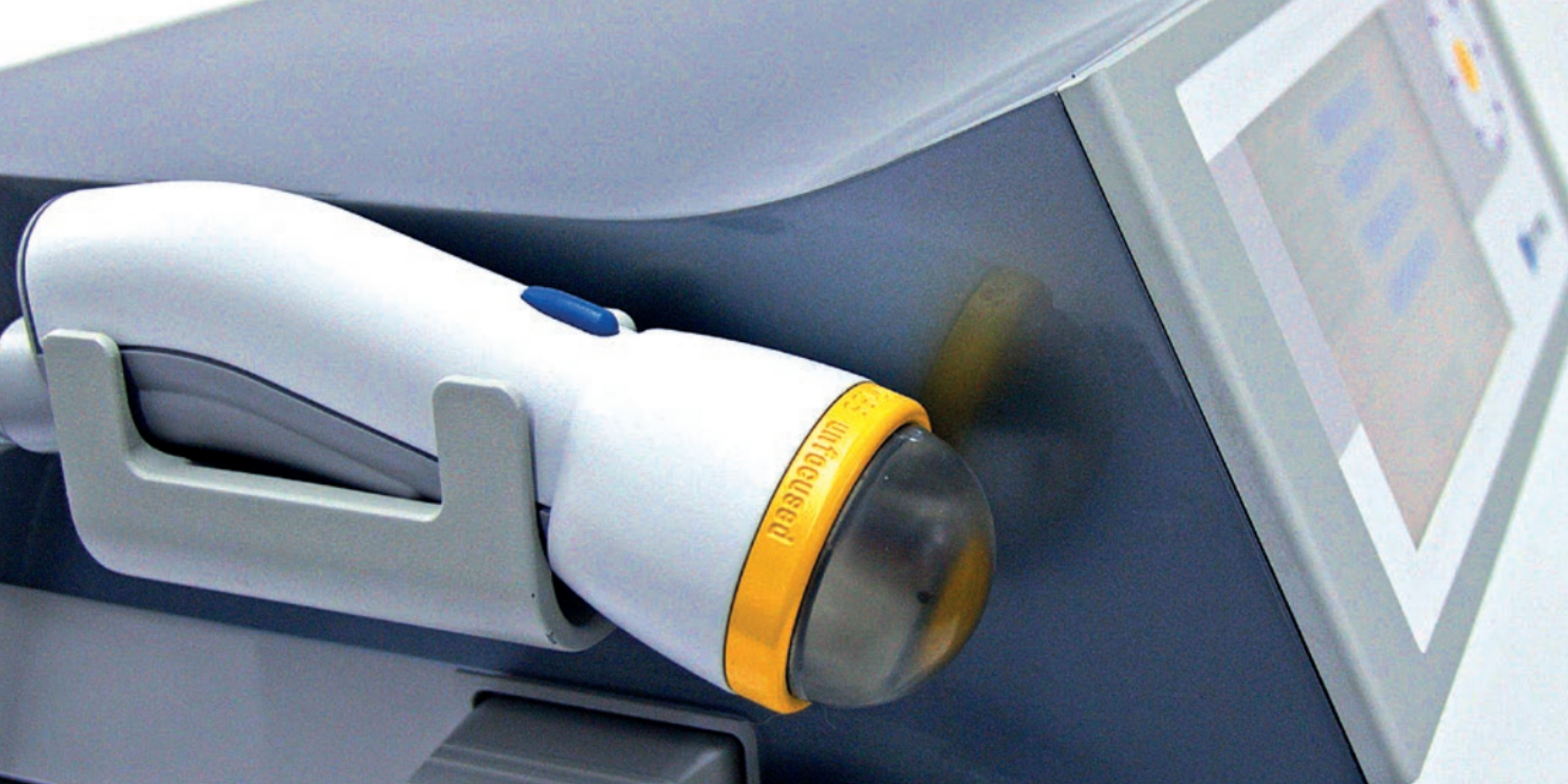
Tibial nerve stimulation has been shown in the literature to be effective for individuals experiencing idiopathic overactive bladder in randomized controlled trials. A systematic review was performed by Schneider, M.P. et al. in 2015 looking at safety and efficacy of its use in neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction. Many variables were examined in this review, which included 16 studies after exclusion. The review looked at:
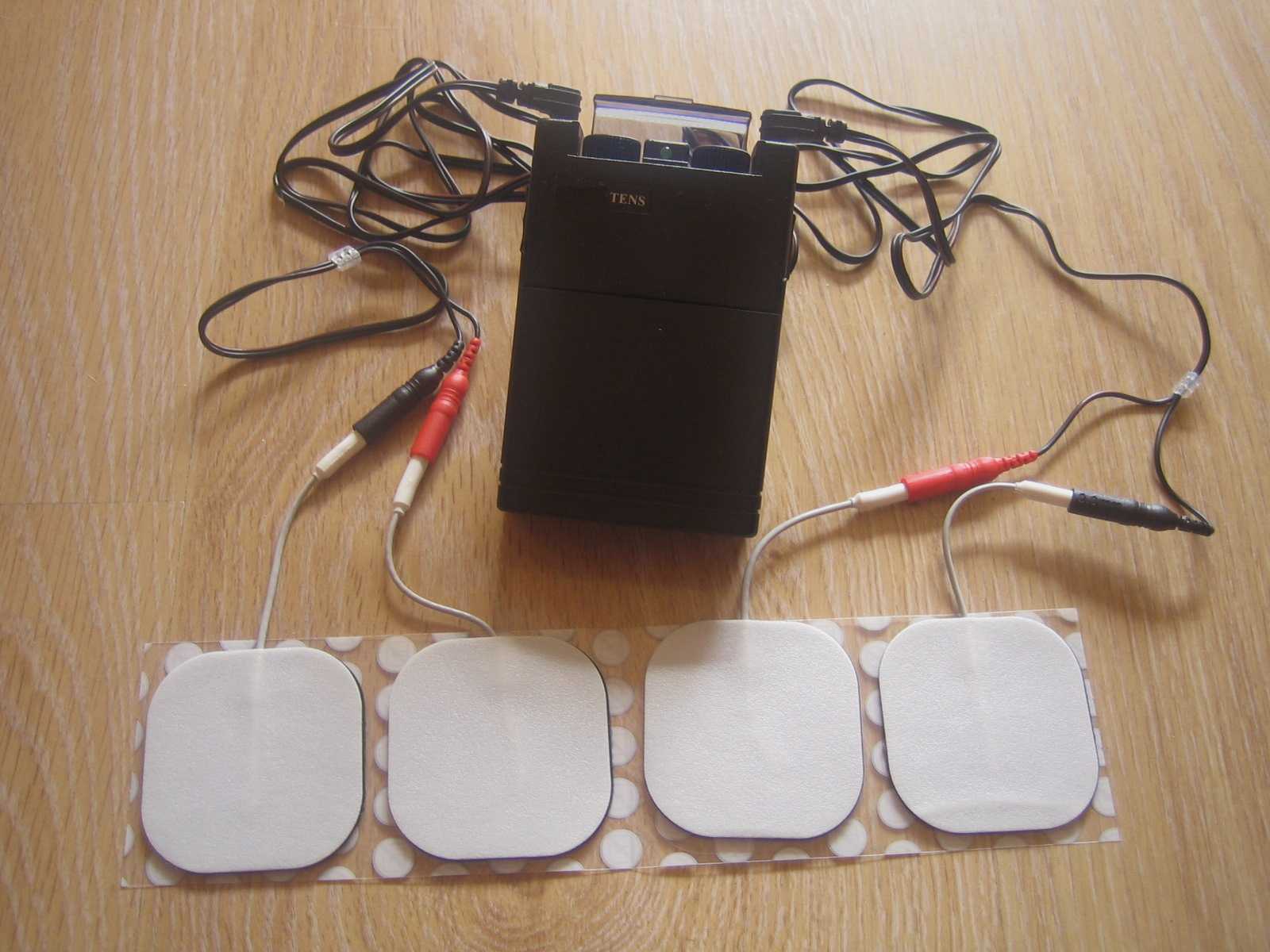
- Acute stimulation (used during urodynamic assessment only)
- Chronic stimulation (6-12 weeks of daily-weekly use)
- Percutaneous or transcutaneous (frequencies, pulse widths, perception thresholds, durations)
- Urodynamic parameter changes baseline to post treatment
- Post void residual changes
- Bladder diary variables
- Patient adherence to tibial nerve stimulation
- Any adverse events
The exact mechanism of these types of neuromodulation stimulation procedures remains unclear, however it does appear to play a role in neuroplastic reorganization of cortical networks via peripheral afferents. No specific literature is currently available for the mechanism on action related to neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction. Different applications of neuromodulation however have been studied in the neurogenic populations.
One of the randomized controlled trials they report on included 13 people with Parkinson disease. The researchers looked at a comparison between the use of transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (n = 8) and sham transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (n=5). Transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation (TTNS) or sham stimulation was delivered to the people with Parkinson disease 2x/week for 5 weeks, 30-minute sessions (10 total sessions). Unilateral electrode placement was utilized, first electrode applied below the left medial malleolus and second electrode 5 cm cephalad. Confirmation of placement was obtained with left great toe plantar flexion. It is important to note the use of the stimulation intensity is reduced to below the motor threshold during the active treatment to direct the stimulation via peripheral afferents.
Urodynamic testing was performed at baseline and post treatment and revealed statistically significant differences with greater volumes at strong desire and urgency in the TTNS group. Additionally, the TTNS group experienced a 50% reduction in nocturia whereas in the sham group nocturia frequency remained the same. A three-day bladder diary completed by each of the groups also revealed significant positive changes in frequency, urgency, urge urinary incontinence and hesitancy only in the TTNS group.
