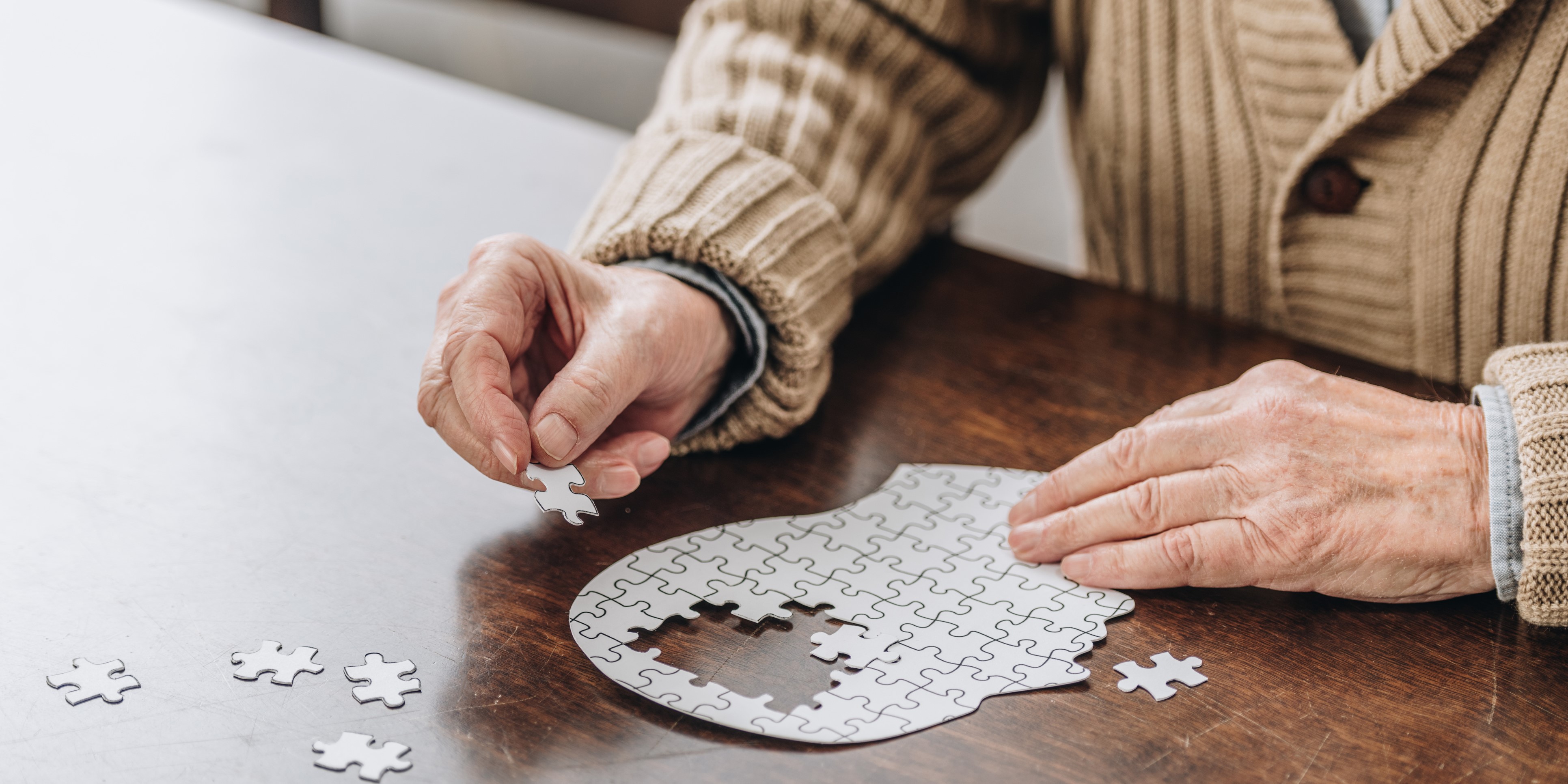
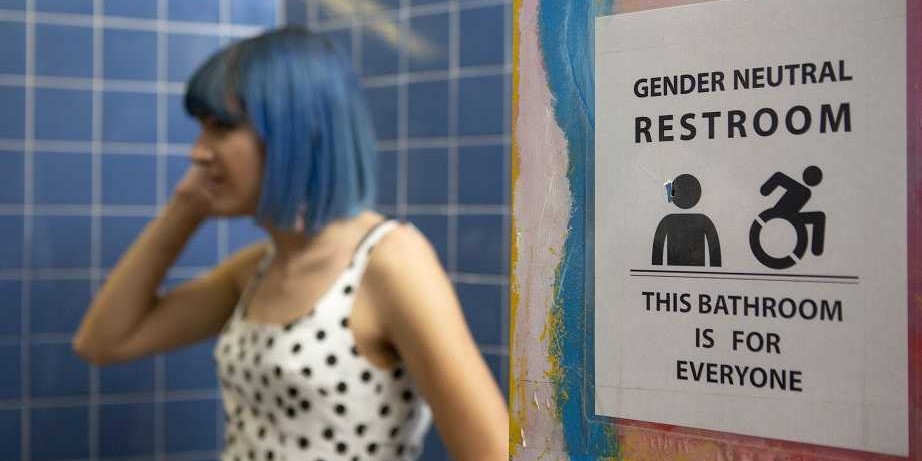With age, many of our patients may be at higher risk of developing dementia. Dementia has a wide range of causes and symptoms, and is most often associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Memory loss, difficulty in communicating, in organizing complex tasks and in coordinating motor functions can add to the challenge of participating in rehabilitation. In pelvic rehabilitation, we are already faced with the importance task of effectively communicating about sensitive topics, obtaining clear consent, and instructing in exercise that may be difficult for the patient to “see” or appreciate in the same way as with a biceps curl or leg raise. How can we set ourselves and our patients up for success when working with a patient who has dementia or other cognitive issues?
