Coaching Patients to Engage in Positive Activities to Improve Outcomes
Substantial attention has been given to the impact of negative emotional states on persistent pain conditions. The adverse effects of anger, fear, anxiety and depression on pain are well-documented. Complementing this emphasis on negative emotions, Hanssen and colleagues suggest that interventions aimed at cultivating positive emotional states may have a role to play in pain reduction and/or improved well-being in patients, despite pain. They suggest positive affect may promote adaptive function and buffer the adversities of a chronic pain condition.
 Hanssen and colleagues propose positive psychology interventions could contribute to improved pain, mood and behavioral measures through various mechanisms. These include the modulation of spinal and supraspinal nociceptive pathways, buffering the stress reaction and reducing stress-induced hyperalgesia, broadening attention, decreasing negative pain-related cognitions, diminishing rigid behavioral responses and promoting behavioral flexibility.
Hanssen and colleagues propose positive psychology interventions could contribute to improved pain, mood and behavioral measures through various mechanisms. These include the modulation of spinal and supraspinal nociceptive pathways, buffering the stress reaction and reducing stress-induced hyperalgesia, broadening attention, decreasing negative pain-related cognitions, diminishing rigid behavioral responses and promoting behavioral flexibility.
In a feasibility trial, 96 patients were randomized to a computer-based positive activity intervention or control condition. The intervention required participants perform at least one positive activity for at least 15 minutes at least 1 day/week for 8 weeks. The positive activity included such tasks as performing good deeds for others, counting blessings, taking delight in life’s momentary wonders and pleasures, writing about best possible future selves, exercising or devoting time to pursuing a meaningful goal. The control group was instructed to be attentive to their surroundings and write about events or activities for at least 15 minutes at least 1 day/week for 8 weeks. Those in the positive activity intervention demonstrated significant improvements in pain intensity, pain interference, pain control, life satisfaction, and depression, and at program completion and 2-month follow-up. Based on these promising results, authors suggest that a full trial of the intervention is warranted.
Rehabilitation professionals often encourage patients with persistent pain conditions to participate in activities they enjoy. This research highlights the importance of this instruction and patient guidelines can include the activities identified in the Muller article. In addition, mindful awareness training may further enhance a patient’s experience as he or she learns to pay close attention to the physical sensations, emotions and thoughts that accompany positive experiences. I look forward to discussing this article as well as sharing the principles and practices of mindfulness in my upcoming course, Mindfulness-Based Pain Treatment at Samuel Merritt University, Oakland, CA. Course participants will learn about mindfulness and pain research, practice mindful breathing, body scan and movement and expand their pain treatment tool box with practical strategies to improve pain treatment outcomes. I hope you will join me!
Hanssen MM, Peters ML, Boselie JJ, Meulders A. Can positive affect attenuate (persistent) pain? Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017;19(12):80.
Muller R, Gertz KJ, Molton IR, et al. Effects of a tailored positive psychology intervention on well-being and pain in individuals with chronic pain and physical disability: a feasibility trial. Clin J Pain.2016;32(1):32-44.
Men who present with chronic pelvic pain frequently have symptoms referred along the penis and into the tip of the penis, or glans. Symptoms may include numbness, tingling, aching, pain, or other sensitivity and discomfort. The tip of the penis, or glans, is a sensory structure, which allows for sexual stimulation and appreciation. This same capacity for valuable sensation can create severe discomfort when signals related to the glans are overactive or irritating. One of the most common complaints with this symptom is a level of annoyance and distraction, with level of bother worsening when a person is less active or not as mentally engaged with tasks. Wearing clothing that touches the tip of the penis (such as underwear, jock straps, jeans, or snug pants) may be limited and may worsen symptoms. When uncovering from where the symptoms originate, the culprit is often the dorsal nerve of the penis, which is sensible given that the glans is innervated by this branch of the pudendal nerve. If we consider this possibility (because certainly there are other potential causes) we find that there are many potential sites of pudendal nerve irritation to consider. First, let’s visualize the anatomy of the nerve.
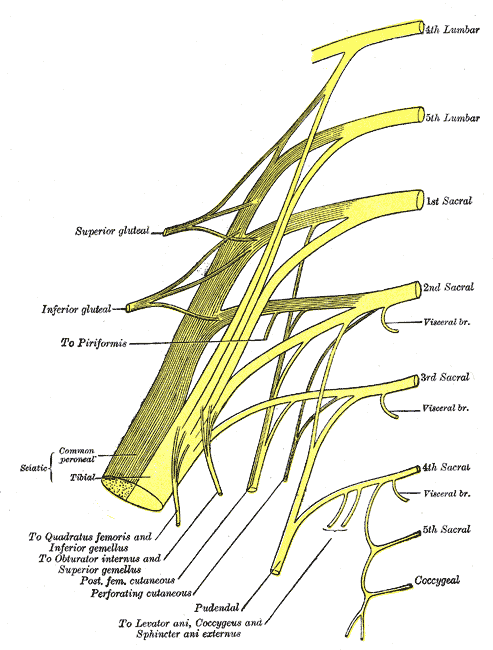
Following the usually accepted descriptions of the dorsal nerve, we know that it is a terminal branch of the pudendal nerve that primarily is created from the mid-sacral nerves. This can lead us to include the lumbosacral region in our examination and treatment, yet in my clinical experience, there are other sites that more often reproduce pain in the glans. As the dorsal nerve branches off of the pudendal, usually after the location of the sacrotuberous ligament, it passes through and among the urogenital triangle layers of fascia where compression or irritation may generate symptoms.