Conservative management of neurogenic bladder in populations such as Parkinson disease is very important. These individuals experience lower quality of life ratings related to lower urinary tract dysfunction, higher risk of falling with needs to rush to the bathroom, their caregivers experience a higher level stress and burden of care, and tolerance to anticholinergic medications is very poor with multiple unwanted side effects that compound and worsen other symptoms that might be present from the disease process.
Please join us for Neurologic Conditions and Pelvic Floor Rehab to learn how you can help your patients using this modality as one option. Participate in a lab session to learn electrode placement and other parameters to achieve best clinical results for your patients.
1. Perissinotto, M. C., D'Ancona, C. A. L., Lucio, A., Campos, R. M., & Abreu, A. (2015). Transcutaneous tibial nerve stimulation in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms and its impact on health-related quality of life in patients with Parkinson disease: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Wound Ostomy & Continence Nursing, 42(1), 94-99.
2. Schneider, M. P., Gross, T., Bachmann, L. M., Blok, B. F., Castro-Diaz, D., Del Popolo, G., ... & Kessler, T. M. (2015). Tibial nerve stimulation for treating neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction: a systematic review. European urology, 68(5), 859-867.
Akinesia is a term typically used to describe the movement dysfunction observed in people with Parkinson disease. It is defined as a poverty of movement, an impairment or loss of the power to move, and a slowness in movement initiation. There is an observable loss of facial expression, loss of associated nonverbal communicative movements, loss of arm swing with gait, and overall small amplitude movements throughout all skeletal muscles in the body. The cause of this characteristic profile of movement is due to loss of dopamine production in the brain which causes a lack of cortical stimulation for movement.
 If the loss of dopamine production in the brain causes this poverty of movement in all skeletal muscles the body, how does the pelvic floor function in the person with Parkinson disease and what should the pelvic floor rehabilitation professional know about treating the pelvic floor in this population of patients?
If the loss of dopamine production in the brain causes this poverty of movement in all skeletal muscles the body, how does the pelvic floor function in the person with Parkinson disease and what should the pelvic floor rehabilitation professional know about treating the pelvic floor in this population of patients?
Let’s take a closer look referencing a very telling article about Parkinson disease and skeletal muscle function. In the Italian town of L’Aquila, a major devastating 6-point Richter scale earthquake occurred on April 6, 2009. 309 people died and there was destruction and collapse of many historical structures, some greater than 100 years old. The nearby movement disorder clinic had been following 31 Parkinson disease patients in the area, 17 of them higher functioning and the other 14 much lower functioning. In fact, of those 14, 10 of them were affected by severe freezing episodes with severe nighttime akinesia requiring assistance with bed mobility tasks, 1 was completely bedridden and the others with major fluctuations in motor performance. 13 of the 14 patients also had fluctuating cognitive functioning.
This devastating earthquake occurred at 3:30 am. All 14 of these patients were able to escape from their homes during or immediately following the event. Caregivers reported that in the majority of the cases, the person with Parkinson’s disease was the first one to be alerted to the earthquake, the first one to get out of the house, ability to alert relatives to run for safety, physically assisting relatives out of the collapsing buildings, and in some cases independently escaping down 1-2 flights of stairs.
Paradoxical kinesia is thought to be the reason for this all but sudden ability to move normally within the presence of an immediate threat to their life and lives of loved ones. Paradoxical kinesia is defined as “a sudden and brief period of mobility typically seen in response to emotional and physical stress in patient’s with advanced idiopathic Parkinson’s disease.” There are a few mechanisms hypothesized to play a role, such as, adrenaline, dopaminergic reserves activating the flight reaction, and compensatory nearby cerebellar circuitry.
There is no pathological evidence that in Parkinson disease there is any break in the continuity of the motor system. The neurologic pathways are all intact and the ability to produce muscle power is retained however requires a strong base of clinic knowledge of the disease to help these patients activate these intact motor pathways. I look forward to sharing the neurologic basis of these deficits in Parkinson disease and strategies in pelvic floor rehab to do just that!
Erica Vitek, a specialist in treating patients with neurologic dysfunction, is the author and instructor of Neurologic Conditions and Pelvic Floor Rehab, taking place September 14-16, 2018 in Grand Rapids, MI.
Bonanni, L., Thomas, A., Anzellotti, F., Monaco, D., Ciccocioppo, F., Varanese, S., Bifolchetti, S., D’Amico, M.C., Di Iorio, A. & Onofrj, M. (2010). Protracted benefit from paradoxical kinesia in typical and atypical parkinsonisms. Neurological sciences, 31(6), 751-756.











