 An article with a focus on communication with older people who have dementia de Vries, 2013 summarizes practical information that can positively affect our skills in communication with patients who have cognitive dysfunction. From the impact of hearing loss on orientation and sense of vulnerability, to the types of listening skills recognized as means to improve communication, the article integrates a wide range of valuable information.
An article with a focus on communication with older people who have dementia de Vries, 2013 summarizes practical information that can positively affect our skills in communication with patients who have cognitive dysfunction. From the impact of hearing loss on orientation and sense of vulnerability, to the types of listening skills recognized as means to improve communication, the article integrates a wide range of valuable information.
Some of the suggestions for enhancing interactions with patients who have dementia come from the work of Wilson et al., 2012, and include the following:
- slow the rate of your speech
- use verbatim repetition
- ask questions that can be answered with a “yes” or “no”
- decrease the complexity of your sentences
- ask one question at a time give instructions for one idea or concept at a time
- avoid use of pronouns when able (can be confusing, refer instead to the person)
Other research-based advice given in the article includes eliminating distraction, such as turning off a radio or television, and avoid interrupting the person who has dementia. Sitting face to face is recommended, as is using non-verbal communication such as facial expressions and gestures. Also very interesting is the idea that using a more controlling tone of voice can lead to increased resistance to care. A terrific strategy that is recommended in the article is this “Ask a colleague to observe your practice…and make notes on how you communicate…” Although being critiqued may feel intimidating, learning how others perceive our use of the above skills can help to optimize communication with patients who have dementia.
Providing optimal communication strategies during rehabilitation is just one of the topics that is discussed in the Institute’s new Geriatric Pelvic Floor Rehab continuing education course. The first opportunity to take this new course is Tampa, Florida this January. The course is taught by Heather Rader who immerses herself in the care of people in the geriatric age range. Her expertise not only in pelvic rehab, but also in adaptations for the geriatric population, billing practices, and marketing will be shared.
De Vries, K. (2013). Communicating with older people with dementia. Nursing older people, (25), 30-7.
Wilson, R., Rochon, E., Mihailidis, A., & Leonard, C. (2012). Examining success of communication strategies used by formal caregivers assisting individuals with Alzheimer’s disease during an activity of daily living. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 55(2), 328-341.
 Mindful awareness has been defined as “the awareness that emerges through paying attention on purpose, in the present moment and non-judgmentally, to the unfolding experience, moment by moment.” Kabat Mindful awareness can be cultivated through training in sitting meditation, mindful body scan, walking meditation and mindful movement. Over the past 3 decades, a growing body of research has identified multiple health benefits from training in mindful awareness. Keng, Lakhan, La Cour One pilot study evaluated the feasibility and efficacy of an 8-week mindfulness program for patients with chronic pelvic pain. Fox Pre- and post-assessments included daily pain scores, the Short Form-36 Health Status Inventory, Kentucky Inventory of Mindfulness Score and the Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology. Upon program completion, participants reported significant improvement in daily maximum pain scores, physical function, mental health, social function and mindfulness scores. These pilot results are positive and promising.
Mindful awareness has been defined as “the awareness that emerges through paying attention on purpose, in the present moment and non-judgmentally, to the unfolding experience, moment by moment.” Kabat Mindful awareness can be cultivated through training in sitting meditation, mindful body scan, walking meditation and mindful movement. Over the past 3 decades, a growing body of research has identified multiple health benefits from training in mindful awareness. Keng, Lakhan, La Cour One pilot study evaluated the feasibility and efficacy of an 8-week mindfulness program for patients with chronic pelvic pain. Fox Pre- and post-assessments included daily pain scores, the Short Form-36 Health Status Inventory, Kentucky Inventory of Mindfulness Score and the Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology. Upon program completion, participants reported significant improvement in daily maximum pain scores, physical function, mental health, social function and mindfulness scores. These pilot results are positive and promising.