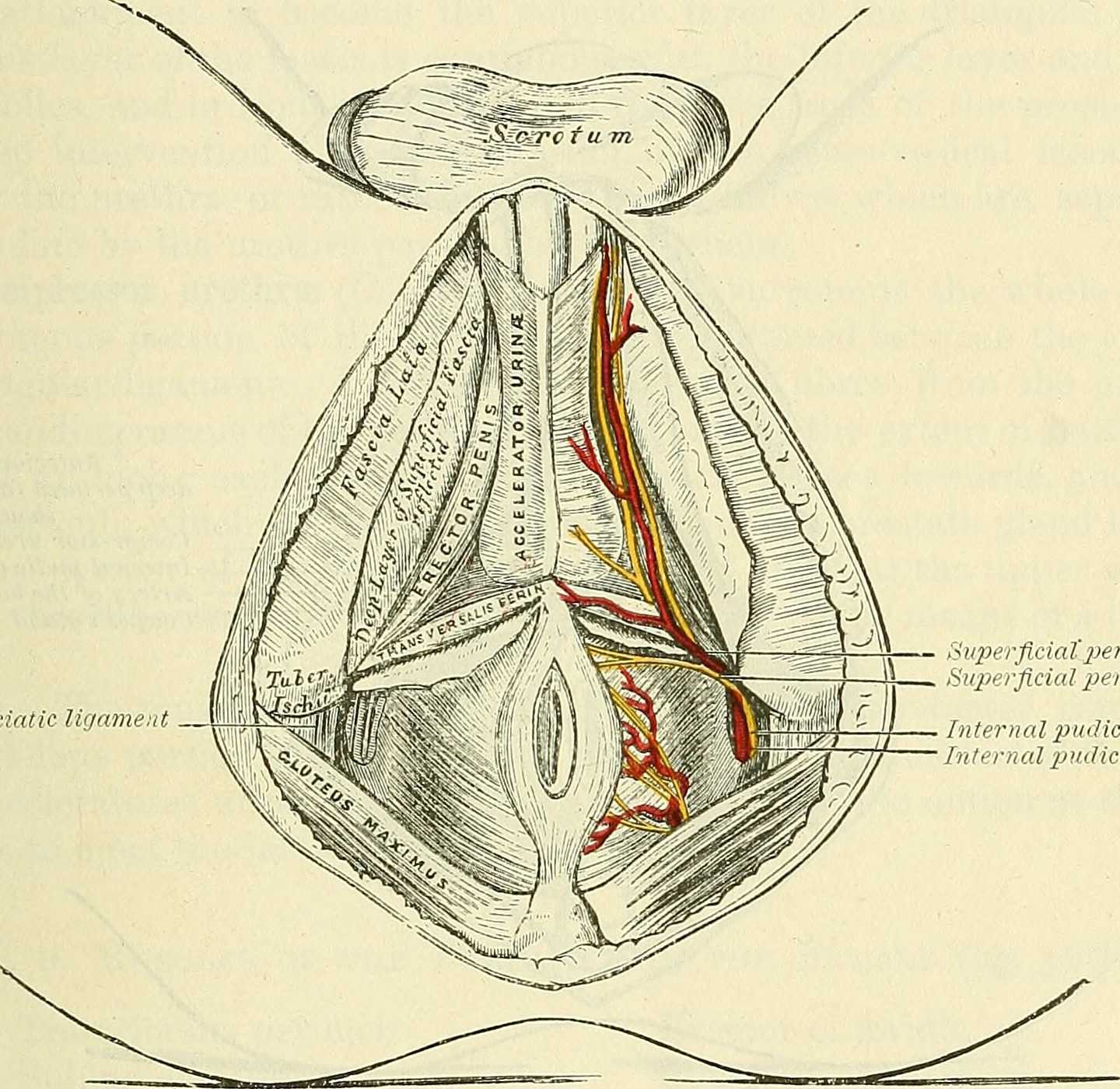
As the nerve travels towards the pubic bone, it will pass inferior to the pubic bone, a location where suspensory ligaments of the penis can be found as well as pudendal vessels and fascia. This is also a site of potential compression and irritation, and palpation to this region may provide information about tissue health. Below is a cross-section of the proximal penis, allowing us to see where the pudendal nerve and vessels would travel inferior to the pubic bone.
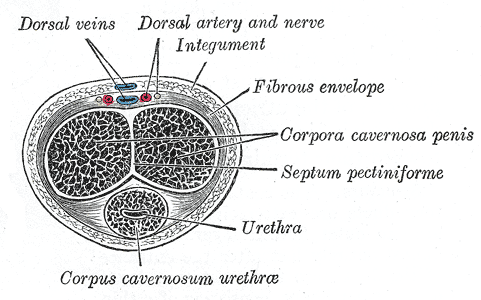
As the dorsal nerve extends along either side of the penis, giving smaller branches along its path towards the glans, the nerve may also be experiencing soft tissue irritation along the length of the penis or even locally at the termination in the glans.