In my experience, mindfulness gives patients the skillful awareness necessary to self-regulate their reactions to pain and stress. Many of these reactions are maladaptive and amplify distress and pain. With training in mindfulness, patients are able to observe physical, cognitive and emotional reactions to pain and stress and adopt healthy choices that de-escalate suffering. I am excited to share my 30 years of experience and training in mindful awareness and its application to patient care and provider self-care through my 2-day course with Herman & Wallace. Join me at "Mindfulness Based Pain Treatment: A Biopsychosocial Approach to the Treatment of Chronic Pain" on January 16-17, 2016 in Silverdale, WA.
1. Kabat Zinn, J.Full Catastrophe Living: Using the Wisdom of Your Body and Mind to Face Stress, Pain and Illness. 2013, 2nd ed. New York: Bantam.
2. Keng, S.L., Smoski M.J., Robins, C.J. Effects of mindfulness on psychological health: a review of empirical studies. Clin Psychol Rev, 2011;31(6), pp. 1041-56.
3. Lakhan, S.E., Schofield, K.L. Mindfulness-based therapies in the treatment of somatization disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 2013;8(8), e71834.
4. La Cour, P., Petersen, M., 2014. Effects of mindfulness meditation on chronic pain: A randomized controlled trial. Pain Med, Nov 7. doi: 10.1111/pme.12605.
5. Fox, SD, Flynn E, Allen RH. Mindfulness meditation for women with chronic pelvic pain: a pilot study. J Reprod Med, 2011;56(3-4):158-62.
![By Mikael Häggström (Own work) [CC0], via Wikimedia Commons](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d9/Symptoms_of_menopause_%28raster%29.png/512px-Symptoms_of_menopause_%28raster%29.png) Sleep difficulties are a common problem among women in the menopausal period, with hot flashes and night sweats commonly interfering with a restful night’s sleep. According to Baker and colleaguesBaker, 2015 , disturbed sleep is present in 40-60% of women in the menopausal transition. The authors also point out that insomnia is not well characterized, with poor identification of a physiologic basis for the sleep disturbances. In the research linked above, perimenopausal women diagnosed with clinical insomnia (n=38) were compared to women who did not have insomnia (n=34). Outcome measures included the Beck Depression Inventory, the Greene Climacteric Scale, sleep diaries, sleep studies, and nocturnal hot flashes via dermal conductance meters.
Sleep difficulties are a common problem among women in the menopausal period, with hot flashes and night sweats commonly interfering with a restful night’s sleep. According to Baker and colleaguesBaker, 2015 , disturbed sleep is present in 40-60% of women in the menopausal transition. The authors also point out that insomnia is not well characterized, with poor identification of a physiologic basis for the sleep disturbances. In the research linked above, perimenopausal women diagnosed with clinical insomnia (n=38) were compared to women who did not have insomnia (n=34). Outcome measures included the Beck Depression Inventory, the Greene Climacteric Scale, sleep diaries, sleep studies, and nocturnal hot flashes via dermal conductance meters.
Results of the study concluded that women with insomnia, compared with controls, had higher levels of psychologic, somatic, vasomotor symptoms, and had higher scores on the depression inventory, shorter sleep duration, and lower sleep efficiency. Women with insomnia were also more likely to have hot flashes, with number of hot flashes predicting awakenings during the sleep study. Episodes of wakefulness after sleep onset, and decreased time of sleep were noted in the women who were diagnosed with new-onset insomnia.
Because untreated insomnia is associated with negative consequences including hypertension, stroke, diabetes, and depression, the authors suggest that women who are diagnosed with insomnia should be treated for their insomnia. If you are interested in learning about natural methods to manage and reduce hot flashes, among many other interesting topics, you will likely enjoy Herman & Wallace faculty Michelle Lyons and her newer course: Special Topics in Women’s Health. The next chance to hear Michelle discuss these topics is in Denver in January. Bring your skis!
Baker, Fiona C. et al. "Insomnia in women approaching menopause: Beyond perception" Psychoneuroendocrinology, Volume 60, 96-104 October 2015
Today we get to hear from Ramona Horton, MPT, who teaches several courses with the Herman & Wallace Institute. Her upcoming course, Visceral Mobilization Level 1: Mobilization of Visceral Fascia for the Treatment of Pelvic Dysfunction in the Urologic System, will be taking place November 6-8, 2015 in Salt Lake City, UT.
 This spring I reached a milestone in my career. I have been working as a licensed physical therapist for 30 years, of which the past 22 have been in the field of pelvic dysfunction. Other than some waitressing stents and a job tending bar while in college this is the only profession I have known. When I entered the US Army-Baylor program in Physical Therapy in the fall of 1983 nowhere was it on my radar screen that I would be dealing with the nether regions of men, women and children, let alone teaching others to do so. As time marches on, I find myself visiting my hair dresser a bit more frequently to deal with that ever progressive grey hair that marks the passage of these years…translation: I am an old dog and I have been forced to learn some new tricks.
This spring I reached a milestone in my career. I have been working as a licensed physical therapist for 30 years, of which the past 22 have been in the field of pelvic dysfunction. Other than some waitressing stents and a job tending bar while in college this is the only profession I have known. When I entered the US Army-Baylor program in Physical Therapy in the fall of 1983 nowhere was it on my radar screen that I would be dealing with the nether regions of men, women and children, let alone teaching others to do so. As time marches on, I find myself visiting my hair dresser a bit more frequently to deal with that ever progressive grey hair that marks the passage of these years…translation: I am an old dog and I have been forced to learn some new tricks.
Like many aspects of our modern life, the profession of physical therapy is under a constant state of evolution. The best example of this is the way we look at pain and physical dysfunction. I was educated under the Cartesian model, one that believed pain is a response to tissue damage. Through quality research and better understanding of neuroscience we now know that this simplistic model is, in a word, too simple. We have come to recognize that pain is an output from the brain, which is acting as an early warning system in response to a threat real or perceived. I wholeheartedly embrace the concept that pain is a biopsychosocial phenomenon; however I am not willing to give up my treatment table for a counselors couch when dealing with persistent pain patients.
As a physical therapist, I still believe that we need to educate, strengthen and yes, touch our patients. Given that paradigm, ultimately I am a musculoskeletal therapist and I believe that when a clinician is designing a treatment program for any patient, applying sound clinical reasoning skills means the clinician needs to take into consideration that there are three primary areas in the individuals life in which they may be encountering a barrier to optimal function: neuro-motor, somatic and psycho-social. After many years of developing and refining my clinical reasoning model, I have chosen to adopt the image of the Penrose triangle. My goal was to provide the clinician with a visual on which to focus their problem solving skills and a reminder to encompass the person as a whole. The goal is to convey the understanding that the barriers which present themselves rarely do so in isolation, and that the source to resolve of all barriers that impede human function, regardless of origin, is ultimately found within the brain.
Neuro-motor barriers include issues of muscle function to include motor strength, length, endurance, timing and coordination. These barriers are improved through therapeutic exercise training. Somatic barriers are those that are addressed through any number of manual therapy interventions which address issues found within multiple structures to include the fascia, osseous/articular tissue, lymphatic congestion, restrictions within the visceral connective tissue, neural/dural restrictions and challenges of the dermal/integumentary system. All of these barriers can contribute to nociceptive afferent activity. Lastly would be the psychosocial barriers which include history of trauma, clear behavior of hypervigilance, catastrophization, current life stressors, perceived threat which includes kinesiophobia (back to neuro-motor) ANS issues which present as autonomic dysregulation and lastly pain model misconceptions.
I suggest that we remember that the body is a self-righting mechanism. If we cut our skin, given the wound is kept free from infection (a barrier), the human body will heal the wound. As clinicians, I believe that we need to come to the realization that we don’t fix anything, we simply remove the barrier to healing and trust the body to do the rest. Our challenge is to recognize and address the barriers.
How many of us have heard a subjective report from a patient that clearly implicates the coccyx as the problem but quickly think, “I’m sure as heck not going there!”? We cross our fingers, hoping the patient will get better anyway by treating around the issue. That is like trying to get a splinter out of a finger by massaging the hand. As nice as the treatment may feel, the tip of the finger still has a sharp, throbbing pain at the end of the day, because the splinter, the source of the pain, has not been touched directly. For most therapists, the coccyx is an overlooked (and even ignored) splinter in the buttocks.
![By Sanba38 (Own work) [GFDL (http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html), CC-BY-SA-3.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/) or FAL], via Wikimedia Commons](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f6/Splinter.jpg/256px-Splinter.jpg) A colleague of mine had a patient with relentless coccyx pain for 7 years and was about to lose a relationship, as well as his mind, if someone did not help him. He had therapy for his lumbar spine with “core stabilization,” and he had pain medicine, anti-inflammatory drugs, and inflatable donuts to sit upon to relieve pressure, but his underlying pain remained unchanged. Luckily for this man, his “last resort” was trained in manual therapy and assessed the need for internal coccyx mobilization to resolve his symptoms. The patient’s desperation for relief overrode any embarrassment or hesitation to receive the treatment. After a few treatments, the man’s life was changed because someone literally dug into the source of pain and skillfully remedied the dysfunction.