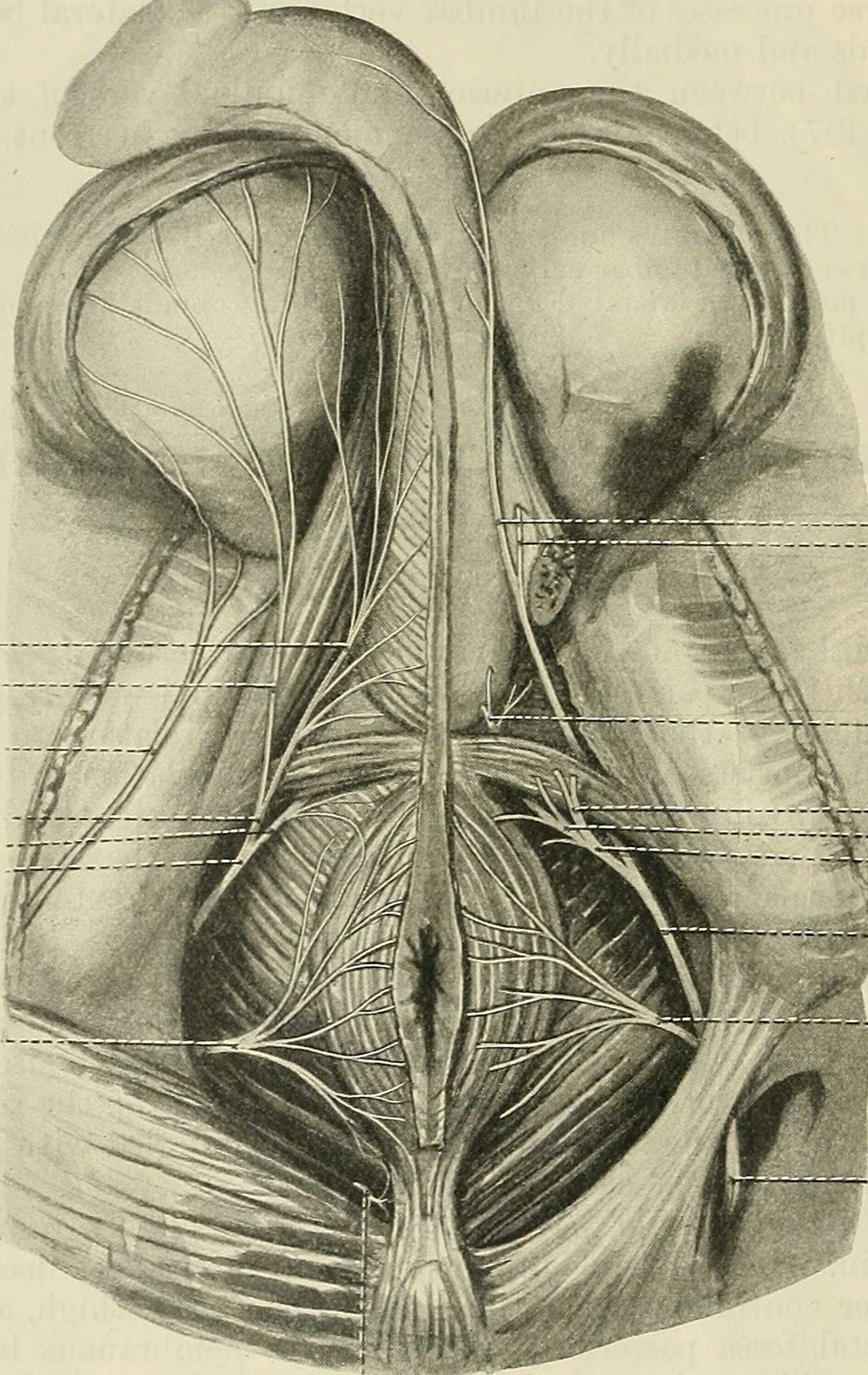
Palpation internally (via rectum) or externally may be a part of the assessment as well as treatment of this condition. Oftentimes, tip of the penis pain can be reproduced with palpation internally and directed towards the anterior levator ani and the connective tissues just inferior to the pubic bone. It may be difficult to know if the muscle is providing referred pain, or if the nerve is being tensioned and reproducing symptoms, however gentle soft tissue work applied to this area is often successful in reducing or resolving symptoms regardless of the tissue involved. In my experience, these symptoms of referred pain at the tip of the penis is often one of the last to resolve, and the use of topical lidocaine may be helpful in managing symptoms while healing takes place. Home program self-care including scar massage if needed, nerve mobilizations, trunk and pelvic mobility and strengthening, and advice for returning to meaningful activities can play a large role in resolution of pain in the glans.
If you would like to learn more about treating genital pain in men, consider joining me in Male Pelvic Floor: Function, Dysfunction, & Treatment. The 2018 courses will be in Freehold, NJ this June, and Houston, TX in September.
Erica Vitek, MOT, OTR, BCB-PMD, PRPC is the author and instructor of Neurologic Conditions and Pelvic Floor Rehab, a new course coming to Grand Rapids, MI and Philadelphia, PA. This post is the next in her series on creating a course about neurologic conditions and pelvic rehabilititation.
Being a clinician, as we evaluate and treat people with pelvic health conditions, we typically take all systems of the body into account. We take the problem presented to us by the client and we examine, from all angles, how we might go about advice and treatment to best achieve their goals in alleviating the problem. We do a full review of medical history and pharmacology. We examine our client in-depth from a musculoskeletal perspective. We look at psychological contributions to the problem they are facing. We can look at their lifestyle and have them make a detailed diary to help us analyze their bladder, bowel, fluid intake and dietary habits. Do we also always include a look at the neurological components? Do we know what we are looking for? What are the best tools we can have in our toolbox as clinicians to look at our client’s problem through a “neuro brain”?
 In writing each lecture of this course, I have had to step back each time I am developing a new concept and look at it with in-depth thought and contemplation about how I will use this in the clinic to assess my client’s concerns using a neuro-based approach. Taking the concepts and facts about the musculoskeletal system that we know well and then taking a look at the neurological systems contributions and relationship to that dysfunction can be challenging. The main reason for this challenge is that neuro system dysfunction is many times hard explain, presents with inconsistent or changing symptoms, may have motor or sensory deficits together or by themselves, may radiate to different locations than where the true dysfunction is located, and may have developed into central sensitization causing a hypervigilance to typically non-painful stimuli.
In writing each lecture of this course, I have had to step back each time I am developing a new concept and look at it with in-depth thought and contemplation about how I will use this in the clinic to assess my client’s concerns using a neuro-based approach. Taking the concepts and facts about the musculoskeletal system that we know well and then taking a look at the neurological systems contributions and relationship to that dysfunction can be challenging. The main reason for this challenge is that neuro system dysfunction is many times hard explain, presents with inconsistent or changing symptoms, may have motor or sensory deficits together or by themselves, may radiate to different locations than where the true dysfunction is located, and may have developed into central sensitization causing a hypervigilance to typically non-painful stimuli.
In brain storming our ideas for course creation, much was said about thinking back to college or other continuing education courses and “learning a little about a lot of things neuro” but not the in-depth knowledge one might want to have when focusing their attention on specific neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson disease, demyelinating diseases such as Multiple Sclerosis, injury to the brain due to cerebral vascular accident or incomplete or complete spinal cord injury.