A colleague of mine had a patient with relentless coccyx pain for 7 years and was about to lose a relationship, as well as his mind, if someone did not help him. He had therapy for his lumbar spine with “core stabilization,” and he had pain medicine, anti-inflammatory drugs, and inflatable donuts to sit upon to relieve pressure, but his underlying pain remained unchanged. Luckily for this man, his “last resort” was trained in manual therapy and assessed the need for internal coccyx mobilization to resolve his symptoms. The patient’s desperation for relief overrode any embarrassment or hesitation to receive the treatment. After a few treatments, the man’s life was changed because someone literally dug into the source of pain and skillfully remedied the dysfunction.
Marinko and Pecci (2014) presented 2 case reports of patients with coccydynia and discussed clinical decision making for the evaluation and management of the patients. The patient with a traumatic onset of pain had almost complete relief of pain and symptoms after 3 treatment sessions of manual therapy to the sacrococcygeal joint. The patient who experienced pain from too much sitting did not respond with any long term relief from the manual therapy and had to undergo surgical excision. The first patient was treated in the acute stage of injury, but the second patient had a cortisone injection initially and then the manual treatment in this study 1 year after onset of pain. Both patients experienced positive outcomes in the end, but at least 1 patient was spared the removal of her coccyx secondary to manual work performed in what some therapists consider “uncharted territory.”
A systematic literature review was published in 2013 by Howard et al. on the efficacy of conservative treatment on coccydinia. The search spanned 10 years and produced 7 articles, which clearly makes this a not-so-popular area of research. No conclusions could be made on how effective the various treatments of manual therapy, injections, or radiofrequency interventions were because of the insufficient amount of research performed on the topic.
In an evidence-based era for physical therapy intervention, sometimes we limit ourselves in our treatment approaches. What if the best interventions just have yet to be oozing with clinical trials and published outcomes? The first person to pull a splinter out of a finger did not have a peer-reviewed guide instructing one to use 2 fingers to wrap around the splinter and pull it out of the skin. Coccyx mobilization internally and externally is a legitimate treatment without a lot of notoriety. The Coccyx Pain, Evaluation, and Treatment course uses the most current evidence to expand your knowledge of anatomy and pathology and hone your palpation skills to evaluate and treat an area where you never thought you’d go.
References: Howard, P. D., Dolan, A. N., Falco, A. N., Holland, B. M., Wilkinson, C. F., & Zink, A. M. (2013). A comparison of conservative interventions and their effectiveness for coccydynia: a systematic review. The Journal of Manual & Manipulative Therapy, 21(4), 213–219. http://doi.org/10.1179/2042618613Y.0000000040
Marinko LN, Pecci M. (2014). Clinical decision making for the evaluation and management of coccydynia: 2 case reports. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther, 44(8):615-21. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2014.4850
Therapists are increasingly learning about and treating pediatric patients who have pelvic floor dysfunction, yet there are still not enough of them to meet the demand. Many therapists I have spoken to are understandably concerned about how to transfer what they have done for adult patients to a younger population. Here are some of the more common concerns therapists express or questions they ask in relation to the pediatric population:

- Can we use biofeedback with children?
- Do we complete internal assessments on kids?
- How do we change the way we talk to the children?
- How much do we have to teach the parents to get the information across?
- Why do we teach strengthening even if some of the kids mostly need relaxation or coordination?
Although each question deserves a longer answer, we can start with biofeedback, and the answer is a resounding “yes”. There is abundant research affirming the potential benefit of biofeedback training for children with pelvic floor dysfunction. And no, we do not typically complete an internal pelvic muscle assessment on children, as that would not be appropriate. Considering that pediatrics can refer to young adults up to age 18-21, there may be a reasonable clinical goal in mind for utilizing internal assessment or treatment. The words we use when we speak to children become very important. Herman & Wallace faculty member Dawn Sandalcidi (known as “Miss Dawn” to her younger patients) gives ample strategies for adapting our language in her continuing education course Pediatric Incontinence and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction. For example, Dawn emphasizes the importance of describing an episode of incontinence as a “bladder leak” and of pointing out to a child that his or her bladder leaked, rather than the child leaking. She also likes to encourage parents and school personnel to drop the term “accident” from vocabulary. In her 2-day course, Dawn also teaches therapists how to train children to become a “Bladder Boss”, and how to teach young patients about relevant anatomy.
The way we teach anatomy to kids is really important in making sure they “get” it. One study published in 2012Equit 2013 describes the results when children are asked to draw a urinary tract in a body diagram. Only half of the children drew a bladder and other organs, and nearly 43% of the children drew “anatomically incorrect pictures.” The authors point out that older children and the ones who had gone through group training for bowel and bladder were more likely to draw correct images. For the last question about teaching contract/relax exercises to children, I had an opportunity to ask Dawn this question recently when she was filming a pediatrics course for MedBridge Education. Her answer emphasized the importance of getting children to develop awareness of the pelvic muscles, and to improve their coordination as well as strength- concepts that participating in an exercise program can work toward.
If you would like to learn more about working with children, the next opportunity to take Dawn’s course is in Boston later this month.
Equit, Monika et al. "Children's concepts of the urinary tract". Journal of Pediatric Urology , Volume 9 , Issue 5 , 648 - 652
You went through Herman and Wallace’s Pelvic Floor 1 course and were ready to treat your clients with incontinence and prolapse……….then you started getting referrals for clients with pelvic pain.
You have 45-60 minutes (or longer if you are lucky) to create a safe and comfortable environment, skillfully establish trust and rapport and gather objective and subjective data to get to the bottom of their pain. You want to give them the summary of your findings, their rehab road map and something to work on at home. By the end of the visit, you need to have completed their problem list and plan of care. Where do you start?
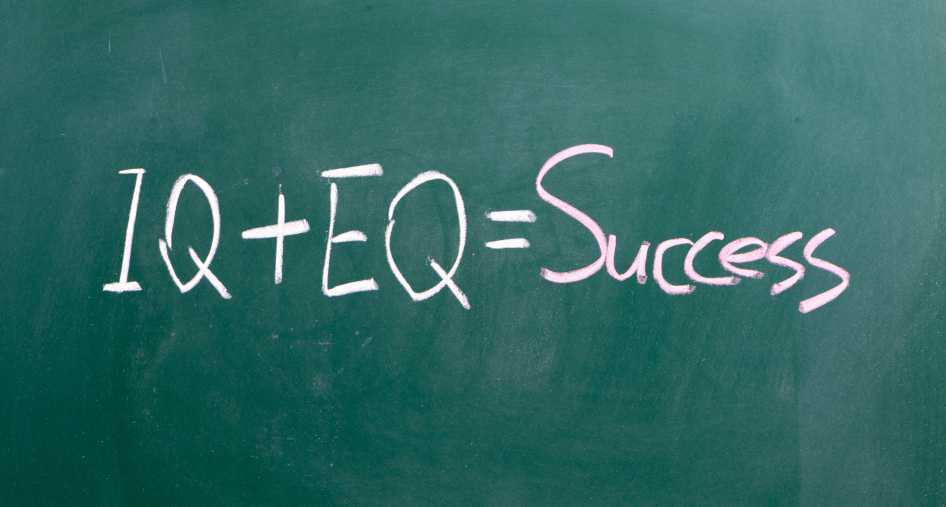 No pressure, right?
No pressure, right?
Clinicians are under a huge amount of pressure to get clients better and faster, which can result in rushing treatment before differential diagnosis is complete. A thorough approach enables us to say, with confidence, what the drivers of their condition are or at the very least what they are not. It is safe to say that no one single issue drives pelvic pain: it is a condition that is unique to each individual and requires a right AND left brain toolbox to unravel the ball of yarn that is pelvic pain.
A client with severe groin and labial pain was referred to my office for a second PT course of care. Her previous course of PT (by an outstanding clinician) focused on intrapelvic visceral work and postural corrections. The client’s pain had remained unchanged. Her visceral mobility, posture, joint biomechanics, neural upregulation, core muscle inhibition, myofascial trigger points, dysfunctional voiding and deconditioning were most definitely significant factors. The initial evaluation aligned with severe OA with a labral tear being the primary driver of her pain. I am no guru: it was with evidence-based sensitive and specific testing I was confident that this woman needed a new hip and that no amount of physical therapy could improve her pain as quickly or efficiently as a hip replacement. She DID need a customized PT pre-op course of care to prepare her for a great outcome. When she got a new hip, we incorporated all key factors into her post op rehab and she is back to her goals of hiking and having sex with her husband. (But not at the same time, as far as I know.)
Before you jump to conclusions, I am not a surgery happy PT. I work with orthopedic surgeons and interventional pain docs as frequently as I work with Reiki healers, craniosacral therapists and acupuncturists. I want to fill my toolbox with right as well as left brained tools, from the most subtle of manual interventions and precise movement re-education to dynamic mobilization and strengthening interventions. As a profession we are called to utilize evidence-based treatment as well as innovative interventions that may be researched one day. Every evidence-based practice was once an unresearched clinical intervention based on clinical reasoning and perhaps gut instinct.
As pelvic health therapists, our work requires high EQ as well as IQ to earn client trust as well as differential diagnosis abilities to design their plan of care. Before we can ask for more visits, we need to justify the reasons behind the request based on solid clinical reasoning including objective data. Certainly in 45 minutes it can be difficult if not impossible to perform a comprehensive pelvic health and musculoskeletal evaluation. That being said, we need to address main categories of foundational evaluation testing to capture their data in a thorough manner.