As I progress deep into the development of this course, I have my “neuro brain” on and a persistent focus set on providing clinicians with as much in-depth information on neurological contributions to pelvic floor function and dysfunction. I want clinicians to walk away from this course feeling confident that through evaluation of a client that has been diagnosed with Parkinson disease, Multiple Sclerosis or suffered a spinal cord injury, they would have the tools to develop an in-depth treatment plan that would provide these clients with the best results possible to improve their quality of life. I also want clinicians to have the confidence to market themselves to their local neurologists. This is an entirely new avenue for developing a referral base in pelvic health work. Many times for clients who have chronic neurological conditions, the problem list is long and bladder, bowel and sexual health concerns might not even be broached within the very short physician appointment times. We can give our neurologists new treatments to be confident in and excited about to improve their patient’s quality of life!
When a woman is given a cancer diagnosis, her entire world is turned upside down and inside out. There are so many things to think about; medical treatments, financial concerns, family concerns, and emotional upheaval. Sex may be the last thing that a woman may think about when she is actively going through treatment. However, at what rate are survivors having issues after treatment is complete?
 A recent study published in the journal Cancer looked at just this. A 2-year longitudinal study was performed that tracked young adults (18-39 years old) through and after their cancer diagnosis. The most common cancers seen in the samples were leukemia, breast cancer, soft-tissue sarcoma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The patients completed the Medical Outcomes Study Sexual Functioning Scale at 4 months, 6 months, and 24 months after diagnosis. At 2 years after diagnosis over 50% of the patients surveyed reported some degree of sexual dysfunction. Women that were in a committed relationship had an increased likelihood for experiencing sexual dysfunction; while men had increased rate of reporting sexual issues regardless of their relationship status.
A recent study published in the journal Cancer looked at just this. A 2-year longitudinal study was performed that tracked young adults (18-39 years old) through and after their cancer diagnosis. The most common cancers seen in the samples were leukemia, breast cancer, soft-tissue sarcoma, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The patients completed the Medical Outcomes Study Sexual Functioning Scale at 4 months, 6 months, and 24 months after diagnosis. At 2 years after diagnosis over 50% of the patients surveyed reported some degree of sexual dysfunction. Women that were in a committed relationship had an increased likelihood for experiencing sexual dysfunction; while men had increased rate of reporting sexual issues regardless of their relationship status.
Women that undergo cancer treatment have several reasons that could be influencing their sexual function. Fatigue is a complaint that is often expressed by cancer patients. Their body image is often altered due to surgeries that have been performed. Chemotherapy and hormonal therapy often push women into menopause which then leads to vaginal dryness. Additionally, radiation and surgical treatment can lead to scar tissue, fibrosis, and stenosis of the vagina and pelvic floor muscles.
This is where physical therapy can help! In the Pelvic Floor Series Capstone course we teach advanced techniques that help treat pelvic floor issues by working on both the muscles, and the fascia. We also cover techniques that decrease the tenderness in the muscles that then allow you to stretch the muscle with less discomfort.
All of the techniques taught in Capstone are gentle but effective. The cancer survivor is the perfect population to use these gentle techniques on! Think of how rewarding our job will be when we help relieve the pain that may be associated with intercourse, and therefore improve intimacy of a cancer survivor with her partner!
Come join us for Capstone and learn techniques that will take your treatment skills to the next level!
Acquati, Zebrack, Faul, et al. Sexual functioning among young adult cancer patients: A 2-year longitudinal study. Cancer. 2018; 124(2): 398-405.
A couple of years ago, I wrote a blog about an interesting article by Hides and Stanton that related size and strength of the multifidus to the risk for lower extremity injury in Australian professional football players.
 Now some of the same researchers are looking above. A prospective cohort study has recently been published that examined factors and their effects on concussions. Physical measurements of risk factors were taken in pre-season among Australian football players. These measurements included balance, vestibular function, and spinal control. To measure these outcomes the following tests were included: for balance the amount of sway across six test conditions were performed; vestibular function was tested with assessments of ocular-motor and vestibular ocular reflex; and for spinal control cervical joint position error, multifidus size, and contraction ability was tested. The objective measure was concussion injury obtained during the season diagnosed by the medical staff.
Now some of the same researchers are looking above. A prospective cohort study has recently been published that examined factors and their effects on concussions. Physical measurements of risk factors were taken in pre-season among Australian football players. These measurements included balance, vestibular function, and spinal control. To measure these outcomes the following tests were included: for balance the amount of sway across six test conditions were performed; vestibular function was tested with assessments of ocular-motor and vestibular ocular reflex; and for spinal control cervical joint position error, multifidus size, and contraction ability was tested. The objective measure was concussion injury obtained during the season diagnosed by the medical staff.
The findings were so interesting! Age, height, weight, and number of years playing football were not associated with concussion. Cross-sectional area of the multifidus at L5 was 10% smaller in players who went on to sustain a concussion compared to players that did not receive a concussion. There were no significant differences observed between the players that received concussion and those who did not with respect to the other physical measures that were obtained.
With all the recent evidence about the harmful effects of concussions amongst our athletes, I find this information amazing and am excited to see where the researchers take this in the future. The next question for the physical therapist is how do we train the multifidus? The multifidus can be difficult to retrain in some individuals. It is a hard muscle for some patients to learn to recruit. Biofeedback using ultrasound imaging can make this daunting task easier for many patients. With the cost of ultrasound units coming down, it is also a very reasonable tool for clinics to look at investing in.
Join me to learn more about the multifidus and how to use ultrasound imaging in the retraining process. Future course offerings include August in New Jersey, and November in San Diego. I look forward to seeing you there!
Hides, Stanton. Can motor control training lower the risk of injury for professional football players? Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014; 46(4): 762-8.
Leung, Hides, Franettovich Smith, et al. Spinal control is related to concussion in professional footballers. Brit J of Sports Med. 2017; 51(11).
When I mentioned to a patient I was writing a blog on yoga for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), she poured out her story to me. Her ex-husband had been abusive, first verbally and emotionally, and then came the day he shook her. Violently. She considered taking her own life in the dark days that followed. Yoga, particularly the meditation aspect, as well as other counseling, brought her to a better place over time. Decades later, she is happily married and has practiced yoga faithfully ever since. Sometimes a therapy’s anecdotal evidence is so powerful academic research is merely icing on the cake.

This study by Walker and Pacik (2017) included 3 voluntary participants: a 75 and a 72 year old male veteran and a 57 year old female veteran, all whom were experiencing a varying cluster of PTSD symptoms for longer than 6 months. Pre- and post-course scores were evaluated from the PTSD Checklist (a 20-item self-reported checklist), the Military Version (PCL-M). All the participants reported decreased symptoms of PTSD after the 5 day training course. The PCL-M scores were reduced in all 3 participants, particularly in the avoidance and increased arousal categories. Even the participant with the most severe symptoms showed impressive improvement. These authors concluded Sudarshan Kriya (SKY) seemed to decrease the symptoms of PTSD in 3 military veterans.
Cushing et al., (2018) recently published online a study testing the impact of yoga on post-9/11 veterans diagnosed with PTSD. The participants were >18 years old and scored at least 30 on the PTSD Checklist-Military version (PCL-M). They participated in weekly 60-minute yoga sessions for 6 weeks including Vinyasa-style yoga and a trauma-sensitive, military-culture based approach taught by a yoga instructor and post-9/11 veteran. Pre- and post-intervention scores were obtained by 18 veterans. Their PTSD symptoms decreased, and statistical and clinical improvements in the PCL-M scores were noted. They also had improved mindfulness scores and decreased insomnia, depression, and anxiety. The authors concluded a trauma-sensitive yoga intervention may be effective for veterans with PTSD symptoms.
Domestic violence, sexual assault, and unimaginable military experiences can all result in PTSD. People in our profession and even more likely, the patients we treat, may live with these horrors in the deepest recesses of their minds. Yoga is gaining acceptance as an adjunctive therapy to improving the symptoms of PTSD. The Trauma Awareness for the Physical Therapist course may assist in shedding light on a dark subject.
Walker, J., & Pacik, D. (2017). Controlled Rhythmic Yogic Breathing as Complementary Treatment for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder in Military Veterans: A Case Series. Medical Acupuncture, 29(4), 232–238.
Cushing, RE, Braun, KL, Alden C-Iayt, SW, Katz ,AR. (2018). Military-Tailored Yoga for Veterans with Post-traumatic Stress Disorder. Military Medicine. doi:org/10.1093/milmed/usx071
Recently, I had a patient present to my practice with unretractable vaginal pain that was causing her quite a bit of suffering. Peyton (name changed) had been referred by a local osteopathic physician. For around a year, she had increasing severe vaginal pain. There was no history of assault, trauma, fall, or injury around the time of onset of symptoms. However, she had a kidney infection that caused back pain in the month prior to her pain onset.
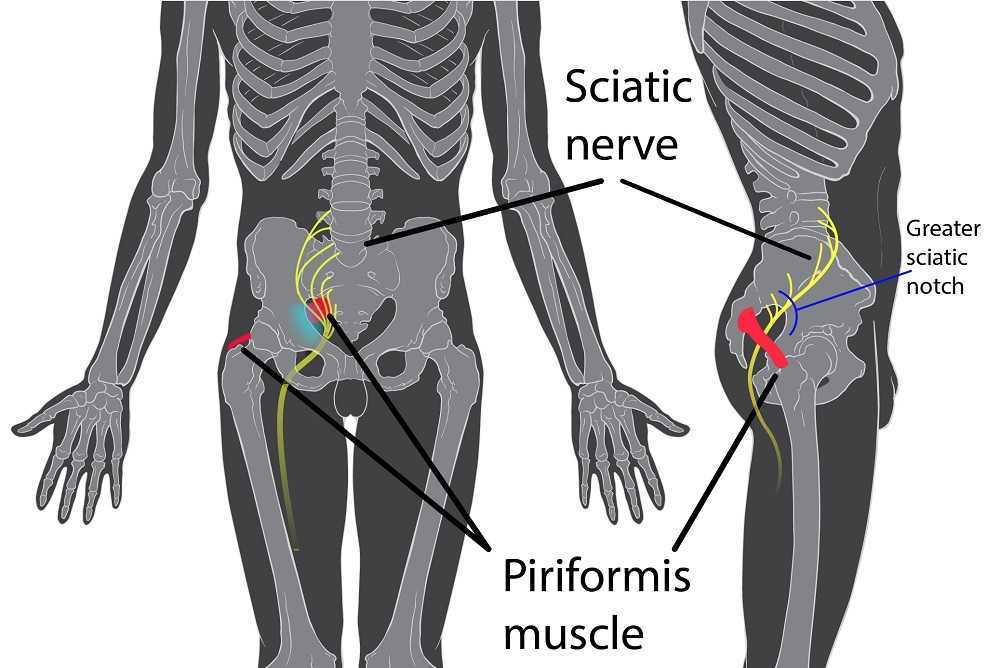 Peyton is home schooled, but she was unable to attend outings that required longer sitting, such as field trips or church. She also was having some urinary retention with start and stop stream and resultant urinary frequency. Peyton’s mother said the pain was distressing to Peyton and would cause her to cry. She had an unremarkable medical history. However, under further questioning, we discovered she did have a history of bed wetting later than usual (until age 7) and she had persistent leg pain. With standing longer than 15 minutes, her legs would hurt and feel weak, which prevented her from performing sports or being physically active. She also had experienced some achy low back sensations since the kidney infection. Peyton had been screened by urology, her primary care, an osteopath, as well as a vulvar pains specialist who diagnosed her with nerve pain, but said there is no good viable treatment.