“Finding the Driver in Pelvic Pain” is a course that enables the clinician to perform a foundational comprehensive musculoskeletal and pelvic health exam to find the evidence based factors in the client’s pain. We are called to deliver care that integrates both the art and science of physical therapy and healing. If we just use the ‘art’, or only the ‘science’, we miss key elements in our differential diagnosis which could delay the client getting better.
Research published in a Nursing journal highlights the need for pelvic rehab providers to assess for sexual dysfunction in women before, during, and after pregnancy. 200 women were interviewed about their return to sexual activity after pregnancy and childbirth, and the results demonstrate that women can (and do) have limitations in their sexual function around the entire peripartum period.
![By Nina Matthews (Flickr: head to head) [CC BY 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/86/Silhouette_or_a_pregnant_woman_and_her_partner-14Aug2011.jpg/492px-Silhouette_or_a_pregnant_woman_and_her_partner-14Aug2011.jpg) The results of the survey concluded that before pregnancy 33.5% of the women reported sexual dysfunction, and this number increased to 76% during pregnancy, and to 43.5% following delivery. The types of sexual dysfunction included dyspareunia, vaginismus, and decreased desire and orgasm. The authors of the study correlated dysfunctions with Catholic religion, vaginal delivery without suture, dyspareunia during pregnancy, vaginismus before pregnancy, and with working more than 8 hours per day.
The results of the survey concluded that before pregnancy 33.5% of the women reported sexual dysfunction, and this number increased to 76% during pregnancy, and to 43.5% following delivery. The types of sexual dysfunction included dyspareunia, vaginismus, and decreased desire and orgasm. The authors of the study correlated dysfunctions with Catholic religion, vaginal delivery without suture, dyspareunia during pregnancy, vaginismus before pregnancy, and with working more than 8 hours per day.
The information collected in this study raise important points with a variety of topics related to sexual function. How we as providers aim to address these topics with women can have a critical impact on the health of a woman and her family. Let’s look at some action items this research can lead us to:
- Include methods of asking about sexual health in your written and verbal evaluations
- Educate colleagues about bringing up sexual health with women throughout the lifespan
- Avoid assuming that a woman would not want to be sexually active during pregnancy
- Recognize that personal beliefs (including religion) play a role in sexual health, and that a patient can be encouraged to talk to her spiritual advisor or a trusted professional if concerns arise
- Talk about healthy workloads, options for modifications at work, and strategize with patients about rest breaks or decreasing work hours if financially able
This type of research can lead to many more questions, such as how religious beliefs impact sexual function during pregnancy, what the effect of physiologic changes versus fatigue can have on libido, or if women who have intervention for dyspareunia prior to pregnancy have decreased sexual dysfunction after pregnancy. Most of us were not instructed in how to dialog about these types of questions, and of course some topics, like religion, are potentially very sensitive to bring up with our patients.
If you would like more practical advice about the clinical implications for sexual medicine across the lifespan and among all genders, consider a trip to San Diego this November to learn from Herman & Wallace co-founder Holly Herman at Sexual Medicine for Men and Women: A Rehabilitation Perspective!
Holanda, J. B. D. L., Abuchaim, E. D. S. V., Coca, K. P., & Abrão, A. C. F. D. V. (2014). Sexual dysfunction and associated factors reported in the postpartum period. Acta Paulista de Enfermagem, 27(6), 573-578.
How often do we hear of patients trying to explain their sexual pain to a partner, only to be doubted, not believed, or guilt tripped into having sex because of the lack of understanding of the condition? I’d say about as often as we hear of the other unfortunate misunderstandings about the nature of painful sexual function, such as people not wanting to be in a relationship for fear of sexual dysfunction limiting their participation, or believing that healthy sex is gone for good. Most of us are familiar with the phrase, “not tonight- I’ve got a headache” yet how often is the truth really that a person has a “pelvic ache?” And do headaches and pelvic pain go together? That is the question posed in research published in the journal Headache.
 For 72 women who were being treated for chronic headache, a survey was administered to assess for associations between sexual pain and libido, a history of abuse, and to determine the number of women being treated for sexual pain. Nearly 71% of the women were diagnosed on the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD)-III criteria with chronic migraines, nearly 17% with medication overuse headache, 10% with both chronic overuse headache and migraine. Below are some of the statistics from the survey.