Peyton is home schooled, but she was unable to attend outings that required longer sitting, such as field trips or church. She also was having some urinary retention with start and stop stream and resultant urinary frequency. Peyton’s mother said the pain was distressing to Peyton and would cause her to cry. She had an unremarkable medical history. However, under further questioning, we discovered she did have a history of bed wetting later than usual (until age 7) and she had persistent leg pain. With standing longer than 15 minutes, her legs would hurt and feel weak, which prevented her from performing sports or being physically active. She also had experienced some achy low back sensations since the kidney infection. Peyton had been screened by urology, her primary care, an osteopath, as well as a vulvar pains specialist who diagnosed her with nerve pain, but said there is no good viable treatment.
Objective findings revealed normal range of motion in her spine with the exception of limited forward flexion (feeling of back tightness at end range). Hip screening was negative for FABERS, labral screening or capsular pain patterns. General dural tension screening was positive for increased lower extremity and sensation of back tightness with slump c sit. Neural tension test was positive bilaterally for sciatic, R genitofemoral, L Iliohypogastric and Ilioinguinal nerves, and bilateral femoral nerves. Patient had a mild, barely perceptible lumbar scoliosis, and development of bilateral lower extremities and feet was symmetric and normal.
Because of the child’s age, we did not perform internal vaginal exam or treatment. This required treating the nerves that supply the vaginal area. All treatments were done with the patient’s mother present with both consent of the child and the mother.
For treatment, we started with the three inguinal nerves (Ilioinguinal, Iliohypogastric and genitofemoral) because of their relationship with the kidney (symptoms came on after kidney infection) as well as the correlation with the patient’s most limiting symptoms (genital pain). We cleared the fascia along the lumbar nerve roots, the lateral trunk fascia, the psoas, the inguinal region, the entrapments along the kidney and psoas, the inguinal rings and canal, and worked on neural rhythm (these techniques can be learned at the Pelvic Nerve Manual Assessment and Treatment class that I will be teaching later this month).
Over the next weeks, we used similar treatments for the sciatic nerve, femoral nerve, pudendal, and coccygeal nerves. We noted that the patient had an area of restricted tissue along her coccyx that was adhered, and her symptoms had some correlation with tethered cord. We did lots of soft tissue work along the coccyx and working along the coccyx roots, including some internal rectal work. We also did fascial and visceral work in the bladder region, as well as in the lumbar and sacro-coccygeal region.
Peyton’s referring physician and mother were notified of findings and possible tethered cord symptoms (leg weakness and pain, bladder symptoms, delayed nocturnal continence). The patient’s family felt she was getting better and was not interested in any kind of surgical intervention, and her physician also felt that with our progress, he was not interested in exploring that referral, unless the family was interested.
After just 4 treatments Peyton was no longer having any vaginal symptoms and was emptying the bladder normally. After 8 treatments Peyton was reporting no more lumbar pain or lower extremity symptoms, and follow up treatments were reduced to once a month. The patient was given a home program of neural flossing in a small yoga program we recorded on her mother’s phone. We had her mother work on the small area that remained adhered along patient’s tailbone. The area is much smaller, but it reproduces some pelvic pain for the patient, so we are carefully and slowly working along this area because of some of the global neural sx it produces.
The patient’s mother reports she is more active, no longer complaining of leg or vaginal pain. The patient has less generalized anxiety and she is able to void fully. When the pt grows in height, there is a return in some symptoms, likely due to increased neural tension. So, we have the family on standby and when the patient grows, they come back in for 2 visits, which is usually enough to get the patient back to her new baseline.
My 6 year old girl (going on 13) asks “Alexa” to play the Descendants II soundtrack over and over again. So the song, “Space Between,” was lingering in my head while reading the most recent articles on pudendal neuralgia, particularly when pudendal entrapment is to blame. After all, entrapment, by medical standards, describes a peripheral nerve basically being caught in between two surrounding anatomical structures.