For 72 women who were being treated for chronic headache, a survey was administered to assess for associations between sexual pain and libido, a history of abuse, and to determine the number of women being treated for sexual pain. Nearly 71% of the women were diagnosed on the International Classification of Headache Disorders (ICHD)-III criteria with chronic migraines, nearly 17% with medication overuse headache, 10% with both chronic overuse headache and migraine. Below are some of the statistics from the survey.
| Symptom | % Respondents who Experienced Symptom |
| Pelvic region pain brought on by sexual activity | 44% |
| Pelvic region pain preventing from engaging in sexual activity | 18% |
| Among women who had pain: | |
| Reported pain for < 1 year | 3% |
| Reported pain for 1-5 years | 35% |
| Reported pain for 6-10 years | 29% |
| Reported pain for > 10 years | 32% |
Although the next statistics should not be so surprising based on prior literature and on our work in the clinics, 50% of the women had not discussed their pelvic pain with a provider. Of the women who had discussed their pelvic pain with a provider, 37.5% were currently receiving treatment, 31% had not received any treatment, 31% had received care in the past, and 1% did not provide an answer. Reasons for not receiving treatment included that no treatment was offered, pain was not severe enough to warrant care, or fear of pursuing treatment due to embarrassment. Unfortunately, rehabilitation was not a significant part of the treatment plan, even though all but one of the women said they would want to pursue care if available.
Other interesting associations were made in the article, which is available as full text in the link above, including rates of sexual abuse, and associations between types of headaches and pelvic pain. The bottom line is that headaches and pelvic pain can occur together, and that based on this research, many women are still suffering for long periods of time without accessing care for pelvic pain. When it comes to headaches, there are many types of headaches, and many other conditions that occur and can cause pain in the head, face, and neck. If you would like to sharpen your clinical tools related to headaches, as well as dizziness and vertigo, you still have time to sign up for the Institute’s new continuing education course on Neck Pain, Headaches, Dizziness, and Vertigo that takes place in Rockville in November.
Today, September 28th, marks the ten year anniversary of the founding of Herman & Wallace! The Institute was founded on this day in 2005 by Holly Herman, PT, DPT, MS, OCS, WCS, BCB-PMD, PRPC and Kathe Wallace, PT, BCB-PMD with a mission of providing the very best evidence-based continuing education related to pelvic floor and pelvic girdle dysfunction in men and women throughout the life cycle.
![By Joey Gannon from Pittsburgh, PA (Candles) [CC BY-SA 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)], via Wikimedia Commons](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/f/f5/Blue_candles_on_birthday_cake.jpg/512px-Blue_candles_on_birthday_cake.jpg) Since our founding, it’s been our privilege to spread this mission through an ever-increasing number of course offerings, products, resources and certification so that therapists can meet their goals and patients can access trained practitioners who can address their needs.
Since our founding, it’s been our privilege to spread this mission through an ever-increasing number of course offerings, products, resources and certification so that therapists can meet their goals and patients can access trained practitioners who can address their needs.
In the past ten years, we’ve significantly expanded our course offerings. Currently-offered courses cover pediatrics and geriatrics, sexual health, yoga and Pilates, oncology, meditation and mindfulness, and a number of other topics instructed by some of the foremost experts in the field, with whom we are thrilled to work and provide a platform to spread their knowledge. In addition to our flagship Pelvic Floor series courses which were the first offered by the Institute, H&W now offers 46 live courses and 14 online courses on topics related to pelvic floor dysfunction, as well as related women’s health, men’s health and orthopedic topics.
We have also had the opportunity to take this mission abroad and have offered pelvic floor courses in Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Chile, Brazil, the UK and Europe. In 2013, H&W launched the first-ever certification recognizing expertise in treating pelvic floor dysfunction in men and women throughout the life cycle, the Pelvic Rehabilitation Practitioner Certification. Since then, 84 practitioners have sat for and passed this exam and earned PRPC as a designation of their competence in evaluating and treating pelvic rehab patients. This coming year and beyond, we are looking forward to continuing with our mission of providing the very best education and resources for pelvic rehab therapists. We are continuing to expand our offerings of intermediate and advanced- level Pelvic Floor coursework for experienced therapists, as well as an increasing number of scheduled events for our introductory courses so that more practitioners can begin learning the skills needed to serve this growing patient population.
Over these years, the best part is hearing from therapists that our mission is changing lives for practitioners and for patients. This recent email we received from a course participant is the best birthday gift we received!:
“I always gain so much from your courses and they are the first ones I look to each year for simply excellent use of my education dollars and to further my knowledge of Women’s/Men’s/Children’s Pelvic Health. Kuddo’s to you, sincerely, for really making a difference in the lives of so many – that you, as therapists, work with directly, AND that you “work with” through each therapist that you train. What a huge ripple effect for making the difference in the lives of many…..and on such personal issues. And I give due credit to you with each patient I see for the training I have and am still receiving! Thank-you!!!!”
By accepting you will be accessing a service provided by a third-party external to https://hermanwallace.com./