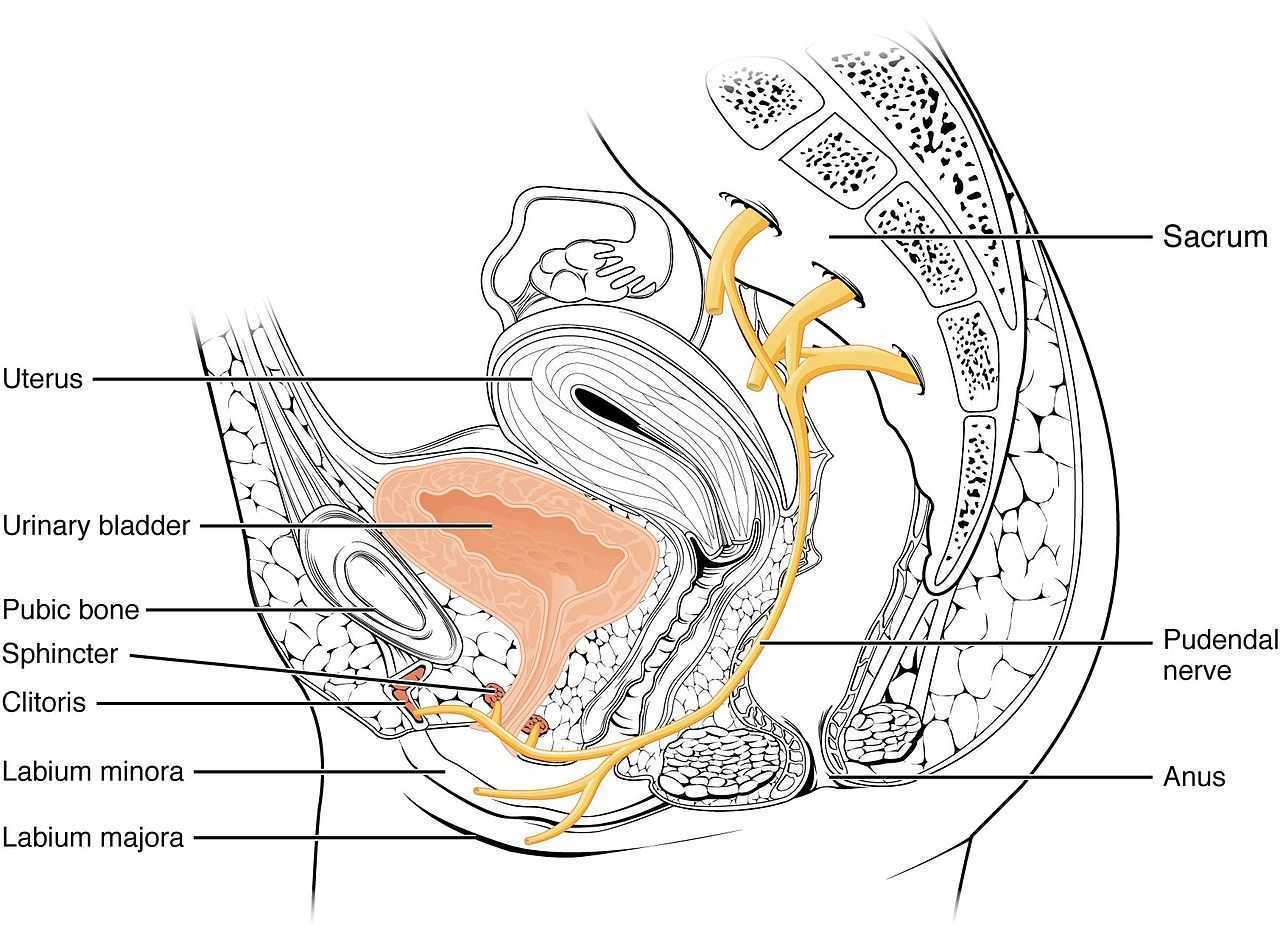 Ploteau et al., (2016) presented 2 case studies highlighting the warning signs when pudendal nerve entrapment does not follow the Nantes criteria. A brief summary of those 5 criteria follows:
Ploteau et al., (2016) presented 2 case studies highlighting the warning signs when pudendal nerve entrapment does not follow the Nantes criteria. A brief summary of those 5 criteria follows:
- Pain in the region of the pudendal nerve innervation from anus to penis or clitoris.
- Pain most predominant while sitting.
- The patient does not wake at night from the pain.
- No sensory impairment can be objectively identified.
- Diagnostic pudendal nerve block relieves the pain.
The case studies of a 31 and a 68 year old female revealed endometrial stromal sarcoma and adenoid cystic carcinoma in the ischiorectal fossa, with night pain was noted in both patients, as well as no pain with sitting or defecation, respectively. Clinicians must always be mindful to resolve red flags in patients.
In 2016, Florian-Rodriguez, et al., studied cadavers to determine the nerves associated with the sacrospinous ligament, focusing on the inferior gluteal nerve. Fourteen cadavers were observed, noting the distance from various nerves to the sacrospinous ligament (from a pelvic approach) and to the ischial spine (from a gluteal approach). The S3 nerve was closest to the sacrospinous ligament, and the pudendal nerve was the closest to the ischial spine. In 85% of subjects, 1 to 3 branches from S3/S4 nerves pierced or ran anterior to the sacrotuberous ligament and pierced the inferior part of the gluteus maximus muscle. The authors concluded the inferior gluteal nerve was less likely to be the source of postoperative gluteal pain after sacrospinous ligament fixation; however, as the pudendal nerve branches from S2-4, it was more likely to be implicated in postoperative gluteal pain.
A study by Ploteau et al. (2017) explored the anatomical position of the pudendal nerve in people with pudendal neuralgia. In 100 patients who met the Nantes criteria, 145 pudendal nerves were surgically decompressed via a transgluteal approach. At least one segment of the pudendal nerve was compressed in 95 of the patients, either in the infrapiriform foramen, ischial spine, or Alcock’s canal. In 74% of patients, nerve entrapment was between the sacrospinous ligament and the sacrotuberous ligament. Anatomical variants were found in 13% of patients, often with a transligamentous course of the nerve.
When the pudendal nerve is caught in the narrow space between ligaments in the pelvis, diagnosing the source of pain is paramount. Research supports a gluteal approach in releasing the entrapped nerve. Post-surgical care falls into the hands of pelvic floor therapists, so taking “Pudendal Neuralgia and Nerve Entrapment: Evaluation and Treatment” may be something to consider in order to provide optimal care.
Ploteau, S, Cardaillac, C, Perrouin-Verbe, MA, Riant, T, Labat, JJ. (2016). Pudendal Neuralgia Due to Pudendal Nerve Entrapment: Warning Signs Observed in Two Cases and Review of the Literature. Pain Physician. 19(3):E449-54
Florian-Rodriguez, ME, Hare, A, Chin, K, Phelan, JN, Ripperda, CM, Corton, MM. (2016). Inferior gluteal and other nerves associated with sacrospinous ligament: a cadaver study. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 215(5):646.e1-646.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2016.06.025
Ploteau, S, Perrouin-Verbe, MA, Labat, JJ, Riant, T, Levesque, A, Robert, R. (2017). Anatomical Variants of the Pudendal Nerve Observed during a Transgluteal Surgical Approach in a Population of Patients with Pudendal Neuralgia. Pain Physician. 20(1):E137-E143
Neurophysiology is a dynamic and highly complex system of neurological connections and interactions that allow for bodily performance. When all of those connections are working correctly, our bodies can function at optimal levels. When there is a break or injury to those connections, dysfunction results but amazingly in some circumstances, our bodies have work arounds to allow for certain functions to continue working.
If we take the sexual neural control system of the male, for instance, a perfect example of this can be described. Many men were injured fighting in World War II. During their time in battle, many experienced spinal cord injuries. Some of these injuries were severe resulting in complete spinal cord damage at level of injury. A physician, Herbert Talbot, in 1949, documented his examination of 200 men with paraplegia. Two thirds of the men were surprisingly able to achieve erections and some were able to experience vaginal penetration and orgasm. Much of their basic functionality had been lost however amazingly there was preservation of erectile function.
The reason these men with paraplegia were able to maintain erectile or orgasm functionality is due to the physiological function in the sacral spinal cord. A reflex arc is present in this region. The definition of a reflex arc is a nerve pathway that has a reflexive action involving sensory input from a peripheral somatic or autonomic nerve synapsing to a relay neuron or interneuron in the sacral cord segment then synapsing to a motor nerve for output to the muscular region. These messages do not need to travel up the spinal cord to the brain in order to be activated. Instead they work within a ‘loop’ at the sacral spinal cord level. In the case of spinal cord injury, erectile function as well as other functions controlled by reflex arcs, can be preserved.
For women, the same is true. In order for a female to have engorgement of the clitoris or orgasm, the sacral spinal reflex arc needs to be intact. If a woman experiences a spinal cord injury above the sacral region, the ability to have a reflexive orgasm within the sacral spinal reflex arc will remain.
The sacral reflex arc also plays an important role in activation of the pelvic floor muscles during the sexual response cycle. During genital stimulation in both the male and female, the bulbospongiosus or bulbocavernosus begins to activate in a reflexive pattern to hinder the outflow of blood from the region which facilitates erectile tissue of the penis and clitoris to become erect. This can then be followed by rhythmic reflexive contractions of the pelvic floor musculature during orgasm.
To learn more about the implications that neurologic disorders can have on the sexual system, please join us for Neurologic Conditions and Pelvic Floor Rehab, coming to Grand Rapids, MI in September.
Goldstein, I. (2000). Male sexual circuitry. Scientific American, 283(2), 70-75.
Sipski, M. L. (2001). Sexual response in women with spinal cord injury: neurologic pathways and recommendations for the use of electrical stimulation. The journal of spinal cord medicine, 24(3), 155-158.
Wald, A. (2012). Neuromuscular Physiology of the Pelvic Floor. In Physiology of the Gastrointestinal Tract (Fifth Edition)(pp. 1023-1040).
In the dim and distant past, before I specialised in pelvic rehab, I worked in sports medicine and orthopaedics. Like all good therapists, I was taught to screen for cauda equina issues – I would ask a blanket question ‘Any problems with your bladder or bowel?’ whilst silently praying ‘Please say no so we don’t have to talk about it…’ Fast forward twenty years and now, of course, it is pretty much all I talk about!
But what about the crossover between sports medicine and pelvic health? The issues around continence and prolapse in athletes is finally starting to get the attention it deserves – we know female athletes, even elite nulliparous athletes, have pelvic floor dysfunction, particularly stress incontinence. We are also starting to recognise the issues postnatal athletes face in returning to their previous level of sporting participation. We have seen the changing terminology around the Female Athlete Triad, as it morphed to the Female Athlete Tetrad and eventually to RED S (Relative Energy Deficiency Syndrome) and an overdue acknowledgement by the IOC that these issues affected male athletes too. All of these issues are extensively covered in my Athlete & The Pelvic Floor’ course, which is taking place twice in 2018.
But what about pelvic pain in athletes?
 How can we ensure that pelvic floor muscle dysfunction is on the radar for a differential diagnosis, or perhaps a concomitant factor, when it comes to athletes presenting with hip, pelvis or groin pain? Gluteal injuries, proximal hamstring injuries, and pelvic floor disorders have been reported in the literature among runners: with some suggestions that hip, pelvis, and/or groin injuries occur in 3.3% to 11.5% of long distance runners.
How can we ensure that pelvic floor muscle dysfunction is on the radar for a differential diagnosis, or perhaps a concomitant factor, when it comes to athletes presenting with hip, pelvis or groin pain? Gluteal injuries, proximal hamstring injuries, and pelvic floor disorders have been reported in the literature among runners: with some suggestions that hip, pelvis, and/or groin injuries occur in 3.3% to 11.5% of long distance runners.
In Podschun’s 2013 paper ‘Differential diagnosis of deep gluteal pain in a female runner with pelvic involvement: a case report’, the author explored the case of a 45-year-old female distance runner who was referred to physical therapy for proximal hamstring pain that had been present for several months. This pain limited her ability to tolerate sitting and caused her to cease running. Examination of the patient's lumbar spine, pelvis, and lower extremity led to the initial differential diagnosis of hamstring syndrome and ischiogluteal bursitis. The patient's primary symptoms improved during the initial four visits, which focused on education, pain management, trunk stabilization and gluteus maximus strengthening, however pelvic pain persisted. Further examination led to a secondary diagnosis of pelvic floor hypertonic disorder. Interventions to address the pelvic floor led to resolution of symptoms and return to running.
‘This case suggests the interdependence of lumbopelvic and lower extremity kinematics in complaints of hamstring, posterior thigh and pelvic floor disorders. This case highlights the importance of a thorough examination as well as the need to consider a regional interdependence of the pelvic floor and lower quarter when treating individuals with proximal hamstring pain.’ (Podschun 2013)
Many athletes who present with proximal hamstring tendinopathy or recurrent hamstring strains, display poor ability to control their pelvic position throughout the performance of functional movements for their sport: along with a graded eccentric programme, Sherry & Best concluded ‘…A rehabilitation program consisting of progressive agility and trunk stabilization exercises is more effective than a program emphasizing isolated hamstring stretching and strengthening in promoting return to sports and preventing injury recurrence in athletes suffering an acute hamstring strain’
If you are interested in learning more about how pelvic floor dysfunction affects both male and female athletes, including broadening your differential diagnosis skills and expanding your external treatment strategy toolbox, then consider coming along to my course ‘The Athlete and the Pelvic Floor’ in Chicago this June or Columbus, OH in October.
The IOC consensus statement: beyond the Female Athlete Triad—Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S), Mountjoy et al 2014: http://bjsm.bmj.com/content/48/7/491
‘DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF DEEP GLUTEAL PAIN IN A FEMALE RUNNER WITH PELVIC INVOLVEMENT: A CASE REPORT’ Podschun A et al Int J Sports Phys Ther. 2013 Aug; 8(4): 462–471. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3812833/
‘A comparison of 2 rehabilitation programs in the treatment of acute hamstring strains’ Sherry MA, Best TM J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2004 Mar;34(3):116-25. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15089024